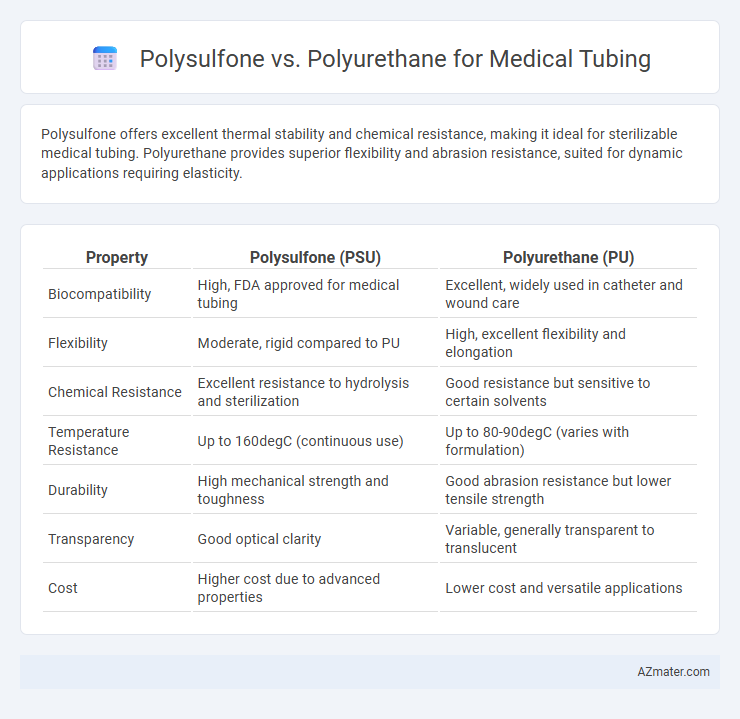
Polysulfone offers excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for sterilizable medical tubing. Polyurethane provides superior flexibility and abrasion resistance, suited for dynamic applications requiring elasticity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfone (PSU) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Biocompatibility | High, FDA approved for medical tubing | Excellent, widely used in catheter and wound care |
| Flexibility | Moderate, rigid compared to PU | High, excellent flexibility and elongation |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to hydrolysis and sterilization | Good resistance but sensitive to certain solvents |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 160degC (continuous use) | Up to 80-90degC (varies with formulation) |
| Durability | High mechanical strength and toughness | Good abrasion resistance but lower tensile strength |
| Transparency | Good optical clarity | Variable, generally transparent to translucent |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Lower cost and versatile applications |
Introduction to Medical Tubing Materials
Polysulfone and polyurethane are widely used materials in medical tubing due to their distinct properties and biocompatibility. Polysulfone offers excellent chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and transparency, making it ideal for applications requiring sterilization and visibility of fluid flow. Polyurethane provides superior flexibility, abrasion resistance, and elasticity, which is crucial for dynamic medical devices and patient comfort during prolonged use.
Overview of Polysulfone and Polyurethane
Polysulfone is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent chemical resistance, thermal stability, and biocompatibility, making it ideal for medical tubing applications requiring sterilization and durability. Polyurethane offers flexibility, abrasion resistance, and biocompatibility, providing comfort and longevity in applications involving body movements and repeated use. Both materials meet stringent medical standards, with polysulfone favored for rigid, high-temperature environments and polyurethane for flexible, patient-contact tubing.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Polysulfone, a thermoplastic polymer characterized by its aromatic ether and sulfone groups, exhibits exceptional thermal stability and resistance to hydrolysis, making it ideal for repeated sterilization in medical tubing. Polyurethane, composed of alternating soft and hard segments of polyols and isocyanates, offers superior flexibility and elasticity but has lower chemical resistance compared to polysulfone. The rigid aromatic backbone of polysulfone provides higher mechanical strength and dimensional stability, whereas polyurethane's segmented structure enhances biocompatibility and abrasion resistance essential for dynamic medical tubing applications.
Biocompatibility and Safety in Medical Applications
Polysulfone exhibits excellent biocompatibility with high resistance to sterilization methods, making it ideal for long-term medical tubing applications requiring durability and chemical stability. Polyurethane offers superior flexibility and biocompatibility, favored in applications needing soft, kink-resistant tubing but may degrade faster under aggressive sterilization. Both materials meet stringent medical safety standards, with polysulfone preferred for high-temperature resistance and polyurethanes for adaptable, patient-comfort-focused designs.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polysulfone exhibits superior mechanical strength and high thermal stability, making it ideal for medical tubing requiring prolonged resistance to pressure and repeated sterilization cycles. Polyurethane offers excellent flexibility and abrasion resistance but typically has lower tensile strength and durability compared to polysulfone in harsh sterilization environments. For applications demanding long-term reliability under mechanical stress, polysulfone tubing provides enhanced durability and structural integrity.
Flexibility and Handling Characteristics
Polysulfone medical tubing offers excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance but tends to be more rigid, limiting flexibility and ease of handling. Polyurethane tubing provides superior flexibility and softness, allowing for enhanced maneuverability and patient comfort, making it ideal for applications requiring frequent movement. The choice between these materials hinges on balancing the need for durability with the requirement for flexible, easy-to-handle medical tubing.
Resistance to Sterilization Methods
Polysulfone exhibits exceptional resistance to high-temperature sterilization methods such as autoclaving and steam sterilization, maintaining structural integrity and clarity without degradation. Polyurethane, while flexible and biocompatible, tends to degrade or lose mechanical properties when exposed to repeated high-temperature sterilization, making it less ideal for autoclave use. Chemical sterilization methods like ethylene oxide are generally compatible with both materials, but polysulfone's thermal and chemical resistance gives it a significant advantage in durability during rigorous sterilization processes.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Polysulfone offers high chemical resistance and thermal stability, making it suitable for medical tubing but generally comes at a higher cost and limited availability compared to polyurethane. Polyurethane provides excellent flexibility and cost-effectiveness, with widespread availability in various formulations ideal for medical tubing applications. Choosing between the two depends on specific requirements where polyurethane is preferred for budget-sensitive projects, while polysulfone is selected for demanding environments requiring superior durability.
Typical Medical Applications for Each Material
Polysulfone tubing is widely used in applications requiring high thermal stability and chemical resistance, such as blood oxygenators, kidney dialysis devices, and sterilizable catheter components. Polyurethane tubing is preferred for its flexibility and biocompatibility in applications like intravenous lines, wound drainage systems, and minimally invasive surgical instruments. Both materials meet stringent medical standards, but polysulfone excels in reusable, high-temperature environments while polyurethane suits disposable, patient-comfort-focused devices.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Tubing Material
Polysulfone offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, making it ideal for sterilization processes and long-term use in medical tubing. Polyurethane provides excellent flexibility and biocompatibility, which is crucial for patient comfort and dynamic applications like catheters. Selecting the optimal tubing material depends on balancing the need for durability and resistance (favoring polysulfone) against flexibility and softness (favoring polyurethane) based on specific clinical requirements.
Infographic: Polysulfone vs Polyurethane for Medical tubing
 azmater.com
azmater.com