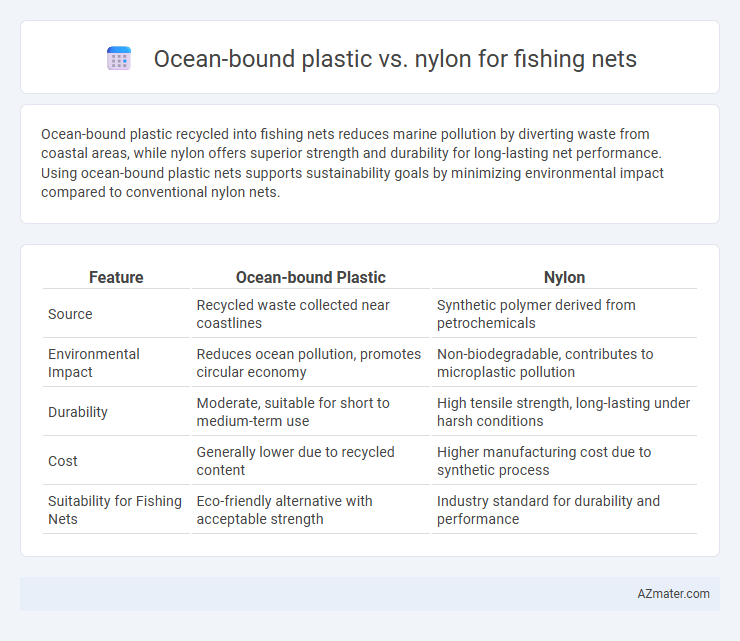
Ocean-bound plastic recycled into fishing nets reduces marine pollution by diverting waste from coastal areas, while nylon offers superior strength and durability for long-lasting net performance. Using ocean-bound plastic nets supports sustainability goals by minimizing environmental impact compared to conventional nylon nets.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ocean-bound Plastic | Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Recycled waste collected near coastlines | Synthetic polymer derived from petrochemicals |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces ocean pollution, promotes circular economy | Non-biodegradable, contributes to microplastic pollution |
| Durability | Moderate, suitable for short to medium-term use | High tensile strength, long-lasting under harsh conditions |
| Cost | Generally lower due to recycled content | Higher manufacturing cost due to synthetic process |
| Suitability for Fishing Nets | Eco-friendly alternative with acceptable strength | Industry standard for durability and performance |
Understanding Ocean-Bound Plastic: Definition and Sources
Ocean-bound plastic refers to plastic waste found within 50 kilometers of coastlines, posing a significant threat to marine ecosystems through entanglement and ingestion by aquatic life. These plastics originate from sources such as improperly managed landfills, urban litter, and river outflows, often entering oceans via stormwater and tidal movements. Compared to traditional nylon fishing nets derived from petroleum, ocean-bound plastic nets utilize recycled materials, reducing environmental impact and promoting circular economy principles in the fishing industry.
Nylon as a Traditional Material in Fishing Nets
Nylon, a synthetic polymer widely used in fishing nets, offers high tensile strength, elasticity, and resistance to abrasion, making it a traditional choice for durable fishing gear. Ocean-bound plastic, sourced from waste collected near coastlines, provides an eco-friendly alternative by reducing marine pollution but often requires processing to achieve the mechanical properties of nylon. Despite environmental benefits, nylon remains preferred for its proven reliability and performance in harsh marine conditions.
Environmental Impact: Ocean-Bound Plastic vs Nylon
Ocean-bound plastic fishing nets significantly reduce ocean pollution by repurposing waste materials that would otherwise degrade marine ecosystems, contrasting with nylon nets whose production relies on non-renewable fossil fuels and emits higher levels of greenhouse gases. Recycling ocean-bound plastic minimizes plastic leakage into oceans, protecting biodiversity and marine habitats from microplastic contamination. Nylon nets, though durable, contribute to environmental degradation through energy-intensive manufacturing and slow decomposition, leading to long-term ecological impacts.
Durability and Performance: Comparing Both Materials
Nylon fishing nets offer superior durability with high tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and elasticity, making them ideal for extended use in harsh marine environments. Ocean-bound plastic nets, made from recycled materials, provide an eco-friendly alternative but generally exhibit lower tensile strength and reduced longevity compared to nylon. Performance-wise, nylon nets maintain shape and resist damage better under heavy loads, whereas ocean-bound plastic nets may degrade more quickly, affecting catch efficiency and durability.
Recyclability and End-of-Life Scenarios
Ocean-bound plastic used in fishing nets offers enhanced recyclability compared to traditional nylon, as it is often sourced from post-consumer waste designed for circular reuse, reducing environmental impact. Nylon nets, while durable and effective, pose significant challenges in end-of-life scenarios due to their synthetic composition, which complicates recycling processes and frequently leads to landfill accumulation or incineration. Utilizing ocean-bound plastic aligns with sustainable fishing practices by enabling closed-loop systems and minimizing ocean pollution through improved waste management and material recovery.
Cost-Effectiveness and Market Availability
Ocean-bound plastic fishing nets offer significant cost-effectiveness due to lower raw material expenses and growing incentives for sustainable products, whereas nylon nets, while durable, tend to have higher production costs from petroleum-based inputs. Market availability for ocean-bound plastic nets is expanding as manufacturers respond to increasing environmental regulations and consumer demand, though nylon nets maintain widespread presence due to established supply chains and performance reliability. The economic advantage of ocean-bound plastics is driving innovation and adoption in regions targeting eco-friendly fishing gear solutions.
Marine Life Safety and Ecosystem Health
Ocean-bound plastic repurposed into fishing nets significantly reduces marine pollution and minimizes harm to marine life by preventing toxic chemical release and entanglement hazards. Nylon fishing nets, although durable and effective, often degrade slowly and contribute to ghost net pollution, posing long-term threats to ecosystem health through habitat destruction and bycatch. Choosing ocean-bound plastic nets supports circular economy practices and enhances marine biodiversity protection by mitigating the negative impacts associated with conventional nylon nets.
Adoption Challenges in the Fishing Industry
Ocean-bound plastic faces significant adoption challenges in the fishing industry due to concerns over durability, strength, and reliability compared to traditional nylon nets. Fishermen often prioritize materials like nylon for their proven resilience in harsh marine conditions and cost-effectiveness, making the transition to alternative materials slow. Regulatory standards and lack of large-scale testing further hinder the widespread integration of ocean-bound plastic into commercial fishing net manufacturing.
Innovative Solutions and Future Trends
Ocean-bound plastic offers an innovative and sustainable alternative to traditional nylon in fishing nets, significantly reducing marine pollution by repurposing waste destined for oceans. This material enhances durability and environmental impact by incorporating recycled plastics sourced within 50 kilometers of coastlines, fostering circular economy practices. Future trends indicate increased adoption of bio-based polymers and hybrid composites, improving net performance while accelerating ocean cleanup efforts and supporting eco-friendly fisheries.
Choosing the Sustainable Option: Key Considerations
Ocean-bound plastic offers a sustainable alternative to conventional nylon for fishing nets by reducing marine pollution and promoting circular economy practices. Nylon, derived from non-renewable petroleum resources, presents higher environmental impacts due to its production emissions and degradation challenges. Key considerations include durability, environmental footprint, recyclability, and the potential to mitigate ocean plastic waste through responsible material sourcing and end-of-life management.
Infographic: Ocean-bound plastic vs Nylon for Fishing net
 azmater.com
azmater.com