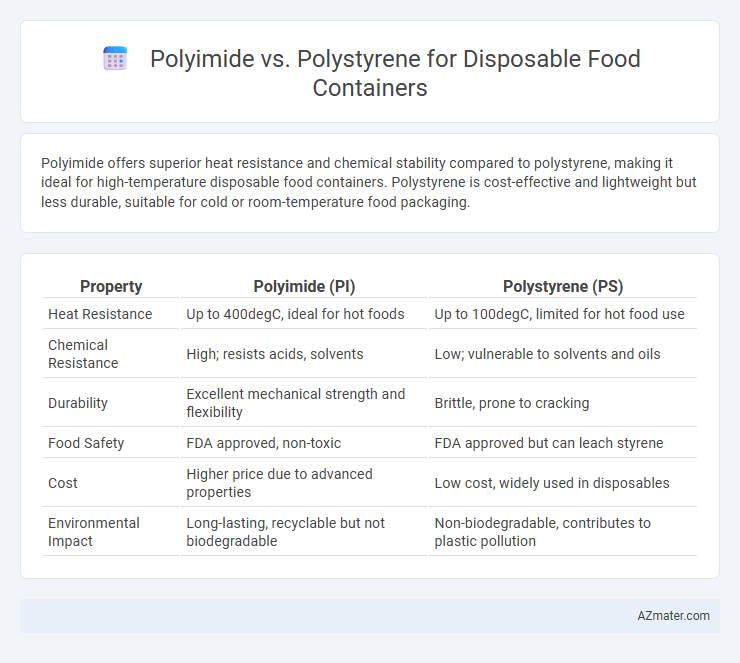
Polyimide offers superior heat resistance and chemical stability compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for high-temperature disposable food containers. Polystyrene is cost-effective and lightweight but less durable, suitable for cold or room-temperature food packaging.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyimide (PI) | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Up to 400degC, ideal for hot foods | Up to 100degC, limited for hot food use |
| Chemical Resistance | High; resists acids, solvents | Low; vulnerable to solvents and oils |
| Durability | Excellent mechanical strength and flexibility | Brittle, prone to cracking |
| Food Safety | FDA approved, non-toxic | FDA approved but can leach styrene |
| Cost | Higher price due to advanced properties | Low cost, widely used in disposables |
| Environmental Impact | Long-lasting, recyclable but not biodegradable | Non-biodegradable, contributes to plastic pollution |
Introduction to Disposable Food Container Materials
Polyimide and polystyrene are prominent materials used in disposable food containers, each offering unique properties suited for different applications. Polyimide provides exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature or microwave-safe containers. Polystyrene is valued for its cost-effectiveness, rigidity, and excellent insulation, commonly used in disposable cups, trays, and clamshell packaging.
Overview of Polyimide
Polyimide is a high-performance polymer known for its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it suitable for disposable food containers that require durability and heat resistance. Its ability to withstand temperatures above 250degC without deforming ensures safe use in microwave and oven applications, unlike polystyrene which typically melts around 100degC. Polyimide's superior barrier properties against gases and moisture also help maintain food freshness and prevent contamination, positioning it as a premium material for disposable food packaging.
Overview of Polystyrene
Polystyrene is a widely used thermoplastic polymer known for its rigidity, clarity, and lightweight properties, making it a popular choice for disposable food containers. Its excellent insulation capability helps maintain food temperature, while its cost-effectiveness supports mass production. However, polystyrene's limited heat resistance and environmental concerns due to poor biodegradability impact its suitability compared to more durable materials like polyimide.
Thermal Resistance Comparison
Polyimide exhibits superior thermal resistance with a high continuous service temperature up to 400degC, making it ideal for disposable food containers exposed to extreme heat. Polystyrene, however, has a lower thermal threshold around 70-100degC, limiting its use to cold or room-temperature foods. The robust thermal stability of polyimide ensures structural integrity and safety in microwave or hot food applications, unlike polystyrene which risks deformation or chemical leaching under high heat.
Chemical Stability and Reactivity
Polyimide exhibits superior chemical stability compared to polystyrene, resisting degradation when exposed to acids, bases, and high temperatures, which makes it ideal for durable disposable food containers. Polystyrene tends to leach styrene monomers and deform under heat due to its lower chemical resistance, posing risks for food safety and container integrity. Polyimide's inert nature ensures minimal chemical reactivity, maintaining food purity and container strength throughout use.
Food Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Polyimide offers superior heat resistance and chemical stability compared to polystyrene, making it a safer choice for disposable food containers exposed to high temperatures or oily foods. Polystyrene, while cost-effective and lightweight, poses potential health risks due to the migration of styrene monomers, which are regulated by the FDA and EFSA for food contact materials. Regulatory compliance favors polyimide in applications requiring stringent food safety standards, as it is less likely to leach harmful substances and meets FDA 21 CFR 177.2510 for food-contact polymers.
Environmental Impact and Biodegradability
Polyimide offers superior thermal stability but poses significant environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradable nature and difficulty in recycling, leading to long-term pollution. Polystyrene, widely used in disposable food containers, is also non-biodegradable and contributes substantially to plastic waste and ocean pollution. Biodegradability is minimal in both materials, but emerging alternatives and recycling innovations focus more on polystyrene waste reduction than on polyimide applications.
Cost and Manufacturing Efficiency
Polyimide offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polystyrene, but it comes with a significantly higher material cost and more complex manufacturing requirements, limiting its use in disposable food containers. Polystyrene is favored for its low cost, ease of molding, and high manufacturing efficiency, making it the preferred choice for mass-produced disposable containers. However, polystyrene's lower heat resistance and environmental concerns can affect its suitability for certain food packaging applications.
Performance in Real-World Applications
Polyimide exhibits superior heat resistance and chemical stability, making it ideal for disposable food containers used in high-temperature environments such as microwaving or hot food storage. Polystyrene, while cost-effective and lightweight, tends to deform under heat and may leach harmful substances when exposed to oily or acidic foods. Real-world applications demonstrate polyimide's enhanced durability and safety for retaining food integrity compared to the limited thermal performance of polystyrene.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Polyimide and Polystyrene
Polyimide offers superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and environmental durability, making it suitable for high-temperature food applications and extended use. Polystyrene provides cost-effective, lightweight options with good insulation properties but lacks the heat resistance and sustainability of polyimide. Selecting between polyimide and polystyrene depends on balancing budget constraints, food type, temperature requirements, and environmental impact priorities.
Infographic: Polyimide vs Polystyrene for Disposable Food Container
 azmater.com
azmater.com