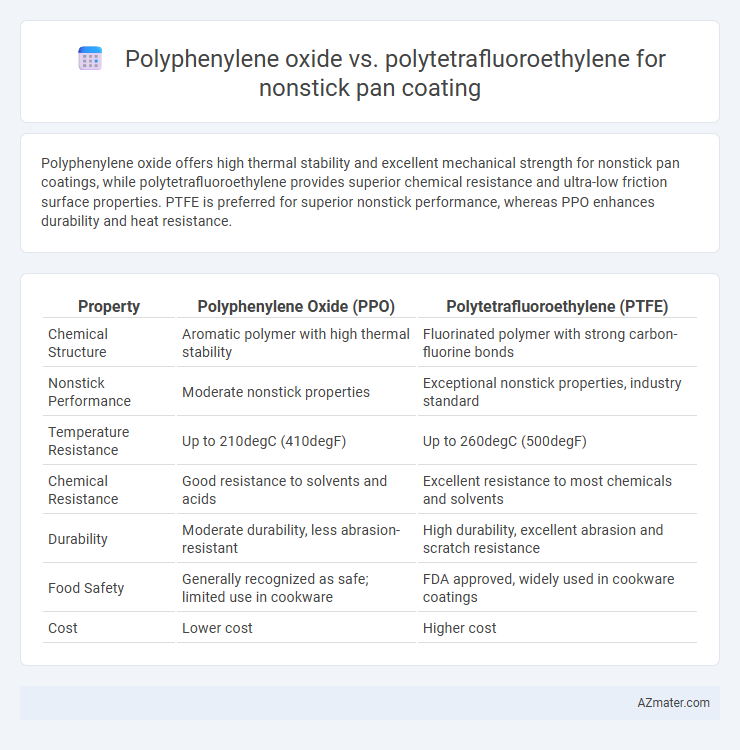
Polyphenylene oxide offers high thermal stability and excellent mechanical strength for nonstick pan coatings, while polytetrafluoroethylene provides superior chemical resistance and ultra-low friction surface properties. PTFE is preferred for superior nonstick performance, whereas PPO enhances durability and heat resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Aromatic polymer with high thermal stability | Fluorinated polymer with strong carbon-fluorine bonds |
| Nonstick Performance | Moderate nonstick properties | Exceptional nonstick properties, industry standard |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 210degC (410degF) | Up to 260degC (500degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to solvents and acids | Excellent resistance to most chemicals and solvents |
| Durability | Moderate durability, less abrasion-resistant | High durability, excellent abrasion and scratch resistance |
| Food Safety | Generally recognized as safe; limited use in cookware | FDA approved, widely used in cookware coatings |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Nonstick Pan Coatings
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are key materials used in nonstick pan coatings, offering distinct performance attributes. PTFE, known for its exceptional nonstick properties and chemical resistance, is widely favored in cookware for easy food release and durability at high temperatures up to 260degC (500degF). PPO, though less common, provides improved mechanical strength and thermal stability but typically requires blending with other polymers to achieve similar nonstick effectiveness as PTFE.
Overview of Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO)
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it suitable for nonstick pan coatings. PPO offers improved heat resistance compared to many polymers, providing durability and maintaining nonstick properties under frequent cooking conditions. Its inherent rigidity and low moisture absorption contribute to the longevity and non-reactivity of cookware surfaces, differentiating it from polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which is primarily valued for its exceptional nonstick and low-friction characteristics.
Overview of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer known for its exceptional nonstick properties, chemical resistance, and high-temperature stability, making it a popular choice in nonstick pan coatings. PTFE's low coefficient of friction prevents food from adhering, while its durability allows it to withstand temperatures up to approximately 260degC (500degF) without degrading. Compared to Polyphenylene oxide (PPO), PTFE exhibits superior release properties and heat resistance, contributing to its widespread use in cookware applications.
Chemical Properties: PPO vs PTFE
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers excellent thermal stability and resistance to oxidation, making it suitable for nonstick pan coatings with moderate heat exposure. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) exhibits superior chemical inertness and an ultra-low coefficient of friction, providing enhanced nonstick performance and resistance to aggressive chemicals. While PPO balances thermal endurance and mechanical strength, PTFE outperforms in temperature tolerance and anti-adhesion properties crucial for cookware applications.
Thermal Stability Comparison
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits excellent thermal stability with a continuous use temperature up to approximately 170degC, making it suitable for moderate heat applications in nonstick pan coatings. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) withstands much higher temperatures, maintaining stability up to 260degC and resisting degradation, which provides superior performance for high-heat cooking. The superior thermal resistance of PTFE over PPO ensures longer lifespan and reliability in nonstick cookware exposed to intense and sustained heat.
Nonstick Performance and Food Release
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers superior nonstick performance with exceptional food release due to its low surface energy and chemical inertness, making it ideal for cookware coatings. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) provides moderate nonstick properties but excels in thermal stability and durability, though it may require additional treatments to match PTFE's slickness. For nonstick pan coating, PTFE remains the preferred choice for effortless food release and enhanced cooking efficiency.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers superior nonstick performance with excellent scratch resistance and chemical inertness, making it highly durable for everyday cookware use. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO), while thermally stable and moderately resistant to abrasion, lacks the exceptional nonstick and slick surface properties of PTFE, which can lead to faster wear over time. For long-term durability and resistance to scratching in nonstick pan coatings, PTFE remains the preferred material due to its robust polymer structure and low friction characteristics.
Safety and Health Considerations
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers a safer alternative to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) for nonstick pan coatings due to its higher thermal stability, reducing the risk of toxic fumes at high temperatures. PTFE can release harmful perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and toxic gases when overheated above 260degC (500degF), posing respiratory and environmental health concerns. PPO coatings avoid such decomposition products, making them preferable for health-conscious consumers seeking durable, non-toxic cookware options.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers a more environmentally friendly alternative to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) in nonstick pan coatings due to its lower persistence in ecosystems and reduced risk of producing harmful perfluorinated compounds during degradation. PTFE, commonly known as Teflon, is associated with significant environmental concerns, including bioaccumulation and the release of toxic per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), which have raised regulatory scrutiny globally. Switching to PPO-based coatings can reduce ecological risks and enhance sustainability by minimizing toxic emissions and supporting better end-of-life recyclability.
Choosing the Right Material for Nonstick Cookware
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers excellent thermal stability and superior scratch resistance, making it a durable choice for nonstick pan coatings. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, provides exceptional nonstick performance and low friction but may degrade at higher temperatures above 260degC. Choosing between PPO and PTFE depends on prioritizing high-temperature resilience and mechanical durability versus superior release properties and ease of cleaning in nonstick cookware.
Infographic: Polyphenylene oxide vs Polytetrafluoroethylene for Nonstick pan coating
 azmater.com
azmater.com