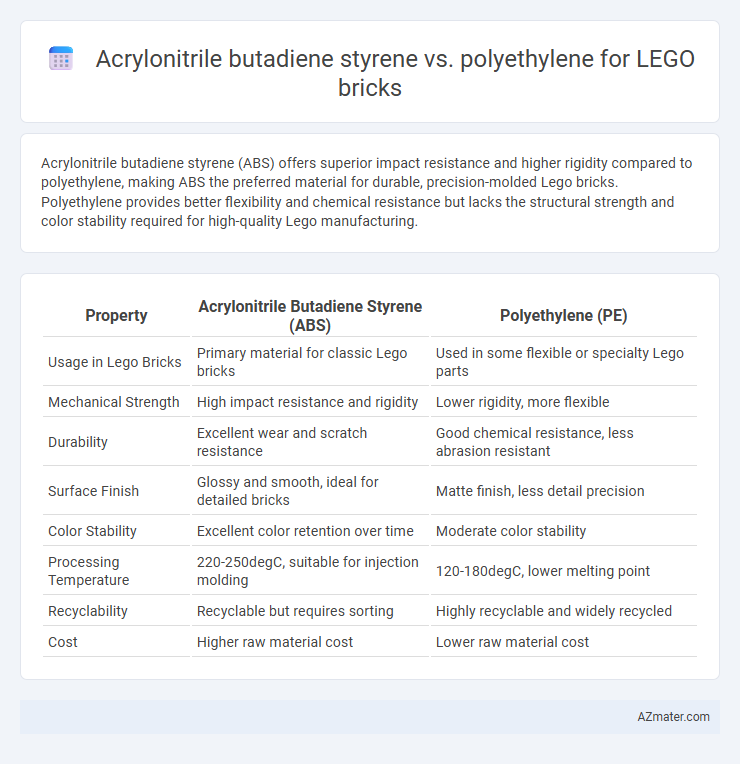
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance and higher rigidity compared to polyethylene, making ABS the preferred material for durable, precision-molded Lego bricks. Polyethylene provides better flexibility and chemical resistance but lacks the structural strength and color stability required for high-quality Lego manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Usage in Lego Bricks | Primary material for classic Lego bricks | Used in some flexible or specialty Lego parts |
| Mechanical Strength | High impact resistance and rigidity | Lower rigidity, more flexible |
| Durability | Excellent wear and scratch resistance | Good chemical resistance, less abrasion resistant |
| Surface Finish | Glossy and smooth, ideal for detailed bricks | Matte finish, less detail precision |
| Color Stability | Excellent color retention over time | Moderate color stability |
| Processing Temperature | 220-250degC, suitable for injection molding | 120-180degC, lower melting point |
| Recyclability | Recyclable but requires sorting | Highly recyclable and widely recycled |
| Cost | Higher raw material cost | Lower raw material cost |
Introduction: ABS vs Polyethylene in Lego Brick Manufacturing
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and polyethylene (PE) differ significantly in Lego brick manufacturing due to their mechanical properties and durability. ABS offers superior rigidity, impact resistance, and color stability, making it the preferred choice for precision interlocking and long-lasting bricks. Polyethylene is softer and less dimensionally stable, leading to less precise fits and reduced structural integrity in building toys.
Material Composition: ABS and Polyethylene Compared
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) features a rigid polymer matrix combining acrylonitrile for chemical resistance, butadiene for impact toughness, and styrene for shine and rigidity, making it ideal for Lego bricks requiring durability and precise molding. Polyethylene, constructed from long chains of ethylene monomers, offers excellent flexibility and chemical resistance but lacks the hardness and surface finish needed for interlocking Lego components. ABS's higher tensile strength and superior dimensional stability compared to polyethylene ensure consistent clutch power and color retention in Lego assemblies.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior mechanical strength and impact resistance compared to polyethylene, making it the preferred material for LEGO bricks. ABS provides high tensile strength, rigidity, and excellent resistance to wear, ensuring long-lasting durability under repeated assembly and disassembly. Polyethylene, while flexible and chemically resistant, lacks the structural integrity and scratch resistance required for precise interlocking and mechanical performance in LEGO components.
Color Retention and Aesthetic Quality
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits superior color retention and aesthetic quality compared to polyethylene in Lego bricks due to its higher resistance to UV light and better pigment adhesion. ABS maintains vibrant colors over time without significant fading or yellowing, enhancing the visual appeal of the bricks. Polyethylene tends to show quicker color degradation and surface dullness, making ABS the preferred choice for maintaining long-lasting, bright Lego brick colors.
Precision and Moldability in Brick Production
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior precision and moldability compared to polyethylene in Lego brick production due to its higher dimensional stability and resistance to deformation under heat. ABS allows for finer detailing and consistent snap-fit performance, ensuring bricks maintain exact tolerances critical for Lego construction quality. Polyethylene, while more flexible, lacks the rigidity and surface finish precision needed for the intricate design demands of Lego bricks.
Safety and Non-Toxicity Considerations
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is widely favored for Lego bricks due to its superior safety profile, including non-toxicity and resistance to chemical leaching, meeting stringent toy safety standards like ASTM F963. Polyethylene, although generally safe and non-toxic, lacks the robustness of ABS in maintaining structural integrity during play, which can lead to microplastics or small fragment ingestion risks. Both materials are BPA-free and phthalate-free, but ABS's higher melting point and durability contribute to enhanced overall safety in long-term use.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) used in Lego bricks has a higher environmental impact due to its production involving more energy and toxic chemical emissions compared to polyethylene (PE), which is sourced from simpler hydrocarbon feedstocks. ABS offers better durability and color retention, leading to longer-lasting products, but its recycling is more complex and less widespread than polyethylene, whose simpler polymer structure enables more efficient mechanical recycling. Despite ABS's robustness, polyethylene's superior recyclability and lower production emissions make it a more environmentally preferable choice for sustainable Lego brick manufacturing.
Cost Efficiency in Large-Scale Manufacturing
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior dimensional stability and impact resistance, making it the preferred material for high-quality Lego bricks despite a higher raw material cost compared to polyethylene (PE). Polyethylene provides cost efficiency due to its lower price and ease of processing, but its reduced mechanical strength and dimensional consistency can increase defect rates in large-scale manufacturing. Factoring in mold longevity, production speed, and post-processing, ABS remains more cost-effective overall for producing durable, precise Lego bricks at scale.
Real-World Performance: Playability and Longevity
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior durability and color retention compared to polyethylene, making it the preferred material for Lego bricks in terms of playability and longevity. ABS provides excellent impact resistance and rigidity, ensuring bricks maintain their shape and clutch power even after extensive use. Polyethylene, while more flexible and resistant to moisture, tends to wear down faster and lose color vibrancy, resulting in diminished performance over time in high-stress play scenarios.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Material for Lego Bricks
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) offers superior durability, impact resistance, and color retention, making it the preferred material for LEGO bricks that require long-term structural integrity and vibrant appearance. Polyethylene, while more flexible and chemically resistant, lacks the rigidity and precise molding properties essential for the tight interlocking design of LEGO pieces. Therefore, ABS remains the optimal choice for LEGO bricks due to its balance of strength, stability, and compatibility with high-precision manufacturing processes.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polyethylene for Lego brick
 azmater.com
azmater.com