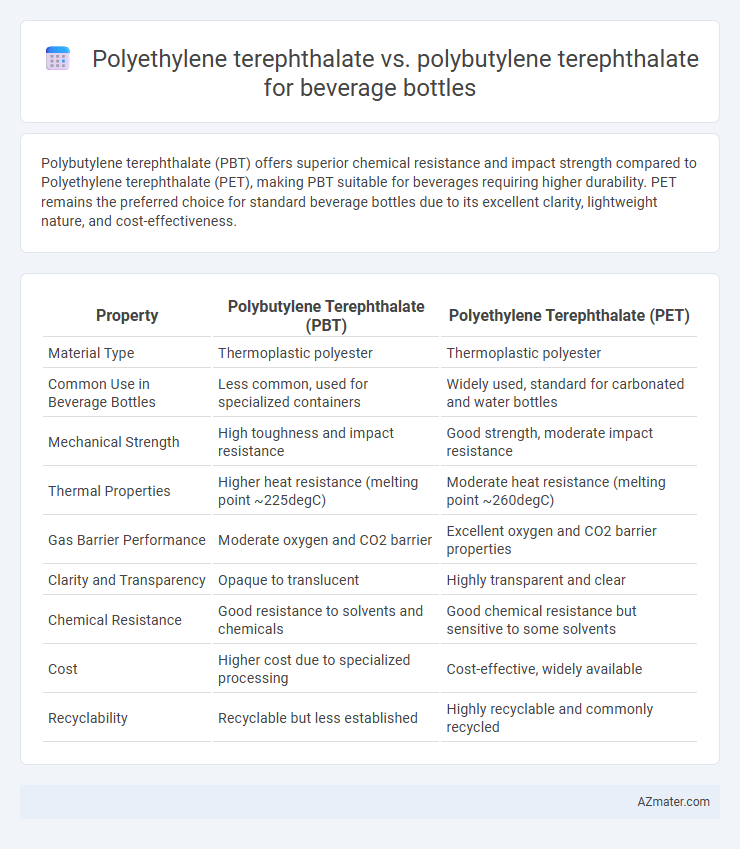
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior chemical resistance and impact strength compared to Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), making PBT suitable for beverages requiring higher durability. PET remains the preferred choice for standard beverage bottles due to its excellent clarity, lightweight nature, and cost-effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polyester | Thermoplastic polyester |
| Common Use in Beverage Bottles | Less common, used for specialized containers | Widely used, standard for carbonated and water bottles |
| Mechanical Strength | High toughness and impact resistance | Good strength, moderate impact resistance |
| Thermal Properties | Higher heat resistance (melting point ~225degC) | Moderate heat resistance (melting point ~260degC) |
| Gas Barrier Performance | Moderate oxygen and CO2 barrier | Excellent oxygen and CO2 barrier properties |
| Clarity and Transparency | Opaque to translucent | Highly transparent and clear |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to solvents and chemicals | Good chemical resistance but sensitive to some solvents |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialized processing | Cost-effective, widely available |
| Recyclability | Recyclable but less established | Highly recyclable and commonly recycled |
Introduction to PBT and PET for Beverage Bottles
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is the most commonly used polymer for beverage bottles due to its excellent clarity, high strength-to-weight ratio, and superior gas barrier properties, making it ideal for carbonated drinks and water packaging. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers higher chemical resistance and thermal stability but lacks the transparency and widespread recyclability of PET, limiting its application in beverage containers. PET's exceptional processability and cost-effectiveness have established it as the industry standard for beverage bottles, whereas PBT is more suitable for engineering applications requiring durability rather than clarity or food-grade packaging.
Chemical and Physical Properties Comparison
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits higher thermal resistance and better impact strength compared to Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), making it suitable for applications demanding durability under varying temperatures. PET offers superior clarity, higher tensile strength, and better gas barrier properties, which are essential for preserving beverage freshness and extending shelf life. Both polymers demonstrate excellent chemical resistance, but PET is preferred in beverage bottles due to its optimal balance of mechanical properties and processability for high-speed bottle manufacturing.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) and Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) differ significantly in their manufacturing processes for beverage bottles, with PET commonly produced through a two-stage injection stretch blow molding (ISBM) process, allowing precise control over bottle strength and clarity. PBT manufacturing involves extrusion blow molding or injection molding, which typically results in lower clarity and less flexibility in design compared to PET bottles. The crystallization behavior of PBT requires higher processing temperatures and longer cycle times, impacting production speed and energy consumption relative to PET's more efficient manufacturing cycle.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior impact resistance and enhanced fatigue endurance compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), making it ideal for reusable beverage bottles requiring mechanical strength. PET exhibits higher tensile strength and stiffness, providing excellent barrier properties and resistance to deformation under pressure, which is critical for single-use beverage containers. PBT's enhanced chemical resistance and better dimensional stability contribute to greater durability in fluctuating temperature conditions typical of beverage storage.
Barrier Properties: Oxygen and Moisture Resistance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits superior moisture resistance compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), making it advantageous for beverages requiring longer shelf life in humid conditions. PET offers better oxygen barrier properties than PBT, which is critical for preventing oxidation and preserving beverage taste and quality. Selecting between PBT and PET depends on the specific packaging needs, with PET preferred for oxygen-sensitive products and PBT for moisture-sensitive applications.
Clarity and Aesthetics in Bottling Applications
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior clarity and gloss, making it the preferred choice for beverage bottles where visual appeal is critical. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) typically exhibits lower transparency and a slightly hazy appearance, which can detract from product visibility on shelves. For applications demanding high optical clarity and consistent aesthetics, PET provides enhanced light transmission and a polished finish better suited to premium beverage packaging.
Cost-Effectiveness and Material Availability
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely favored for beverage bottles due to its cost-effectiveness and abundant availability, benefiting from a well-established global supply chain and economies of scale. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), while offering superior chemical resistance and mechanical strength, is typically more expensive and less readily available, limiting its use in large-scale beverage packaging. Manufacturers prioritize PET to optimize production costs and material sourcing efficiency in beverage bottle applications.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) and Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) differ significantly in environmental impact and recyclability for beverage bottles. PET is widely recycled with established collection systems and high recycled content, reducing landfill waste and energy consumption compared to virgin production. PBT, less common in beverage packaging, has limited recycling infrastructure and may lead to higher environmental burdens due to lower recyclability rates and fewer reuse options.
Regulatory Compliance and Food Safety
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is the preferred choice for beverage bottles due to its established regulatory compliance with FDA and EFSA standards, ensuring safety for direct food contact. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) lacks widespread approval for food-grade applications, limiting its use in beverage packaging. PET's superior transparency, chemical resistance, and recyclability further reinforce its dominance in the beverage industry's strict food safety requirements.
Applications and Future Trends in Beverage Packaging
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely preferred over polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) for beverage bottles due to its superior clarity, lightweight properties, and excellent gas barrier performance, which ensure prolonged shelf life and product freshness. PBT's higher crystallinity and thermal stability make it suitable for specific niche applications but limit its use in standard beverage packaging where transparency and recyclability are critical. Future trends in beverage packaging emphasize enhancing PET recycling technologies and developing bio-based PET to meet sustainability goals and reduce plastic waste in the industry.
Infographic: Polybutylene terephthalate vs Polyethylene terephthalate for Beverage bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com