Ocean-bound plastic offers a sustainable alternative for shoe soles by repurposing waste with high environmental impact, while ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) provides durability, flexibility, and lightweight cushioning. Choosing ocean-bound plastic reduces marine pollution and carbon footprint, whereas EVA delivers enhanced performance and comfort in footwear.
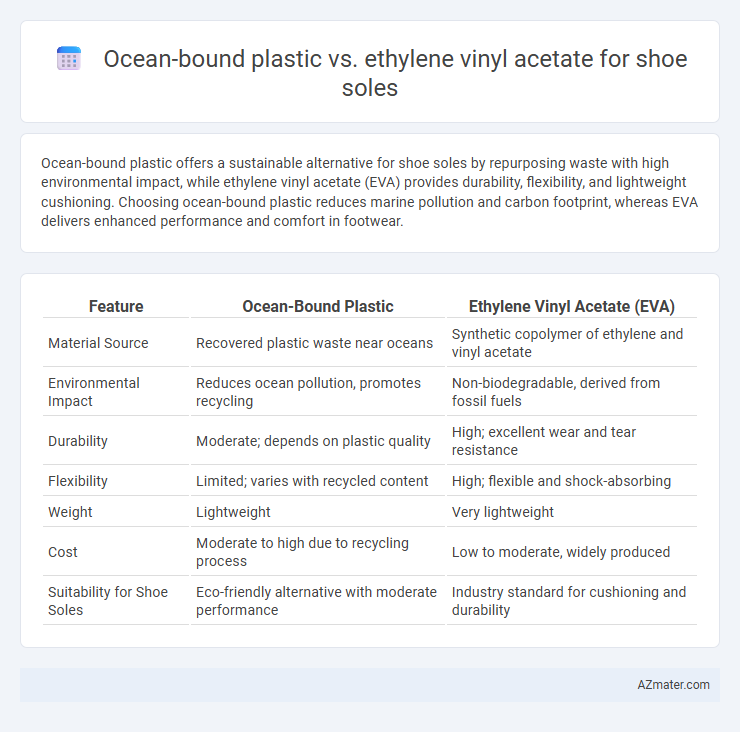
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ocean-Bound Plastic | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Recovered plastic waste near oceans | Synthetic copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces ocean pollution, promotes recycling | Non-biodegradable, derived from fossil fuels |
| Durability | Moderate; depends on plastic quality | High; excellent wear and tear resistance |
| Flexibility | Limited; varies with recycled content | High; flexible and shock-absorbing |
| Weight | Lightweight | Very lightweight |
| Cost | Moderate to high due to recycling process | Low to moderate, widely produced |
| Suitability for Shoe Soles | Eco-friendly alternative with moderate performance | Industry standard for cushioning and durability |
Introduction to Sustainable Shoe Soles
Ocean-bound plastic and ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) represent innovative materials transforming sustainable shoe soles by addressing environmental impact and performance. Ocean-bound plastic repurposes recovered waste plastic near coastal areas, reducing ocean pollution and offering a recycled, eco-friendly alternative to traditional sole materials. EVA provides lightweight cushioning and flexibility but often relies on petrochemical sources, prompting sustainable designs to combine or replace EVA with ocean-bound plastic to enhance durability while minimizing ecological footprint.
What Is Ocean-Bound Plastic?
Ocean-bound plastic refers to discarded plastic waste collected from coastal areas within 50 kilometers of shorelines before it enters the ocean, offering a sustainable raw material option for manufacturing. This material reduces environmental pollution by repurposing plastic debris, which contrasts with ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), a synthetic polymer commonly used for shoe soles due to its lightweight and cushioning properties. Utilizing ocean-bound plastic in shoe soles promotes circular economy principles by transforming marine-bound waste into durable, eco-friendly footwear components.
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA): Overview and Uses
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is a lightweight, flexible, and durable polymer widely used in shoe soles for its excellent shock absorption and cushioning properties. Unlike ocean-bound plastic, which is repurposed waste material from coastal regions, EVA is a synthetic material known for resistance to cracking and UV radiation, enhancing footwear longevity. Its adaptability in molding and resilience to environmental stress makes EVA a preferred choice in athletic and casual shoe manufacturing.
Environmental Impact: Ocean-Bound Plastic vs. EVA
Ocean-bound plastic used in shoe soles helps reduce marine pollution by repurposing waste collected near coastlines, significantly lowering plastic leakage into oceans. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), a petrochemical-based polymer, contributes to fossil fuel depletion and generates non-biodegradable waste, exacerbating landfill and pollution issues. Incorporating ocean-bound plastic promotes circular economy principles by valorizing waste, whereas EVA soles demand more energy-intensive production and lack end-of-life biodegradability.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Ocean-bound plastic shoe soles provide eco-friendly durability with moderate flexibility, offering resistance to abrasion but potentially lower impact absorption compared to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA). EVA soles excel in lightweight cushioning, shock absorption, and long-lasting elasticity, enhancing overall performance in athletic and casual footwear. While ocean-bound plastic promotes sustainability, EVA remains a superior choice for durability and comfort under rigorous wear conditions.
Comfort and Weight Factors
Ocean-bound plastic used in shoe soles offers eco-friendly benefits with moderate flexibility but tends to be heavier compared to Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), which is renowned for its lightweight and superior cushioning properties enhancing overall foot comfort. EVA's low density and excellent shock absorption contribute to reduced fatigue during prolonged wear, whereas ocean-bound plastic soles might compromise some comfort due to increased rigidity. Weight optimization in EVA soles supports agility and support, making it the preferred choice in performance footwear, while ocean-bound plastic appeals more to sustainability-focused consumers despite potential trade-offs in comfort and weight.
Recycling and End-of-Life Considerations
Ocean-bound plastic offers a sustainable alternative for shoe soles by repurposing waste materials destined for marine pollution, contributing to reduced environmental impact through circular recycling processes. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), while highly durable and lightweight, poses challenges in recycling due to its synthetic polymer structure, often requiring specialized facilities and processes to reclaim or degrade effectively. End-of-life considerations favor ocean-bound plastic for its biodegradability potential and closed-loop recovery, whereas EVA soles may persist in landfill environments, emphasizing the need for improved material recovery technologies.
Manufacturing Process and Supply Chain
Ocean-bound plastic shoe soles require sourcing and processing of recovered plastics, involving extensive cleaning, shredding, and pelletizing before compound mixing, which adds complexity to the supply chain due to variability in raw material quality. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) soles use petrochemical feedstocks processed through well-established polymerization and molding techniques, ensuring consistent quality and streamlined manufacturing with readily available materials. The ocean-bound plastic supply chain faces challenges in collection and standardization, whereas EVA benefits from mature industrial infrastructure and predictable logistics.
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
Ocean-bound plastic shoe soles are gaining traction due to rising consumer demand for sustainable and eco-friendly products, reflecting a broader market trend toward circular economy practices. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) remains popular for its lightweight, cushioning properties and cost-effectiveness, but sustainability concerns are driving innovation toward bio-based and recycled alternatives. Market data indicates a growing preference among environmentally conscious consumers for footwear incorporating ocean-bound plastic, pushing brands to integrate recycled materials without compromising performance or comfort.
Future Perspectives in Eco-Friendly Footwear Materials
Ocean-bound plastic offers a sustainable alternative for shoe soles by repurposing waste debris collected near coastlines, significantly reducing marine pollution and reliance on virgin plastics. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) remains popular due to its lightweight, cushioning properties, but innovations are pushing for bio-based or recycled EVA blends to enhance biodegradability and reduce carbon footprints. Future perspectives emphasize combining ocean-bound plastics with advanced EVA composites, aiming to create durable, eco-friendly soles that align with circular economy principles and emerging environmental regulations.
Infographic: Ocean-bound plastic vs Ethylene vinyl acetate for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com