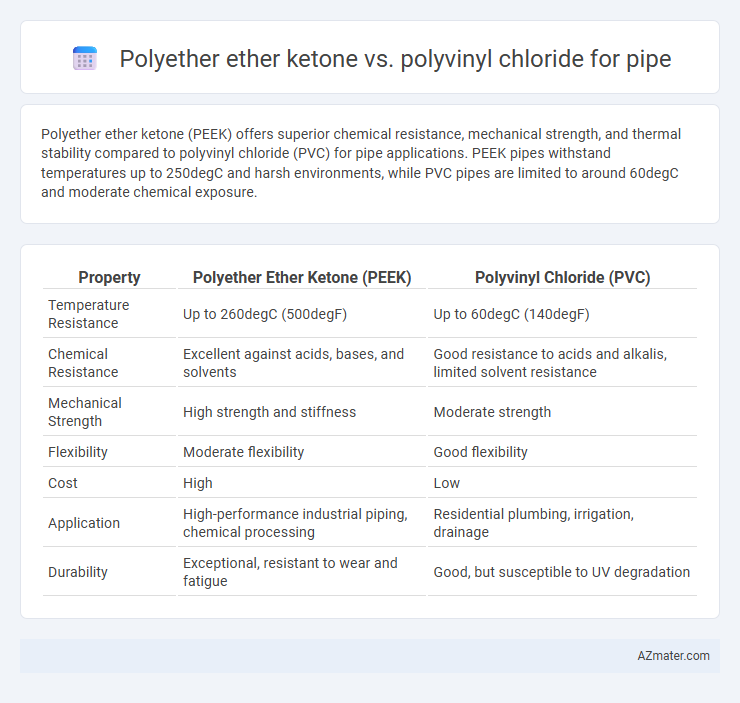
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and thermal stability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) for pipe applications. PEEK pipes withstand temperatures up to 250degC and harsh environments, while PVC pipes are limited to around 60degC and moderate chemical exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 260degC (500degF) | Up to 60degC (140degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against acids, bases, and solvents | Good resistance to acids and alkalis, limited solvent resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength and stiffness | Moderate strength |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | Good flexibility |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Application | High-performance industrial piping, chemical processing | Residential plumbing, irrigation, drainage |
| Durability | Exceptional, resistant to wear and fatigue | Good, but susceptible to UV degradation |
Introduction to Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Pipes
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for exceptional chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and thermal stability up to 250degC, making it ideal for demanding pipe applications in aerospace and medical industries. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a widely used plastic pipe material characterized by cost-effectiveness, corrosion resistance, and excellent electrical insulation, typically rated for temperatures up to 60degC, commonly applied in construction and plumbing. The significant differences in thermal tolerance, durability, and cost define the selection criteria between PEEK and PVC pipes for industrial versus standard utility purposes.
Chemical Structure and Composition: PEEK vs PVC
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) features a rigid aromatic backbone with ether and ketone linkages, offering exceptional thermal and chemical resistance due to its semi-crystalline structure. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) consists of a polymer chain of vinyl chloride monomers with chlorine atoms providing flame retardancy and corrosion resistance but lower thermal stability compared to PEEK. The chemical composition of PEEK imparts superior mechanical strength and durability in aggressive environments, while PVC is more cost-effective and versatile for standard piping applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison of PEEK and PVC Pipes
PEEK pipes exhibit superior mechanical properties compared to PVC pipes, including higher tensile strength (90-100 MPa vs. 40-50 MPa) and exceptional impact resistance. The modulus of elasticity for PEEK is around 3.6 GPa, significantly exceeding PVC's 2.5 GPa, enabling better dimensional stability under load. PEEK also demonstrates remarkable fatigue resistance and thermal stability, maintaining mechanical integrity at temperatures up to 250degC, while PVC typically softens above 60degC.
Temperature Resistance: PEEK vs PVC in Piping Applications
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) exhibits exceptional temperature resistance, maintaining structural integrity at continuous use temperatures up to 250degC, making it ideal for high-temperature piping applications. In contrast, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) has a significantly lower maximum operating temperature, typically around 60degC, which limits its use in environments with elevated thermal demands. The superior thermal stability of PEEK ensures reliable performance in chemical processing and industrial piping systems where PVC would fail due to thermal degradation or deformation.
Corrosion and Chemical Resistance: Which Pipe Performs Better?
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) exhibits superior corrosion and chemical resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it ideal for harsh industrial environments. PEEK withstands aggressive chemicals, high temperatures, and solvents without degrading, whereas PVC can become brittle or swell when exposed to certain solvents and acids. The enhanced durability of PEEK pipes translates to longer service life and reduced maintenance in corrosive applications.
Installation and Fabrication Differences between PEEK and PVC
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making PEEK pipes suitable for high-temperature and harsh chemical environments where PVC may degrade. Fabrication of PEEK pipes involves advanced processing techniques such as injection molding and extrusion at elevated temperatures, whereas PVC pipes are easier to fabricate and install using conventional solvent welding and mechanical joining at lower temperatures. Installation of PEEK pipes requires specialized equipment for fusion bonding and is typically more labor-intensive and costly than the simpler, quicker assembly methods available for PVC pipe systems.
Longevity and Lifecycle Costs: PEEK vs PVC Pipes
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) pipes exhibit superior longevity compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes due to their exceptional chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and mechanical strength, resulting in a service life exceeding 50 years under harsh conditions. Lifecycle costs of PEEK pipes are lower than PVC when factoring in reduced maintenance, fewer replacements, and resistance to corrosion and UV degradation, making PEEK a cost-effective solution for long-term industrial applications. PVC pipes, although initially cheaper, require frequent replacement and have higher maintenance expenses, which increase total ownership costs over time.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability of PEEK and PVC
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) exhibits superior environmental sustainability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) due to its exceptional chemical resistance, high recyclability, and longer lifespan, reducing the frequency of replacements and waste generation. PVC production and disposal release harmful chlorine-based dioxins and other toxic substances, contributing to environmental pollution and posing challenges for recycling. PEEK's ability to withstand harsh conditions without degradation minimizes environmental impact, making it a more eco-friendly choice for piping applications where durability and sustainability are critical.
Common Applications: Where PEEK or PVC Pipes Excel
PEEK pipes are commonly used in high-performance applications requiring exceptional chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance up to 260degC, and superior mechanical strength, such as aerospace, medical devices, and semiconductor manufacturing. PVC pipes excel in cost-effective plumbing, water distribution, and irrigation systems due to their lightweight nature, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation in temperatures typically below 60degC. The choice between PEEK and PVC pipes depends on operational demands, with PEEK suited for extreme environments and PVC ideal for general-purpose infrastructure.
Choosing the Right Pipe: Key Considerations for PEEK vs PVC
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) pipes offer superior chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance up to 250degC, and excellent mechanical strength, making them ideal for demanding industrial applications. In contrast, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes provide cost-effective solutions with moderate chemical resistance and temperature limits around 60degC, suitable for residential plumbing and low-pressure systems. Selecting between PEEK and PVC pipes requires evaluating factors such as operating temperature, chemical exposure, mechanical load, and budget constraints to ensure optimal long-term performance and durability.
Infographic: Polyether ether ketone vs Polyvinyl chloride for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com