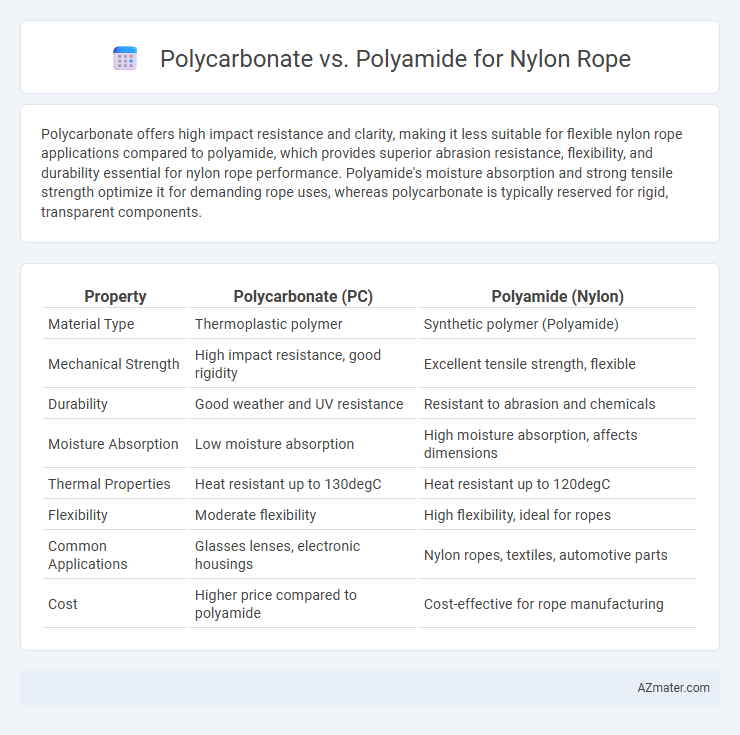
Polycarbonate offers high impact resistance and clarity, making it less suitable for flexible nylon rope applications compared to polyamide, which provides superior abrasion resistance, flexibility, and durability essential for nylon rope performance. Polyamide's moisture absorption and strong tensile strength optimize it for demanding rope uses, whereas polycarbonate is typically reserved for rigid, transparent components.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polycarbonate (PC) | Polyamide (Nylon) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Synthetic polymer (Polyamide) |
| Mechanical Strength | High impact resistance, good rigidity | Excellent tensile strength, flexible |
| Durability | Good weather and UV resistance | Resistant to abrasion and chemicals |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorption | High moisture absorption, affects dimensions |
| Thermal Properties | Heat resistant up to 130degC | Heat resistant up to 120degC |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | High flexibility, ideal for ropes |
| Common Applications | Glasses lenses, electronic housings | Nylon ropes, textiles, automotive parts |
| Cost | Higher price compared to polyamide | Cost-effective for rope manufacturing |
Introduction to Polycarbonate and Polyamide
Polycarbonate is a durable, lightweight thermoplastic known for its high impact resistance and clarity, making it ideal for applications requiring strength and transparency. Polyamide, commonly referred to as Nylon, is a strong, flexible synthetic polymer prized for its excellent abrasion resistance and elasticity, frequently used in rope manufacturing. Comparing these materials highlights polycarbonate's rigidity and toughness versus polyamide's flexibility and resilience in nylon rope applications.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Polycarbonate features a carbonate group linking aromatic rings, providing high impact resistance and clarity, whereas polyamide (nylon) consists of amide bonds connecting aliphatic chains, contributing to excellent tensile strength and abrasion resistance. The ester linkage in polycarbonate results in higher rigidity and thermal stability, while the hydrogen bonding in polyamide's amide groups enhances flexibility and moisture absorption. These structural distinctions influence the performance characteristics of nylon ropes, with polyamide fibers offering superior elasticity and polycarbonate materials providing enhanced durability under harsh chemical conditions.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyamide (nylon) ropes typically exhibit superior mechanical strength and exceptional durability compared to polycarbonate ropes due to their high tensile strength and excellent abrasion resistance. Polyamide fibers maintain flexibility and resilience under heavy loads and harsh environmental conditions, making them ideal for demanding applications like marine and climbing ropes. Polycarbonate ropes, while offering good impact resistance and lightweight properties, generally lack the sustained mechanical strength and longevity required for high-stress rope uses.
Flexibility and Elasticity
Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, boasts superior flexibility and elasticity compared to polycarbonate, making it ideal for dynamic applications requiring stretch and resilience. Polycarbonate is rigid and less elastic, often used where strength and impact resistance are prioritized over flexibility. For nylon rope, polyamide fibers provide better stretch recovery and durability during repeated bending and flexing, enhancing performance in climbing and marine environments.
Resistance to UV and Weathering
Polyamide (Nylon) ropes exhibit superior UV resistance and weathering durability compared to polycarbonate materials, making them ideal for prolonged outdoor use. Polycarbonate tends to degrade and yellow under extended UV exposure, reducing its mechanical integrity. Polyamide's molecular structure provides greater resistance to moisture, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations, ensuring longer lifespan in harsh environments.
Abrasion and Impact Resistance
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance compared to polyamide, making it highly effective in applications where shock absorption and durability under sudden force are critical. Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, excels in abrasion resistance, allowing it to withstand prolonged friction and wear, which is essential for rope applications exposed to rough surfaces. When selecting nylon rope, polyamide fibers provide enhanced abrasion durability, whereas polycarbonate components contribute better impact resilience in hybrid designs.
Water Absorption and Moisture Behavior
Polyamide (Nylon) exhibits higher water absorption, typically around 2-8%, leading to swelling and reduced mechanical strength when exposed to moisture, whereas polycarbonate absorbs less than 0.2% water, maintaining dimensional stability. The moisture uptake of nylon causes changes in elasticity and tensile properties, making it less suitable for applications requiring minimal moisture impact. Polycarbonate's low moisture absorption ensures consistent performance in wet environments, making it preferable for ropes needing minimal water-related degradation.
Cost and Availability for Rope Production
Polycarbonate rope production typically incurs higher material costs due to the polymer's premium pricing and limited availability compared to polyamide. Polyamide, commonly known as Nylon, benefits from widespread manufacturing infrastructure and abundant raw materials, resulting in lower costs and easier procurement for rope manufacturers. The greater accessibility and economic efficiency of polyamide make it the preferred choice for large-scale nylon rope production.
Typical Applications in Nylon Rope Manufacturing
Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, is the primary material used in nylon rope manufacturing due to its excellent tensile strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for marine, climbing, and industrial applications. Polycarbonate, although not typically used as the main fiber in ropes, serves as a protective coating or component in composite ropes to enhance impact resistance and durability in specialized settings. The superior moisture resistance and chemical stability of polyamide ensure reliable performance in wet environments, which is critical for typical nylon rope applications.
Choosing the Right Material: Polycarbonate or Polyamide
Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, offers exceptional strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for high-stress rope applications requiring durability and flexibility. Polycarbonate, while known for its impact resistance and clarity in plastics, lacks the tensile strength and stretch properties essential for effective rope performance compared to polyamide. Choosing polyamide ensures superior load-bearing capacity and resilience in dynamic environments, while polycarbonate is less suited for rope manufacturing due to its rigidity and lower mechanical flexibility.
Infographic: Polycarbonate vs Polyamide for Nylon Rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com