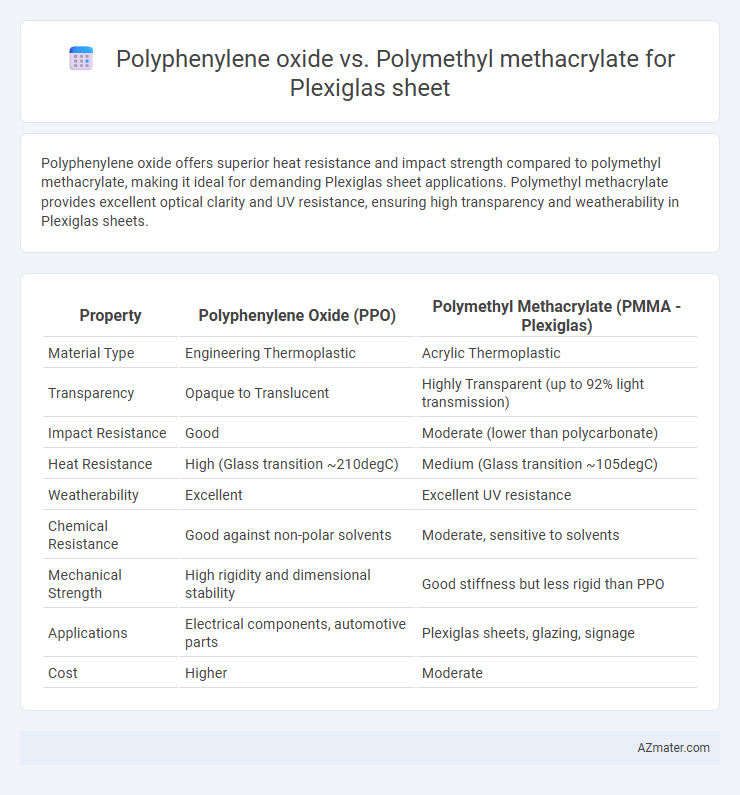
Polyphenylene oxide offers superior heat resistance and impact strength compared to polymethyl methacrylate, making it ideal for demanding Plexiglas sheet applications. Polymethyl methacrylate provides excellent optical clarity and UV resistance, ensuring high transparency and weatherability in Plexiglas sheets.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA - Plexiglas) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Engineering Thermoplastic | Acrylic Thermoplastic |
| Transparency | Opaque to Translucent | Highly Transparent (up to 92% light transmission) |
| Impact Resistance | Good | Moderate (lower than polycarbonate) |
| Heat Resistance | High (Glass transition ~210degC) | Medium (Glass transition ~105degC) |
| Weatherability | Excellent | Excellent UV resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against non-polar solvents | Moderate, sensitive to solvents |
| Mechanical Strength | High rigidity and dimensional stability | Good stiffness but less rigid than PPO |
| Applications | Electrical components, automotive parts | Plexiglas sheets, glazing, signage |
| Cost | Higher | Moderate |
Introduction to Plexiglas Alternatives
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) and Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) serve as prominent alternatives to traditional Plexiglas sheets, each offering distinct chemical and physical properties. PPO provides superior thermal stability and impact resistance compared to PMMA, which excels in optical clarity and UV resistance. Choosing between these materials depends on specific application requirements such as durability, transparency, and environmental exposure.
Overview of Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO)
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent dimensional stability, thermal resistance up to 210degC, and inherent flame retardancy, making it ideal for demanding applications. PPO exhibits superior moisture resistance and electrical insulating properties compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), contributing to enhanced durability in harsh environments. Unlike PMMA, which is valued for its optical clarity in Plexiglas sheets, PPO prioritizes mechanical strength and chemical resistance, positioning it as a complementary material rather than a direct optical substitute.
Overview of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), commonly known as acrylic or Plexiglas, offers excellent optical clarity, UV resistance, and weatherability, making it ideal for glazing, signage, and display applications. Compared to polyphenylene oxide (PPO), PMMA exhibits superior transparency and surface hardness but lower heat resistance and impact strength. Its lightweight nature and ease of fabrication enhance its versatility for both indoor and outdoor use where high optical quality is paramount.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) features a backbone of aromatic rings linked by oxygen atoms, providing excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, while polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) consists of a linear chain of methacrylate units with ester side groups, offering transparency and UV resistance. The rigid aromatic structure of PPO yields higher dimensional stability compared to the more flexible aliphatic backbone of PMMA, which influences mechanical properties and solvent resistance. Chemical susceptibilities differ as PPO resists many solvents due to its aromatic ethers, whereas PMMA is more prone to attack by organic solvents but excels in optical clarity and weathering performance.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers high thermal stability but lower optical clarity compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), which is known for its superior transparency and excellent light transmission. PMMA Plexiglas sheets provide up to 92% light transmission, making them ideal for applications demanding clear visibility and minimal optical distortion. PPO materials generally exhibit more haze and reduced clarity, limiting their suitability for optical-grade Plexiglas alternatives.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior mechanical strength and impact resistance compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), making it more suitable for applications requiring high durability. PMMA, commonly known as Plexiglas, offers excellent optical clarity but is more prone to scratching and brittle failure under stress. The enhanced toughness of PPO results in better long-term performance for structural components where mechanical load and environmental factors are critical.
Thermal and Weather Resistance
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal stability with a heat deflection temperature typically above 180degC, compared to Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), which withstands temperatures up to around 90degC before deformation. PPO also exhibits excellent weather resistance due to its aromatic polymer structure, maintaining mechanical integrity and color under prolonged UV exposure, whereas PMMA, commonly branded as Plexiglas, demonstrates good but lower long-term UV resistance, prone to yellowing and surface degradation without protective coatings. The enhanced thermal and weather resistance of PPO makes it suitable for demanding outdoor and high-temperature applications beyond the standard capabilities of PMMA sheets.
Workability and Fabrication
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it easier to machine and thermoform without deformation compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). PMMA, commonly known as Plexiglas, provides excellent clarity and UV resistance but requires more careful temperature control during fabrication to prevent cracking and stress whitening. Workability of PPO is enhanced by its dimensional stability, while PMMA demands precise handling during cutting, drilling, and polishing to maintain its optical properties.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior heat resistance and dimensional stability compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) but typically comes at a higher production cost, making PMMA a more cost-effective option for standard Plexiglas sheet applications. PMMA dominates market availability due to its widespread use in transparent sheet manufacturing, benefiting from established production processes and economies of scale. The cost analysis favors PMMA for budget-sensitive projects, while PPO's niche high-performance applications justify its premium pricing despite limited market presence.
Best Applications: PPO vs PMMA for Plexiglas Sheets
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior heat resistance and dimensional stability, making it ideal for applications requiring high thermal endurance and mechanical strength, such as industrial components and electrical housings. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), commonly known as Plexiglas, excels in optical clarity and UV resistance, making it the preferred choice for display panels, signage, and outdoor glazing. For Plexiglas sheets specifically, PMMA remains the best application due to its excellent transparency and weatherability, while PPO is better suited when mechanical and thermal performance are prioritized over optical properties.
Infographic: Polyphenylene oxide vs Polymethyl methacrylate for Plexiglas sheet
 azmater.com
azmater.com