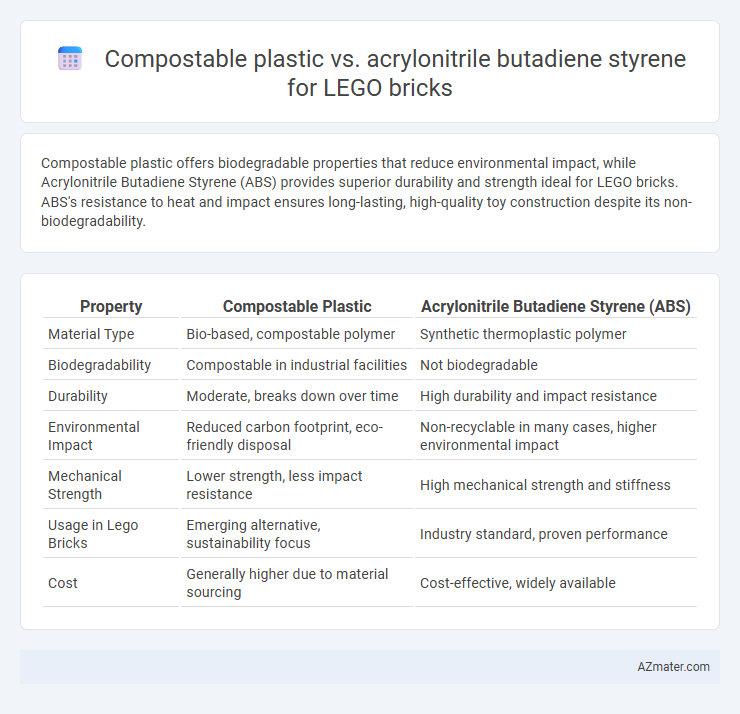
Compostable plastic offers biodegradable properties that reduce environmental impact, while Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides superior durability and strength ideal for LEGO bricks. ABS's resistance to heat and impact ensures long-lasting, high-quality toy construction despite its non-biodegradability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Compostable Plastic | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Bio-based, compostable polymer | Synthetic thermoplastic polymer |
| Biodegradability | Compostable in industrial facilities | Not biodegradable |
| Durability | Moderate, breaks down over time | High durability and impact resistance |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced carbon footprint, eco-friendly disposal | Non-recyclable in many cases, higher environmental impact |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower strength, less impact resistance | High mechanical strength and stiffness |
| Usage in Lego Bricks | Emerging alternative, sustainability focus | Industry standard, proven performance |
| Cost | Generally higher due to material sourcing | Cost-effective, widely available |
Introduction to Sustainable Materials in Toy Manufacturing
Compostable plastics offer an eco-friendly alternative to traditional acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) in Lego brick manufacturing by reducing environmental impact through biodegradability and lower carbon emissions. ABS is favored for its durability, impact resistance, and precision molding, ensuring high-quality and long-lasting toy bricks, but its petroleum-based composition contributes to plastic pollution. Sustainable materials in toy manufacturing aim to balance performance with environmental responsibility, promoting circular economy principles and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Understanding Compostable Plastics: Composition and Properties
Compostable plastics used in Lego bricks are primarily derived from renewable biomass sources such as cornstarch and polylactic acid (PLA), designed to biodegrade under industrial composting conditions. These materials exhibit properties like flexibility and moderate durability but typically have lower impact resistance and heat tolerance compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which is a petroleum-based thermoplastic known for its high strength, rigidity, and thermal stability. Understanding the molecular composition and biodegradability of compostable plastics highlights their environmental benefits alongside performance trade-offs relative to ABS in manufacturing Lego bricks.
What is Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)?
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a durable thermoplastic polymer widely used in manufacturing LEGO bricks due to its high impact resistance, rigidity, and ease of molding. Unlike compostable plastics that break down under specific environmental conditions, ABS offers long-lasting structural integrity, maintaining vibrant colors and precise dimensions over time. Its chemical composition and physical properties make ABS ideal for creating interlocking bricks that are both strong and safe for repeated assembly and disassembly.
Mechanical Performance: Strength and Durability Comparison
Compostable plastics used for Lego bricks generally exhibit lower mechanical strength and durability compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which is renowned for its high impact resistance and toughness. ABS maintains structural integrity under repeated stress and exposure to varying temperatures, making it ideal for long-lasting, resilient Lego components. In contrast, compostable plastics tend to degrade faster and have reduced load-bearing capacity, impacting the longevity and mechanical reliability of the bricks.
Environmental Impact: Biodegradability vs. Longevity
Compostable plastic used for Lego bricks offers significant environmental benefits through rapid biodegradability, reducing landfill accumulation and minimizing microplastic pollution. In contrast, Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) exhibits exceptional durability and longevity, ensuring prolonged product lifespan but contributing to persistent plastic waste if not properly recycled. The trade-off between compostable plastics' environmental friendliness and ABS's robustness highlights the need for innovation in sustainable polymer alternatives that combine biodegradability with mechanical strength.
Safety Considerations for Children’s Toys
Compostable plastic used in Lego bricks offers environmental benefits but may lack the durability and chemical resistance required for long-term safety in children's toys, potentially degrading and releasing harmful substances over time. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is the industry standard for Lego bricks due to its non-toxic, robust, and impact-resistant properties, ensuring the brick's integrity and safety during prolonged use. Safety assessments prioritize ABS for minimizing choking hazards and chemical exposure, whereas compostable plastics require rigorous testing to meet stringent toy safety regulations.
Cost Analysis: Production, Scalability, and Market Implications
Compostable plastics generally incur higher production costs than Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) due to raw material expenses and less mature manufacturing processes, impacting scalability for mass production of Lego bricks. ABS remains cost-effective and widely adopted in the toy industry, benefiting from established supply chains and economies of scale that reduce unit costs significantly. Market implications suggest using compostable plastics could elevate retail prices and challenge large-scale adoption but may appeal to eco-conscious consumers seeking sustainable alternatives.
Challenges in Switching Lego Bricks to Compostable Plastics
Switching Lego bricks from Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) to compostable plastics poses significant challenges due to ABS's superior durability, strength, and color retention essential for Lego's quality standards. Compostable plastics often lack the mechanical robustness and precise molding capabilities of ABS, leading to potential issues with brick fit, longevity, and user experience. Additionally, compostable materials may degrade prematurely under typical play conditions and require specialized composting facilities, complicating widespread adoption in Lego manufacturing.
Consumer Perception and Demand for Eco-Friendly Toys
Consumer perception favors compostable plastics for Lego bricks as eco-friendly alternatives align with increasing environmental awareness and demand for sustainable toys. Studies reveal a growing preference among parents for products that reduce plastic waste and support circular economies without compromising durability. While acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) remains valued for its strength and longevity, shifting market trends highlight a rising demand for biodegradable materials that minimize ecological impact.
Future Outlook: Innovations and Trends in Lego Brick Materials
Innovations in Lego brick materials are increasingly focused on sustainability, with compostable plastics emerging as a promising alternative to traditional Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) due to their biodegradability and reduced environmental impact. Research and development efforts are accelerating to enhance the durability and colorfastness of compostable bioplastics, aiming to match the mechanical strength and precision molding capabilities of ABS. Future trends suggest a hybrid approach combining bio-based polymers with advanced manufacturing techniques to create eco-friendly Lego bricks without compromising the iconic quality and safety standards.
Infographic: Compostable plastic vs Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene for Lego brick
 azmater.com
azmater.com