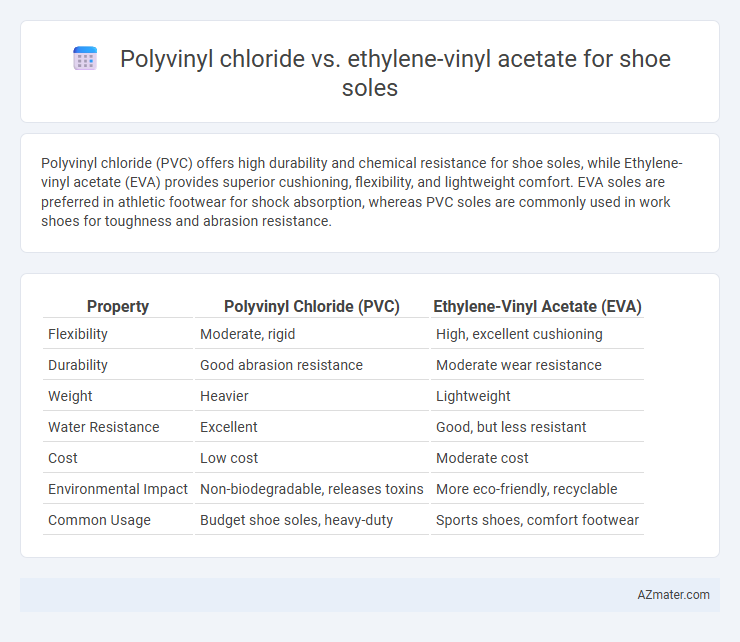
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers high durability and chemical resistance for shoe soles, while Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) provides superior cushioning, flexibility, and lightweight comfort. EVA soles are preferred in athletic footwear for shock absorption, whereas PVC soles are commonly used in work shoes for toughness and abrasion resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | Moderate, rigid | High, excellent cushioning |
| Durability | Good abrasion resistance | Moderate wear resistance |
| Weight | Heavier | Lightweight |
| Water Resistance | Excellent | Good, but less resistant |
| Cost | Low cost | Moderate cost |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, releases toxins | More eco-friendly, recyclable |
| Common Usage | Budget shoe soles, heavy-duty | Sports shoes, comfort footwear |
Introduction to Shoe Sole Materials
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) are prominent materials used in shoe sole manufacturing, each offering distinct performance characteristics. PVC is known for its durability, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice for heavy-duty and industrial footwear. EVA provides superior cushioning, flexibility, and lightweight comfort, often preferred in athletic and casual shoe soles for enhanced shock absorption and wearability.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a widely used synthetic plastic polymer in shoe sole manufacturing, valued for its durability, chemical resistance, and low cost. PVC offers excellent versatility with its rigid or flexible formulations, making it suitable for various shoe styles requiring wear resistance and grip. Its inherent flame retardance and ease of molding enhance production efficiency while maintaining performance standards in footwear applications.
Overview of Ethylene-vinyl Acetate (EVA)
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) is a lightweight, flexible, and shock-absorbent material widely used for shoe soles, offering superior cushioning compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC). EVA's excellent elasticity and resistance to cracking enhance comfort and durability in athletic and casual footwear. Its eco-friendlier profiles and non-toxicity make EVA a preferred choice over PVC, which is heavier and less flexible.
Physical Properties Comparison: PVC vs EVA
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) exhibits higher density and rigidity, making it more durable and resistant to abrasion compared to ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), which offers superior flexibility and cushioning due to its lightweight and soft structure. EVA provides excellent shock absorption and is less prone to cracking in cold temperatures, whereas PVC tends to be stiffer and more resistant to chemicals and oils. The balance between stiffness and cushioning significantly influences durability, comfort, and overall performance in shoe sole applications.
Cushioning and Comfort Analysis
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) shoe soles offer moderate cushioning but tend to be firmer and less flexible compared to ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), which is renowned for its superior shock absorption and lightweight comfort. EVA's open-cell structure provides enhanced cushioning, reducing foot fatigue during extended wear, making it ideal for athletic and casual footwear. The flexibility and resilience of EVA contribute to better comfort and support, whereas PVC's durability often comes with reduced cushioning performance.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers excellent durability and high wear resistance, making it a common choice for shoe soles subjected to rough surfaces and frequent use. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) provides superior cushioning and flexibility but tends to wear out faster under heavy abrasion compared to PVC. For long-lasting shoe soles with enhanced abrasion resistance, PVC is generally preferred, while EVA is favored for comfort and lightweight applications.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) shoe soles are heavier due to their dense polymer structure, while ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) soles are significantly lighter because of their foam-like, porous composition. EVA offers superior flexibility and cushioning, enhancing comfort and shock absorption, whereas PVC soles tend to be stiffer and less flexible. The weight difference impacts overall shoe performance, with EVA favored for athletic and casual footwear requiring lightweight, flexible soles.
Cost-effectiveness and Manufacturing
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers superior cost-effectiveness for shoe sole manufacturing due to its low raw material cost and efficient processing methods, including injection molding and extrusion. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), while more expensive, provides enhanced flexibility and lightweight properties, resulting in higher production costs and specialized manufacturing requirements like compression molding. PVC is favored for mass production with budget constraints, whereas EVA suits premium footwear lines where comfort and performance justify the increased expenditure.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) used in shoe soles poses significant environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradability, release of toxic chemicals during production, and difficulties in recycling, contributing to long-term pollution. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) offers a more sustainable alternative with its lower density, better recyclability, and reduced environmental toxicity, although it is still derived from petrochemical sources. Choosing EVA over PVC for shoe soles decreases ecological footprint by minimizing hazardous waste and facilitating easier end-of-life management.
Which Material Is Best for Shoe Soles?
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers durability, chemical resistance, and affordability, making it a common choice for shoe soles requiring toughness and water resistance. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) provides superior cushioning, flexibility, and lightweight comfort, ideal for athletic and casual footwear prioritizing shock absorption. For shoe soles, EVA is best suited for performance and comfort, while PVC excels in durability and cost-effectiveness.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride vs Ethylene-vinyl acetate for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com