Polyoxymethylene offers superior chemical resistance and dimensional stability for food containers, minimizing odor absorption and maintaining structural integrity under repeated use. Polypropylene provides enhanced flexibility and heat resistance, making it ideal for microwave-safe food storage solutions.
Table of Comparison
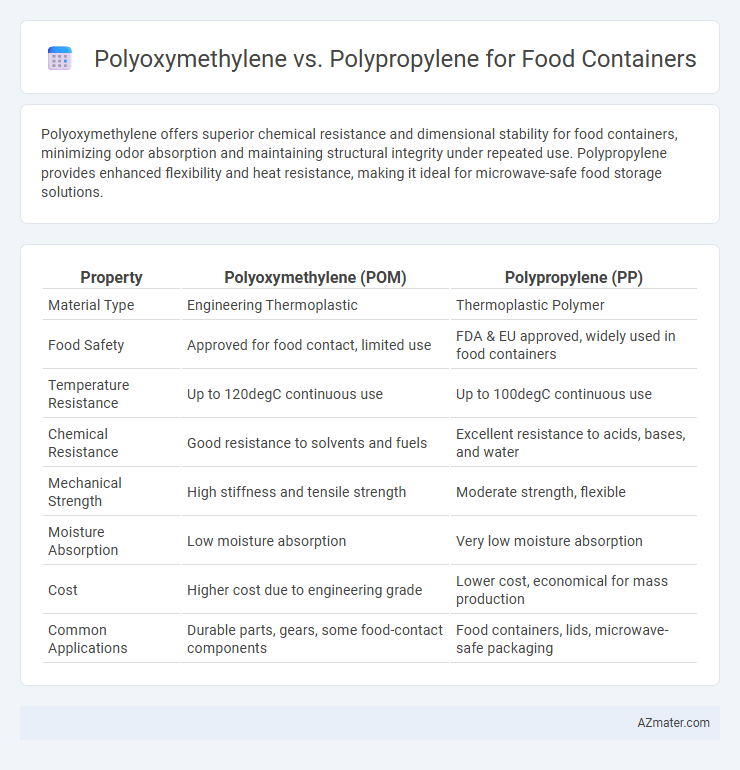
| Property | Polyoxymethylene (POM) | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Engineering Thermoplastic | Thermoplastic Polymer |
| Food Safety | Approved for food contact, limited use | FDA & EU approved, widely used in food containers |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 120degC continuous use | Up to 100degC continuous use |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to solvents and fuels | Excellent resistance to acids, bases, and water |
| Mechanical Strength | High stiffness and tensile strength | Moderate strength, flexible |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorption | Very low moisture absorption |
| Cost | Higher cost due to engineering grade | Lower cost, economical for mass production |
| Common Applications | Durable parts, gears, some food-contact components | Food containers, lids, microwave-safe packaging |
Introduction to Polyoxymethylene and Polypropylene
Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, is a high-performance thermoplastic characterized by its rigidity, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability, making it suitable for precise food container components requiring durability and resistance to wear. Polypropylene (PP) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer distinguished by its chemical resistance, lightweight nature, and high melting point, which ensures safety and longevity in food storage applications. Both materials offer food-safe qualities compliant with FDA regulations, but POM excels in mechanical strength while PP provides superior flexibility and moisture resistance.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polyoxymethylene (POM) features a repeating unit of -CH2-O-, forming a highly crystalline acetal polymer known for its stiffness and chemical resistance, whereas polypropylene (PP) consists of a hydrocarbon backbone with methyl side groups (-CH2-CH(CH3)-), providing flexibility and good chemical stability. The polar oxygen atoms in POM's ether linkages enable superior resistance to solvents and oils compared to the nonpolar, hydrophobic nature of polypropylene, which enhances its resistance to moisture and chemical corrosion. These structural differences affect their suitability for food containers, where POM offers durability and chemical resistance, and PP provides lightweight and heat resistance properties.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits superior mechanical strength, stiffness, and dimensional stability compared to polypropylene (PP), making it highly resistant to deformation and wear in food container applications. PP offers better impact resistance and flexibility but has lower tensile strength and rigidity than POM. The high fatigue resistance and low friction coefficient of POM provide enhanced durability for repeated use, whereas PP is more prone to creep under load over time.
Food Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Polyoxymethylene (POM) and Polypropylene (PP) are both used in food containers, but Polypropylene is generally preferred for food safety due to its excellent resistance to chemicals, heat, and its non-toxicity, meeting FDA and EU food contact regulations. Polyoxymethylene, while strong and durable, may pose concerns related to formaldehyde release under certain conditions, making it less favorable for prolonged food contact. Polypropylene's compliance with stringent regulatory standards like FDA 21 CFR 177.1520 and EU Regulation 10/2011 ensures safer usage in food storage and packaging applications.
Heat Resistance and Temperature Performance
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior heat resistance with a melting point around 175degC, making it suitable for hot food containers and dishwasher-safe applications. Polypropylene (PP) exhibits a melting point near 160degC, providing good heat resistance but slightly lower than POM, ideal for microwave-safe containers. Both materials maintain structural integrity under typical food storage temperatures, but POM's higher thermal stability ensures better performance in prolonged or high-heat conditions.
Durability and Longevity in Food Storage
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits superior durability and mechanical strength compared to polypropylene (PP), making it ideal for long-term food storage applications that require resistance to wear and impact. POM's low moisture absorption and excellent dimensional stability ensure minimal deformation over time, maintaining container integrity during repeated use and cleaning cycles. While polypropylene offers chemical resistance and flexibility, it is more prone to degradation from heat and UV exposure, limiting its longevity relative to polyoxymethylene in demanding food storage environments.
Ease of Cleaning and Maintenance
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior ease of cleaning for food containers due to its low surface energy and resistance to staining, which prevents food particles from adhering tightly. Polypropylene (PP) is also relatively easy to clean, but its slightly higher surface porosity can retain residues, requiring more thorough washing and occasional use of stronger detergents. Maintenance of POM containers is generally simpler because they resist chemical degradation and maintain smooth surfaces over time, while PP containers may experience surface wear and slight deformation after repeated cleaning cycles.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance compared to polypropylene (PP), but it generally comes at a higher cost, impacting overall cost efficiency for food container applications. Polypropylene is widely available and favored in the market due to its affordability, ease of processing, and adequate performance for most food storage needs. Market availability of polypropylene remains robust globally, making it the preferred choice for large-scale food container production with balanced cost-efficiency benefits.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high durability but has limited recyclability and a greater environmental footprint due to its complex chemical structure and energy-intensive production process. Polypropylene (PP) is widely favored for food containers because of its lower carbon emissions during manufacturing and excellent recyclability, supported by established recycling streams for food-grade plastics. Choosing PP enhances sustainability in food packaging by reducing waste and promoting circular economy principles through efficient recycling practices.
Choosing the Right Material for Food Containers
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior rigidity, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, making it ideal for durable food containers subject to frequent washing and exposure to oils or acids. Polypropylene (PP) provides excellent flexibility, heat resistance, and is widely recognized for its food-safe properties, making it a cost-effective choice for microwaveable containers. Selecting the right material involves assessing the container's intended use, such as temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress, with POM suited for high-performance applications and PP favored for general-purpose food storage.
Infographic: Polyoxymethylene vs Polypropylene for Food Container
 azmater.com
azmater.com