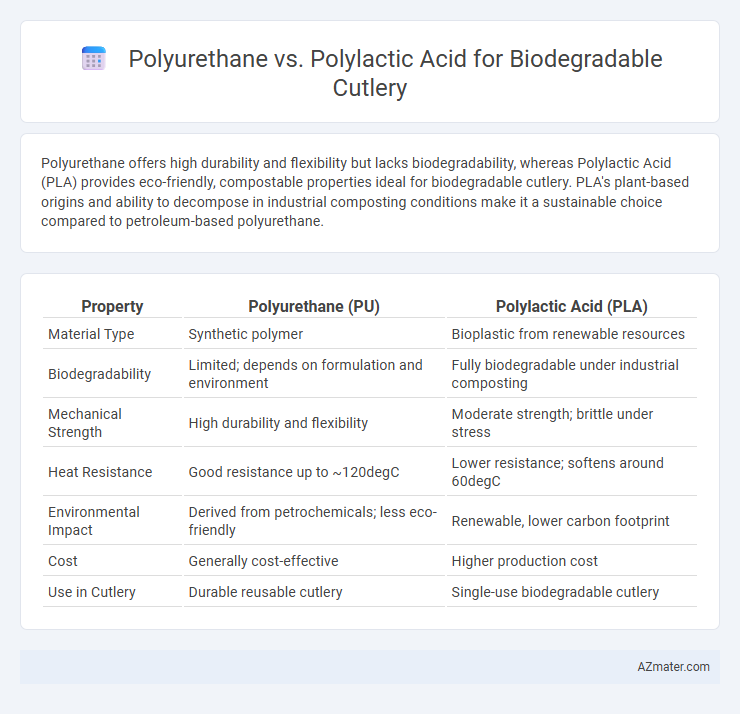
Polyurethane offers high durability and flexibility but lacks biodegradability, whereas Polylactic Acid (PLA) provides eco-friendly, compostable properties ideal for biodegradable cutlery. PLA's plant-based origins and ability to decompose in industrial composting conditions make it a sustainable choice compared to petroleum-based polyurethane.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane (PU) | Polylactic Acid (PLA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic polymer | Bioplastic from renewable resources |
| Biodegradability | Limited; depends on formulation and environment | Fully biodegradable under industrial composting |
| Mechanical Strength | High durability and flexibility | Moderate strength; brittle under stress |
| Heat Resistance | Good resistance up to ~120degC | Lower resistance; softens around 60degC |
| Environmental Impact | Derived from petrochemicals; less eco-friendly | Renewable, lower carbon footprint |
| Cost | Generally cost-effective | Higher production cost |
| Use in Cutlery | Durable reusable cutlery | Single-use biodegradable cutlery |
Introduction to Biodegradable Cutlery Materials
Biodegradable cutlery materials primarily include polyurethane and polylactic acid (PLA), both known for their eco-friendly properties. Polyurethane offers flexibility and durability while maintaining biodegradability under specific conditions, whereas PLA is derived from renewable resources like cornstarch, promoting compostability and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Understanding the chemical structure and decomposition rates of these materials is essential for optimizing sustainable cutlery production and environmental impact.
What is Polyurethane?
Polyurethane is a versatile polymer widely used in manufacturing due to its durability, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals and abrasion. Unlike polylactic acid (PLA), which is derived from renewable resources like corn starch and is fully biodegradable, traditional polyurethane is typically petroleum-based and less eco-friendly. Innovations in bio-based polyurethane are emerging to reduce environmental impact while maintaining the material's robust performance in products such as biodegradable cutlery.
Understanding Polylactic Acid (PLA)
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane, making it an eco-friendly alternative to conventional plastics. PLA offers excellent compostability under industrial conditions and exhibits good stiffness and clarity, ideal for cutlery manufacturing. Its biodegradability contrasts with polyurethane, which is typically petroleum-based and less environmentally sustainable due to slower degradation rates.
Biodegradability Comparison: Polyurethane vs. PLA
Polyurethane, a synthetic polymer, exhibits limited biodegradability under natural environmental conditions, often requiring specialized industrial processes for partial breakdown, whereas Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources like corn starch, and degrades more efficiently in commercial composting facilities. PLA's biodegradation rate surpasses polyurethane's due to its lactic acid-based structure, enabling microbial activity to convert it into water, carbon dioxide, and biomass within months. Polyurethane's resistance to hydrolysis and microbial attack results in prolonged environmental persistence, making PLA a more sustainable choice for eco-friendly biodegradable cutlery options.
Environmental Impact of Polyurethane and PLA
Polyurethane cutlery, derived from petrochemicals, poses significant environmental challenges due to its persistence in landfills and resistance to biodegradation, contributing to long-term pollution. Polylactic acid (PLA), sourced from renewable biomass such as corn starch, offers a more eco-friendly alternative with its ability to biodegrade under industrial composting conditions, reducing plastic waste accumulation. While PLA's production involves agricultural resources, its lower carbon footprint and improved end-of-life options make it preferable for sustainable biodegradable cutlery.
Strength and Durability in Cutlery Applications
Polyurethane exhibits superior strength and durability compared to polylactic acid (PLA) in biodegradable cutlery applications, offering enhanced resistance to bending and breakage under typical use conditions. PLA, while biodegradable and environmentally friendly, tends to be more brittle and less heat resistant, limiting its performance in heavy-duty or hot food scenarios. The molecular flexibility of polyurethane polymers contributes to greater impact resistance and longevity, making them more suitable for high-stress cutlery usage where durability is critical.
Cost Analysis: Polyurethane vs. PLA Utensils
Polyurethane cutlery typically incurs higher production costs due to its synthetic polymer composition and complex manufacturing processes compared to polylactic acid (PLA) utensils, which are derived from renewable resources like corn starch. PLA cutlery offers cost advantages with lower raw material expenses and compatibility with mass production methods, making it more economically feasible for large-scale biodegradable utensil manufacturing. However, the cost-benefit balance for polyurethane lies in its superior durability and heat resistance, potentially reducing replacement frequency despite a higher upfront price.
Food Safety and Regulatory Considerations
Polyurethane cutlery often contains synthetic chemicals that may pose food safety concerns due to potential leaching of toxic substances, necessitating strict regulatory approval and compliance with FDA or EU standards for food contact materials. Polylactic Acid (PLA), derived from renewable resources like corn starch, is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) and complies more readily with food safety regulations, making it a preferred choice for biodegradable cutlery in eco-friendly food service. Regulatory frameworks emphasize migration limits and biodegradability certifications, with PLA frequently meeting compostability requirements under standards such as ASTM D6400 and EN 13432, enhancing its suitability for safe, sustainable disposable tableware.
Consumer Perception and Market Trends
Consumer perception favors polylactic acid (PLA) cutlery for its natural origin and compostability, aligning with growing environmental awareness and demand for eco-friendly products. Market trends indicate a rising preference for PLA due to its biodegradability and certification standards, while polyurethane cutlery faces challenges related to synthetic composition and slower decomposition rates. Increasing regulations and consumer shifts toward sustainable alternatives continue to drive PLA's dominance in the biodegradable cutlery market.
Conclusion: Best Choice for Sustainable Cutlery
Polylactic acid (PLA) stands out as the best choice for sustainable cutlery due to its biodegradability and compostability, derived from renewable resources like corn starch and sugarcane. Polyurethane, while durable and versatile, is less environmentally friendly because it is petroleum-based and not readily biodegradable. For eco-conscious consumers seeking cutlery that minimizes environmental impact, PLA offers a superior balance of functionality and sustainability.
Infographic: Polyurethane vs Polylactic Acid for Biodegradable Cutlery
 azmater.com
azmater.com