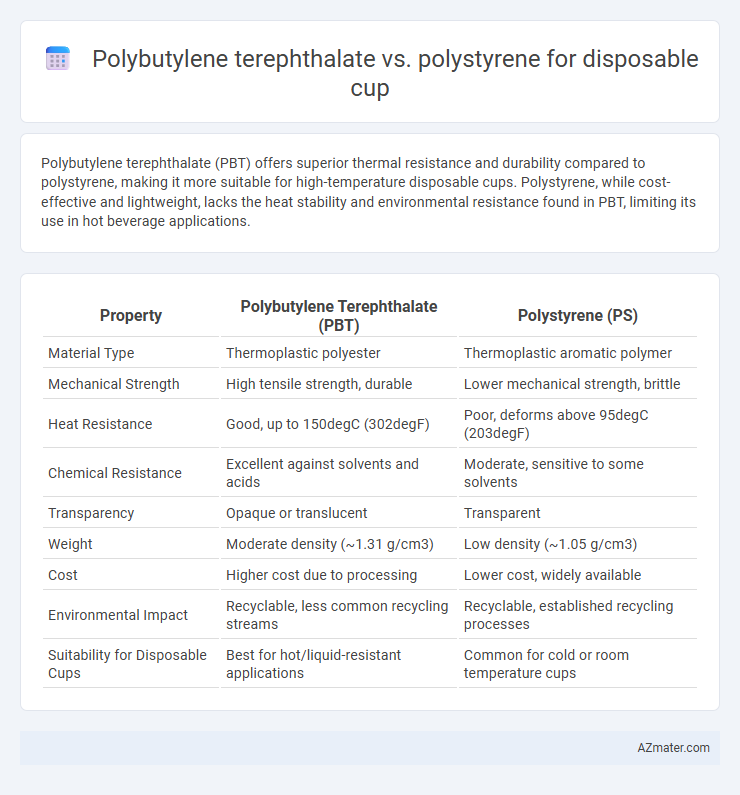
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior thermal resistance and durability compared to polystyrene, making it more suitable for high-temperature disposable cups. Polystyrene, while cost-effective and lightweight, lacks the heat stability and environmental resistance found in PBT, limiting its use in hot beverage applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polyester | Thermoplastic aromatic polymer |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, durable | Lower mechanical strength, brittle |
| Heat Resistance | Good, up to 150degC (302degF) | Poor, deforms above 95degC (203degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against solvents and acids | Moderate, sensitive to some solvents |
| Transparency | Opaque or translucent | Transparent |
| Weight | Moderate density (~1.31 g/cm3) | Low density (~1.05 g/cm3) |
| Cost | Higher cost due to processing | Lower cost, widely available |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, less common recycling streams | Recyclable, established recycling processes |
| Suitability for Disposable Cups | Best for hot/liquid-resistant applications | Common for cold or room temperature cups |
Introduction to Polybutylene Terephthalate and Polystyrene
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a durable thermoplastic polyester known for its high mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and excellent thermal stability, making it suitable for reusable or more robust disposable cups. Polystyrene (PS), a lightweight and inexpensive plastic, offers good clarity and rigidity but exhibits lower heat resistance and durability compared to PBT, commonly used for single-use disposable cups. The choice between PBT and polystyrene impacts the cup's performance in terms of environmental sustainability, thermal insulation, and structural integrity.
Chemical Structure and Material Properties
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) features a semi-crystalline polymer structure with ester linkages that provide superior thermal resistance and mechanical strength compared to polystyrene, which is an amorphous polymer composed of styrene monomers known for its rigidity but lower heat tolerance. PBT's chemical structure lends enhanced chemical resistance and dimensional stability, making it more suitable for hot beverage cups, whereas polystyrene cups often suffer from brittleness and deformation at elevated temperatures. The glass transition temperature of polystyrene (~100degC) is significantly lower than PBT's melting point (~225degC), influencing their performance and durability in disposable cup applications.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is produced through a polycondensation reaction of terephthalic acid and 1,4-butanediol, followed by melt extrusion and injection molding, offering high thermal resistance and mechanical strength ideal for disposable cups. Polystyrene (PS) manufacturing involves the polymerization of styrene monomers via suspension or bulk polymerization, with thermoforming or injection molding commonly used to shape cups due to its ease of processing and cost efficiency. PBT's manufacturing process requires higher processing temperatures around 230-260degC, whereas polystyrene processes at lower temperatures near 180-240degC, influencing cycle times and energy consumption in disposable cup production.
Thermal Resistance and Performance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior thermal resistance compared to polystyrene (PS), with a melting point around 225degC versus PS's 240degC but a higher heat deflection temperature, typically around 140degC for PBT against PS's 90-100degC, making PBT more suitable for hot beverage cups. PBT exhibits enhanced mechanical strength and chemical resistance, improving performance under thermal stress and repeated use conditions, whereas PS cups may deform or leach chemicals at elevated temperatures. The thermal stability and durability of PBT ensure better insulation and structural integrity in disposable cups designed for hot liquids.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits superior mechanical strength and durability compared to polystyrene when used for disposable cups, offering enhanced resistance to impact and deformation under thermal stress. PBT's higher tensile strength and toughness make it more suitable for hot beverage applications, maintaining integrity without cracking or warping. Polystyrene, while cost-effective and lightweight, tends to have lower impact resistance and can become brittle with temperature fluctuations, reducing its overall durability in disposable cup use.
Cost Analysis: PBT vs Polystyrene
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) generally exhibits higher raw material and processing costs compared to polystyrene due to its superior thermal resistance and mechanical strength, which require more complex manufacturing techniques. Polystyrene, being cheaper and easier to mold, offers lower initial production expenses, making it economically favorable for large-scale disposable cup production. However, PBT's durability and recyclability can lead to long-term cost savings and reduced environmental impact, potentially offsetting the higher upfront investment in sustainable packaging applications.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior recyclability compared to polystyrene (PS) due to its compatibility with existing polyester recycling streams and lower environmental persistence. Polystyrene, commonly used in disposable cups, poses significant environmental challenges because it degrades slowly and often accumulates as non-biodegradable waste in landfills and oceans. PBT's biodegradability and potential for closed-loop recycling reduce carbon footprint and landfill burden, making it a more sustainable option for disposable cup manufacturing.
Safety and Food Contact Regulations
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is favored for disposable cups due to its excellent chemical resistance and compliance with FDA and EU food contact regulations, ensuring safe use with hot and cold beverages. Polystyrene (PS), while cost-effective and lightweight, poses safety concerns as it can leach styrene monomers, raising potential health risks and facing stricter regulatory scrutiny in some regions. Manufacturers often choose PBT over PS to meet stringent safety standards and maintain the integrity of food contact materials during appliance and temperature variations.
Consumer Experience and Usability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior heat resistance and durability compared to polystyrene, enhancing the consumer experience by maintaining cup shape and temperature control even with hot beverages. PBT's higher chemical resistance minimizes leakage and odors, improving usability in various drink types. Polystyrene, while cost-effective, tends to lose structural integrity and insulating properties quickly, resulting in less comfort and higher risk of spills during typical disposable cup use.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Disposable Cups
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior thermal resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for hot beverage cups, while polystyrene (PS) excels in cost-efficiency and lightweight properties suited for cold drinks. The environmental impact of PBT is generally lower due to better recyclability and biodegradability options compared to polystyrene's common association with pollution and landfill accumulation. Selecting the right material depends on balancing performance requirements, cost considerations, and sustainability goals in disposable cup production.
Infographic: Polybutylene terephthalate vs Polystyrene for Disposable cup
 azmater.com
azmater.com