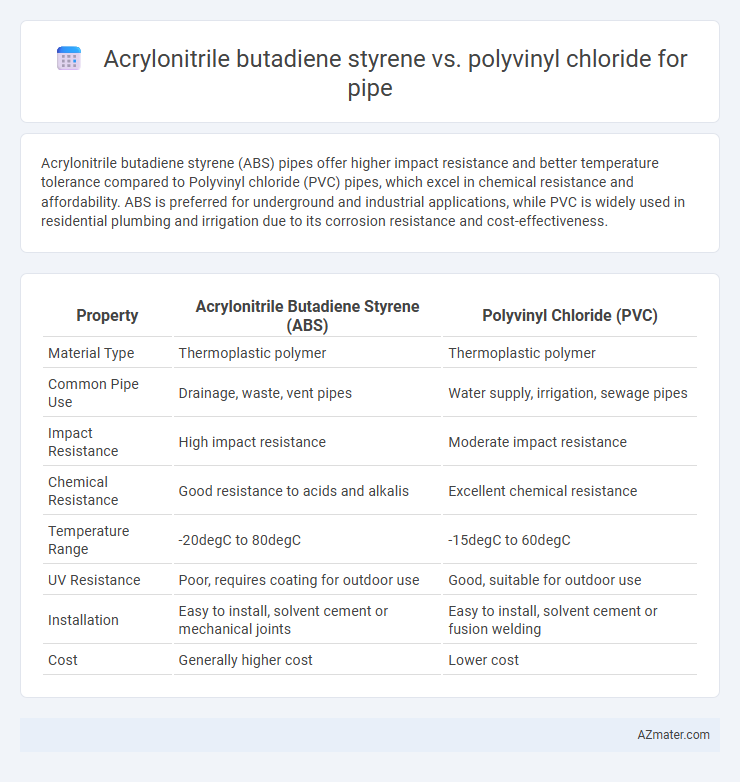
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) pipes offer higher impact resistance and better temperature tolerance compared to Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes, which excel in chemical resistance and affordability. ABS is preferred for underground and industrial applications, while PVC is widely used in residential plumbing and irrigation due to its corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Common Pipe Use | Drainage, waste, vent pipes | Water supply, irrigation, sewage pipes |
| Impact Resistance | High impact resistance | Moderate impact resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and alkalis | Excellent chemical resistance |
| Temperature Range | -20degC to 80degC | -15degC to 60degC |
| UV Resistance | Poor, requires coating for outdoor use | Good, suitable for outdoor use |
| Installation | Easy to install, solvent cement or mechanical joints | Easy to install, solvent cement or fusion welding |
| Cost | Generally higher cost | Lower cost |
Introduction to ABS and PVC Pipes
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) pipes are known for their toughness, impact resistance, and ease of installation in plumbing and drainage systems. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes offer excellent chemical resistance, durability, and affordability, making them widely used for water supply and irrigation systems. Both materials provide distinct advantages in terms of performance, with ABS excelling in low-temperature environments and PVC favored for its cost-effectiveness and versatility.
Chemical Composition: ABS vs PVC
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer composed of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, offering chemical resistance and toughness due to the butadiene rubber component. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a polymer made from vinyl chloride monomers, notable for its rigidity, chemical inertness, and chlorine content that provides fire resistance. While ABS has superior impact resistance and flexibility, PVC's chlorine-based chemical structure makes it more resistant to corrosive substances and ideal for applications requiring strong chemical stability.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) pipes offer superior mechanical strength with high impact resistance and toughness, making them ideal for applications requiring durability under stress. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes provide excellent chemical resistance and longevity but generally show lower impact strength and brittleness under heavy mechanical loads. Both materials exhibit strong durability, yet ABS pipes excel in impact-related mechanical performance while PVC is preferred for corrosion resistance and structural stability in varied environments.
Temperature and Pressure Resistance
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) pipes offer better impact resistance and tolerate temperatures up to 80degC, making them suitable for residential drainage systems under moderate pressure conditions. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes withstand higher pressures and temperatures up to 60degC, ideal for both cold water and irrigation systems but may become brittle under extreme cold. ABS provides superior performance in environments requiring higher thermal tolerance and impact endurance, whereas PVC excels in high-pressure applications with moderate thermal demands.
Installation Processes: Ease and Methods
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) pipes offer simplified installation with solvent welding and snap-fit joints, reducing the need for specialized tools and minimizing curing times. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes require solvent cementing or threading, which involves more precise surface preparation and often extended curing periods, impacting overall installation speed. ABS's lightweight and flexible properties enhance maneuverability in tight spaces, while PVC's rigidity demands careful alignment but provides robust mechanical strength once installed.
Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance but has moderate chemical resistance, making it less suitable for highly corrosive environments compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC). PVC exhibits excellent corrosion resistance and is highly resistant to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and salts, making it ideal for aggressive chemical transport and long-term durability in pipe applications. The choice between ABS and PVC pipes hinges on the specific corrosive agents present and the required longevity of the piping system in chemically harsh environments.
Cost Analysis: ABS vs PVC Pipes
ABS pipes generally have a higher initial cost compared to PVC pipes due to their stronger material properties and better impact resistance. PVC pipes offer a more cost-effective solution for large-scale plumbing projects because of their lower raw material and production expenses. Long-term maintenance and installation costs tend to be comparable, but ABS may offer cost savings in applications requiring higher durability and temperature tolerance.
Applications and Suitability in Plumbing
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) pipes are widely used in plumbing due to their impact resistance, ease of installation, and suitability for underground drainage and vent systems. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes offer excellent chemical resistance, making them ideal for potable water distribution and irrigation, with superior durability in both hot and cold water applications. Both materials provide cost-effective solutions, but ABS is preferred for strength in impact-prone environments, while PVC excels in versatility and resistance to corrosion and chemicals.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) pipes have a lower environmental impact due to their ability to be more easily recycled and their reduced release of hazardous chemicals during production compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes. PVC pipes pose significant environmental concerns because their manufacturing involves toxic additives like phthalates and chlorine, which can release harmful dioxins upon incineration. ABS pipes demonstrate higher recyclability rates, contributing to reduced landfill waste, while PVC recycling is limited by contamination and degradation of material properties.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Pipe Material
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance and ease of installation, making it ideal for residential drainage systems, while polyvinyl chloride (PVC) excels in chemical resistance and durability, suitable for industrial and underground plumbing. PVC's versatility and cost-effectiveness often make it the preferred choice for long-term applications requiring exposure to harsh chemicals or outdoor conditions. Selecting the right pipe material depends on the specific application requirements, including environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polyvinyl chloride for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com