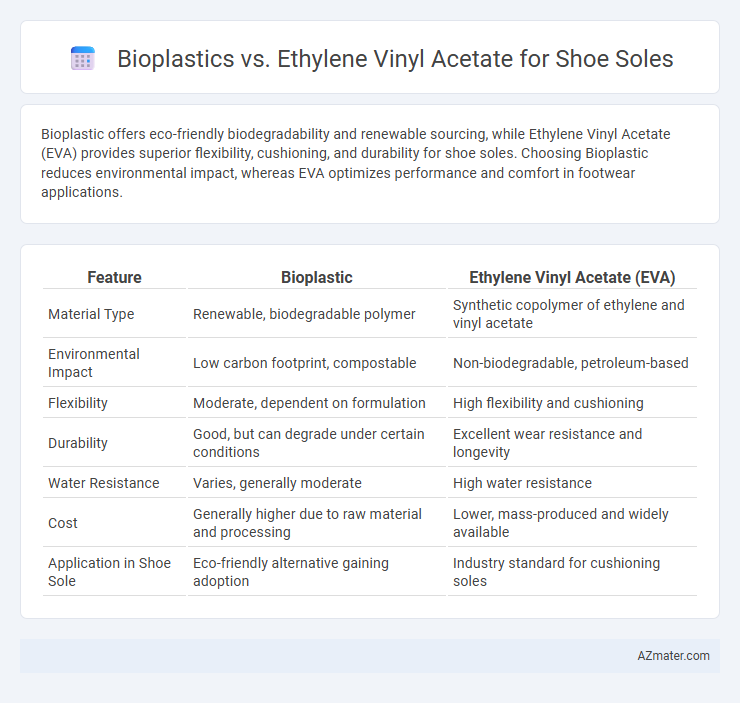
Bioplastic offers eco-friendly biodegradability and renewable sourcing, while Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) provides superior flexibility, cushioning, and durability for shoe soles. Choosing Bioplastic reduces environmental impact, whereas EVA optimizes performance and comfort in footwear applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bioplastic | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Renewable, biodegradable polymer | Synthetic copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, compostable | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based |
| Flexibility | Moderate, dependent on formulation | High flexibility and cushioning |
| Durability | Good, but can degrade under certain conditions | Excellent wear resistance and longevity |
| Water Resistance | Varies, generally moderate | High water resistance |
| Cost | Generally higher due to raw material and processing | Lower, mass-produced and widely available |
| Application in Shoe Sole | Eco-friendly alternative gaining adoption | Industry standard for cushioning soles |
Introduction to Bioplastic and Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA)
Bioplastics are derived from renewable biological sources such as corn starch, sugarcane, or cellulose, offering biodegradable and eco-friendly alternatives to traditional plastics. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is a synthetic copolymer known for its excellent flexibility, durability, and cushioning properties, widely used in shoe soles for comfort and shock absorption. The comparison of bioplastics and EVA in footwear focuses on sustainability, material performance, and environmental impact in sole manufacturing.
Composition and Material Properties
Bioplastic shoe soles are primarily derived from renewable plant-based polymers such as polylactic acid (PLA) or polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), offering biodegradability and a reduced carbon footprint. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is a copolymer consisting of ethylene and vinyl acetate units, known for its exceptional flexibility, cushioning, and resistance to cracking. While bioplastics emphasize sustainability through natural composition and compostability, EVA excels in durability, elasticity, and impact absorption for high-performance footwear applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bioplastic shoe soles reduce reliance on fossil fuels by utilizing renewable plant-based materials, significantly lowering carbon emissions and promoting biodegradability compared to traditional ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA). EVA, while durable and lightweight, is derived from petrochemicals and poses challenges in recycling and environmental degradation due to its non-biodegradable nature. Choosing bioplastic over EVA in shoe soles supports circular economy principles and reduces plastic pollution, contributing to enhanced sustainability in the footwear industry.
Durability and Performance in Footwear
Bioplastic shoe soles offer eco-friendly advantages but generally have lower durability compared to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA), which provides superior shock absorption, flexibility, and resilience under various conditions. EVA is widely favored in athletic and performance footwear for its high impact resistance and long-lasting cushioning properties, enhancing overall comfort and wearability. While bioplastics contribute to sustainability, EVA remains the industry standard for shoe sole performance and durability.
Comfort and Flexibility Comparison
Bioplastic shoe soles typically offer enhanced comfort due to their natural elasticity and breathability, which reduces foot fatigue during prolonged wear. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) soles are renowned for their superior flexibility and shock absorption, providing excellent cushioning and impact resistance in athletic footwear. While bioplastic materials emphasize sustainability and biodegradability, EVA balances comfort with durability, especially in performance and casual shoe designs.
Manufacturing Process and Scalability
Bioplastic shoe soles are manufactured through biopolymer synthesis involving renewable resources such as cornstarch or sugarcane, utilizing extrusion or injection molding processes that align with sustainable production goals. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) soles are produced by polymerization of ethylene and vinyl acetate monomers, followed by foaming techniques to achieve lightweight cushioning, benefiting from well-established industrial manufacturing infrastructure. Scalability favors EVA due to its long-standing presence in the footwear industry, consistent material properties, and cost-effectiveness, whereas bioplastics face challenges in raw material variability and processing optimization for mass production.
Cost Analysis: Bioplastic vs EVA
Bioplastic shoe soles typically have higher manufacturing costs due to the use of renewable raw materials and complex processing techniques, making them less affordable than Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA), which benefits from mass production and lower raw material expenses. EVA offers cost efficiency and consistent performance, contributing to its widespread adoption in the footwear industry. Price sensitivity and volume production give EVA a competitive edge over bioplastics in large-scale shoe manufacturing.
Consumer Perceptions and Market Trends
Consumer perceptions favor bioplastic shoe soles for their environmental benefits and biodegradability, driving growing demand in sustainable footwear segments. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) remains popular due to its lightweight, cushioning properties, and affordability, maintaining strong market presence in athletic and casual shoes. Market trends indicate increasing investment in bioplastic innovation, reflecting a shift towards eco-friendly materials, while EVA continues to evolve with enhanced performance formulations.
Innovations and Future Prospects
Bioplastic materials in shoe soles offer significant innovations through enhanced biodegradability and sustainable sourcing, reducing environmental impact compared to traditional polymers. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) remains a leading material due to its lightweight, flexibility, and shock absorption, with ongoing advancements improving its recyclability and performance. Future prospects highlight the integration of bio-based EVA blends and fully compostable bioplastics to meet increasing eco-conscious consumer demands and regulatory standards.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Shoe Soles
Bioplastic offers a sustainable and biodegradable alternative to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA), which is valued for its lightweight, flexible, and shock-absorbing properties in shoe soles. Selecting the right material depends on balancing environmental impact with performance requirements, where bioplastic suits eco-friendly designs and EVA excels in durability and cushioning. For high-performance athletic footwear, EVA remains dominant, while bioplastic is gaining traction in casual and eco-conscious markets.
Infographic: Bioplastic vs Ethylene Vinyl Acetate for Shoe Sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com