Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers high impact resistance and dimensional stability, making it durable for reusable water bottles. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) provides excellent clarity, lightweight properties, and superior gas barrier performance, ideal for single-use and recyclable water bottles.
Table of Comparison
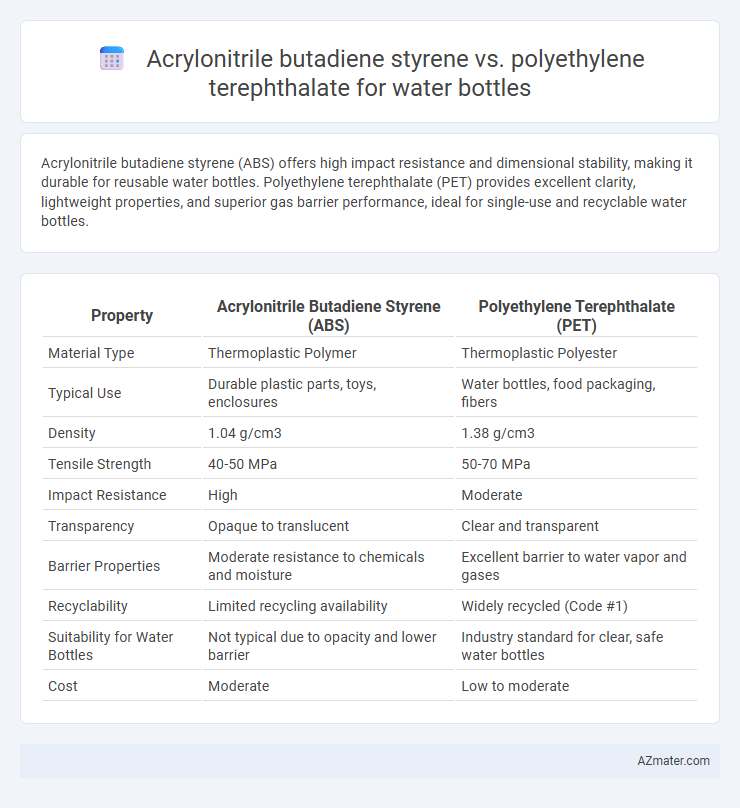
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polymer | Thermoplastic Polyester |
| Typical Use | Durable plastic parts, toys, enclosures | Water bottles, food packaging, fibers |
| Density | 1.04 g/cm3 | 1.38 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 40-50 MPa | 50-70 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Transparency | Opaque to translucent | Clear and transparent |
| Barrier Properties | Moderate resistance to chemicals and moisture | Excellent barrier to water vapor and gases |
| Recyclability | Limited recycling availability | Widely recycled (Code #1) |
| Suitability for Water Bottles | Not typical due to opacity and lower barrier | Industry standard for clear, safe water bottles |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
Introduction: ABS vs PET for Water Bottles
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) are two common polymers used in water bottle manufacturing, each with distinct properties affecting performance and sustainability. ABS offers high impact resistance and durability but has lower chemical resistance compared to PET, which excels in barrier properties and clarity, making it ideal for safe beverage storage. PET also demonstrates better recyclability and lighter weight, contributing to reduced environmental impact in water bottle production.
Material Composition and Properties
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic composed of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, offering high impact resistance, rigidity, and good chemical resistance, making it durable but less flexible for water bottles. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a polyester made from ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid, provides superior clarity, excellent moisture barrier properties, and is lightweight, which enhances its suitability for single-use and reusable water bottles. PET's higher resistance to carbonation and odor retention compared to ABS makes it the preferred choice in beverage packaging, while ABS is more common in applications requiring toughness and heat resistance.
Durability and Impact Resistance
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), making it more durable against drops and physical stress in water bottle applications. PET excels in chemical resistance and maintains structural integrity under repeated use but is more prone to cracking under extreme impact. Choosing ABS for water bottles enhances longevity and resistance to deformation, while PET provides lightweight durability with moderate impact tolerance.
Chemical Resistance and Safety
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate chemical resistance but can degrade when exposed to strong acids or alkalis, making it less suitable for prolonged contact with certain beverages. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) exhibits superior chemical resistance, maintaining structural integrity and purity even with acidic drinks, which enhances its safety profile for water bottles. PET is also widely recognized for food-grade safety certifications, ensuring minimal risk of leaching harmful substances.
Weight and Portability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) water bottles are generally heavier and less portable compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles due to ABS's higher density and rigidity. PET bottles offer superior lightweight properties, enhancing portability and ease of transport, making them ideal for active lifestyles and on-the-go hydration. The material's excellent strength-to-weight ratio ensures PET bottles maintain durability without compromising user convenience.
Temperature Tolerance
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate temperature tolerance withstanding up to 80degC, making it suitable for everyday water bottles that don't require high heat resistance. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) surpasses ABS by tolerating temperatures up to 120degC, offering better performance in hot fill and sterilization processes. PET's superior thermal stability also helps maintain structural integrity and prevents deformation in higher temperature water bottle applications.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits lower recyclability compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), as ABS is less commonly processed in standard municipal recycling streams for water bottles. PET's high recyclability and widespread acceptance in bottle-to-bottle recycling programs significantly reduce environmental impact by conserving raw materials and lowering energy consumption. Environmental studies highlight PET's superior lifecycle metrics, including reduced greenhouse gas emissions and lower toxicity, making it the preferred choice for sustainable water bottle production.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate cost-effectiveness with good durability but is generally more expensive than polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which is highly affordable and widely used for water bottles due to its excellent availability. PET's lightweight nature and recyclability enhance its economic appeal, making it the preferred choice in large-scale water bottle production. ABS's lower availability and higher processing costs limit its use compared to the extensive global supply chain established for PET.
Common Uses in Water Bottle Manufacturing
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is less common in water bottle manufacturing due to its rigidity and lower chemical resistance, making it more suitable for durable components like caps and lids. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely used for water bottles because of its excellent clarity, lightweight properties, and strong barrier against moisture and gases, ensuring product freshness. PET's recyclability and food safety certifications further contribute to its dominance in the beverage container industry.
Conclusion: Choosing Between ABS and PET
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance and rigidity, making it suitable for durable water bottles requiring high strength. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) excels in clarity, lightweight properties, and recyclability, which aligns with eco-friendly bottle applications and consumer safety standards. Selecting between ABS and PET depends on prioritizing durability and toughness versus sustainability and transparency for water bottle manufacturing.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polyethylene terephthalate for Water bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com