Recycled plastic for water bottles significantly reduces environmental impact by lowering carbon emissions and conserving resources compared to virgin plastic, which is made from new raw materials and contributes to higher energy consumption. Using recycled plastic supports circular economy practices and minimizes plastic waste in landfills and oceans.
Table of Comparison
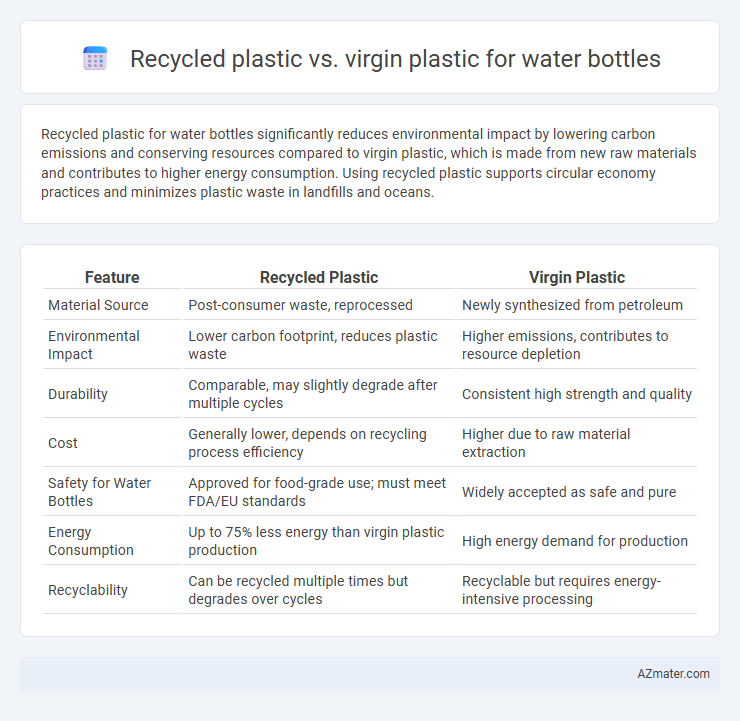
| Feature | Recycled Plastic | Virgin Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Post-consumer waste, reprocessed | Newly synthesized from petroleum |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, reduces plastic waste | Higher emissions, contributes to resource depletion |
| Durability | Comparable, may slightly degrade after multiple cycles | Consistent high strength and quality |
| Cost | Generally lower, depends on recycling process efficiency | Higher due to raw material extraction |
| Safety for Water Bottles | Approved for food-grade use; must meet FDA/EU standards | Widely accepted as safe and pure |
| Energy Consumption | Up to 75% less energy than virgin plastic production | High energy demand for production |
| Recyclability | Can be recycled multiple times but degrades over cycles | Recyclable but requires energy-intensive processing |
Introduction: Understanding Recycled vs Virgin Plastic
Recycled plastic water bottles are made from post-consumer waste, reducing environmental impact by lowering the demand for new raw materials and decreasing landfill waste. Virgin plastic is produced from newly extracted petroleum, offering consistent purity and strength but contributing to resource depletion and higher carbon emissions. Comparing these materials involves evaluating factors like durability, cost, and ecological footprint to determine the most sustainable choice for water bottle production.
Environmental Impacts of Recycled Plastic Bottles
Recycled plastic bottles significantly reduce environmental impacts by lowering greenhouse gas emissions and conserving natural resources compared to virgin plastic production. Utilizing recycled plastics decreases plastic waste in landfills and oceans, helping to mitigate pollution and its harmful effects on ecosystems. Energy consumption during manufacturing is substantially reduced when recycled materials are used, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint for water bottle production.
Carbon Footprint Comparison: Recycled vs Virgin Plastic
Recycled plastic water bottles have a significantly lower carbon footprint than virgin plastic bottles, reducing greenhouse gas emissions by up to 79%. The production of recycled plastic consumes less energy, as it bypasses the extraction and refinement processes required for virgin materials. This reduction in energy use translates directly to decreased carbon emissions, making recycled plastic a more sustainable choice for water bottle manufacturing.
Water Quality and Safety Concerns
Recycled plastic water bottles undergo rigorous testing to ensure compliance with FDA and EPA safety standards, maintaining water quality comparable to virgin plastic bottles. Microplastic contamination and chemical leaching are minimized through advanced recycling processes and strict quality controls, reducing health risks. Studies show no significant difference in taste or safety between recycled and virgin plastic bottles when proper manufacturing protocols are followed.
Durability and Performance Differences
Recycled plastic water bottles often exhibit lower durability and reduced impact resistance compared to virgin plastic, making them more prone to cracking and deformation under stress. Virgin plastic maintains superior structural integrity, ensuring consistent performance and extended shelf life by resisting wear and chemical degradation. Despite slightly compromised mechanical properties, advances in recycling technology have improved recycled plastic's viability for non-critical applications while prioritizing sustainability.
Cost Analysis: Production and Market Prices
Recycled plastic water bottles generally cost 15-30% less to produce than virgin plastic due to lower raw material expenses and reduced energy consumption in the recycling process. However, virgin plastic often maintains more consistent quality, leading to higher market prices despite increased production costs. Market demand for sustainable products is driving increased pricing competitiveness for recycled plastic bottles, narrowing the cost gap with virgin plastic alternatives.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Recycled plastic water bottles must comply with FDA regulations ensuring food-grade safety, similar to virgin plastic standards, but often require additional testing for contaminants. Certifications like the Global Recycled Standard (GRS) verify the recycled content and environmental compliance of recycled plastics used in water bottles. Virgin plastics benefit from established regulatory pathways with consistent material purity, while recycled options emphasize traceability and adherence to stringent quality controls to meet regulatory certifications.
Consumer Perception and Market Trends
Recycled plastic water bottles gain increasing consumer trust due to their environmental benefits and growing market demand for sustainable products. Virgin plastic bottles remain preferred for perceived purity and strength but face declining popularity as eco-conscious buyers prioritize recyclability and reduced carbon footprint. Market trends indicate a significant shift towards recycled materials, driven by regulatory pressure and consumer awareness of plastic pollution.
Innovations in Plastic Recycling Technology
Innovations in plastic recycling technology have significantly improved the quality of recycled plastic used in water bottles, enabling properties comparable to virgin plastic such as durability and clarity. Advanced chemical recycling methods break down used plastics into their original monomers, allowing the production of high-purity recycled resin suitable for food-grade water bottles. These technological advancements reduce dependency on fossil fuels and lower carbon emissions while maintaining safety and performance standards.
Future Prospects for Sustainable Water Bottles
Recycled plastic offers significant environmental benefits over virgin plastic by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and minimizing landfill waste, making it a key material for future sustainable water bottles. Advances in polymer recycling technologies and increased consumer demand are driving the scale-up of recycled content usage, improving both performance and cost-efficiency in water bottle production. Innovations such as chemical recycling and biodegradable additives are expected to further enhance the lifecycle sustainability and circular economy integration of recycled plastic water bottles.
Infographic: Recycled plastic vs Virgin plastic for Water bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com