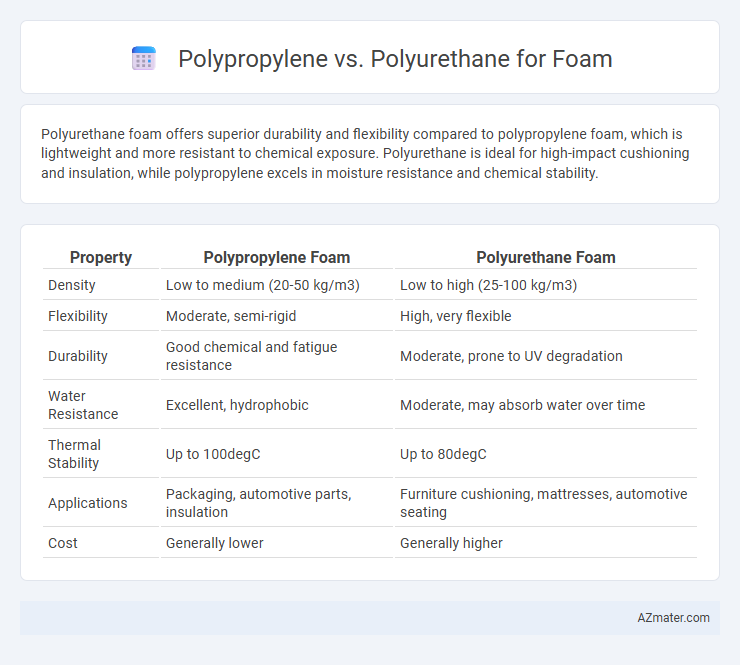
Polyurethane foam offers superior durability and flexibility compared to polypropylene foam, which is lightweight and more resistant to chemical exposure. Polyurethane is ideal for high-impact cushioning and insulation, while polypropylene excels in moisture resistance and chemical stability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene Foam | Polyurethane Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low to medium (20-50 kg/m3) | Low to high (25-100 kg/m3) |
| Flexibility | Moderate, semi-rigid | High, very flexible |
| Durability | Good chemical and fatigue resistance | Moderate, prone to UV degradation |
| Water Resistance | Excellent, hydrophobic | Moderate, may absorb water over time |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 100degC | Up to 80degC |
| Applications | Packaging, automotive parts, insulation | Furniture cushioning, mattresses, automotive seating |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
Introduction to Polypropylene and Polyurethane Foams
Polypropylene foam is a lightweight, durable material known for its excellent chemical resistance and high impact strength, making it ideal for automotive and packaging applications. Polyurethane foam offers superior flexibility, cushioning properties, and thermal insulation, commonly used in furniture, bedding, and automotive interiors. Both foams are versatile, but polypropylene excels in structural support while polyurethane is preferred for comfort and shock absorption.
Chemical Structure Differences
Polypropylene foam consists of long chains of repeating propylene units, characterized by a non-polar, semi-crystalline hydrocarbon backbone that provides high chemical resistance and rigidity. Polyurethane foam, on the other hand, is formed from a reaction between polyols and diisocyanates, resulting in a polymer with urethane linkages (-NH-CO-O-) that offer flexibility and variable density. The presence of polar urethane groups in polyurethane foam leads to greater elasticity and moisture absorption compared to the hydrophobic polypropylene foam.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Polypropylene foam is typically produced through a bead expansion process involving steam activation and compression molding, resulting in a lightweight, rigid structure with high chemical resistance. Polyurethane foam is manufactured by a chemical reaction between polyol and diisocyanate, often using a foaming agent to create a flexible or rigid cellular structure, adaptable to spray, slabstock, or integral skin molding processes. The polypropylene manufacturing process emphasizes thermal stability and recyclability, whereas polyurethane production offers greater versatility in density and cushioning properties due to its reactive polymer chemistry.
Physical Properties and Performance
Polypropylene foam exhibits high tensile strength, excellent chemical resistance, and low water absorption, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and moisture resistance. Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning, flexibility, and excellent energy absorption, which enhances comfort and shock protection. The choice between polypropylene and polyurethane foam depends on the specific needs of strength and rigidity versus softness and resilience in the application.
Durability and Longevity
Polyurethane foam offers superior durability and longevity compared to polypropylene foam due to its higher resilience and resistance to wear and tear in various environments. Polyurethane's molecular structure provides enhanced flexibility and improved compression recovery, making it ideal for applications requiring long-term cushioning and support. In contrast, polypropylene foam, while lightweight and moisture-resistant, tends to degrade faster under prolonged mechanical stress and UV exposure.
Applications in Various Industries
Polypropylene foam is extensively used in automotive, packaging, and construction industries due to its lightweight, chemical resistance, and excellent cushioning properties. Polyurethane foam, favored in furniture, bedding, and insulation sectors, offers superior flexibility, durability, and thermal insulation. Both foams play critical roles in medical devices and sports equipment, with polypropylene excelling in rigidity and polyurethane providing enhanced comfort.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polypropylene foam offers superior environmental sustainability due to its recyclability and lower carbon footprint compared to polyurethane foam, which is often derived from petrochemicals and involves toxic isocyanates in production. Polypropylene's resistance to moisture and chemicals enhances its durability, reducing the frequency of replacement and waste generation. Polyurethane foams, while versatile and widely used, pose challenges for recycling and can release harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during degradation, impacting indoor air quality and the environment.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Polypropylene foam offers a cost-effective solution with lower raw material and production expenses compared to polyurethane foam, making it an affordable choice for large-scale applications. Polyurethane foam, while generally more expensive due to its superior cushioning properties and versatility, often justifies the higher cost in specialized uses requiring enhanced durability and comfort. Budget-conscious projects typically favor polypropylene for its balance of performance and economical pricing, whereas polyurethane is preferred when performance demands justify the investment.
Health and Safety Considerations
Polyurethane foam is known for its superior cushioning and flexibility but can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during manufacturing and breakdown, posing respiratory risks if not properly ventilated. Polypropylene foam, often used in packaging and insulation, is generally inert and less likely to emit harmful chemicals, making it a safer option for indoor environments. Both materials require careful handling during production and disposal to minimize exposure to dust and potential irritants.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Needs
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning and flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring comfort and shock absorption, such as upholstery and mattresses. Polypropylene foam provides higher resistance to chemicals, moisture, and UV exposure, making it suitable for outdoor use and environments requiring durability and weather resistance. Selecting the right foam depends on prioritizing factors like comfort, durability, moisture resistance, and environmental exposure relevant to your specific application.
Infographic: Polypropylene vs Polyurethane for Foam
 azmater.com
azmater.com