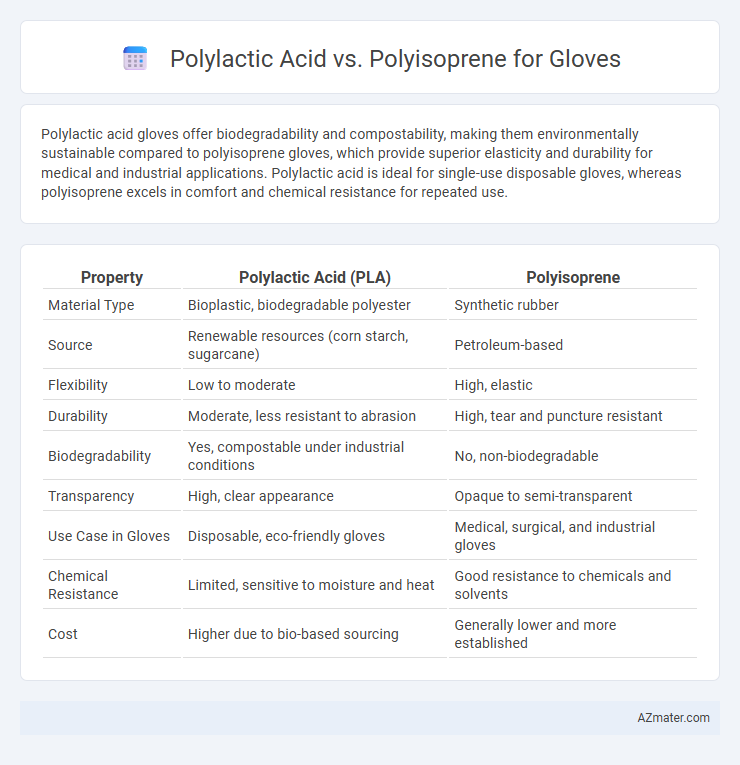
Polylactic acid gloves offer biodegradability and compostability, making them environmentally sustainable compared to polyisoprene gloves, which provide superior elasticity and durability for medical and industrial applications. Polylactic acid is ideal for single-use disposable gloves, whereas polyisoprene excels in comfort and chemical resistance for repeated use.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polylactic Acid (PLA) | Polyisoprene |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Bioplastic, biodegradable polyester | Synthetic rubber |
| Source | Renewable resources (corn starch, sugarcane) | Petroleum-based |
| Flexibility | Low to moderate | High, elastic |
| Durability | Moderate, less resistant to abrasion | High, tear and puncture resistant |
| Biodegradability | Yes, compostable under industrial conditions | No, non-biodegradable |
| Transparency | High, clear appearance | Opaque to semi-transparent |
| Use Case in Gloves | Disposable, eco-friendly gloves | Medical, surgical, and industrial gloves |
| Chemical Resistance | Limited, sensitive to moisture and heat | Good resistance to chemicals and solvents |
| Cost | Higher due to bio-based sourcing | Generally lower and more established |
Introduction to Polylactic Acid and Polyisoprene
Polylactic acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane, making it an environmentally friendly material used in glove manufacturing. Polyisoprene, a synthetic or natural rubber, offers excellent elasticity, durability, and comfort, widely favored for disposable and medical gloves. While PLA provides compostability and reduced carbon footprint, polyisoprene is preferred for superior elasticity and tactile sensitivity in protective gloves.
Material Composition and Sources
Polylactic acid (PLA) gloves are derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane, making them biodegradable and compostable. Polyisoprene gloves are synthesized from natural rubber tapped from Hevea brasiliensis trees, offering high elasticity and durability. The distinct material composition influences their environmental impact and mechanical properties, with PLA prioritizing sustainability and polyisoprene delivering superior flexibility.
Manufacturing Processes
Polylactic acid (PLA) gloves are manufactured using injection molding or extrusion processes that capitalize on PLA's thermoplastic properties, enabling precise shaping and biodegradable alternatives to conventional gloves. Polyisoprene gloves rely on latex dipping methods, where liquid synthetic rubber is dipped onto hand-shaped molds and then vulcanized, creating gloves with high elasticity and durability. The manufacturing of PLA gloves emphasizes environmental sustainability with compostable materials, while polyisoprene production focuses on mechanical resilience and skin sensitivity through established latex-based techniques.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Polylactic acid (PLA) gloves exhibit moderate tensile strength and rigidity with lower elasticity, making them biodegradable but less flexible compared to polyisoprene gloves. Polyisoprene gloves demonstrate superior elongation at break and excellent elasticity, providing enhanced dexterity and durability under mechanical stress. The higher tear resistance and tensile modulus of polyisoprene contribute to its preferred use in medical and industrial gloves requiring both comfort and mechanical performance.
Biodegradability and Environmental Impact
Polylactic acid (PLA) gloves offer superior biodegradability compared to polyisoprene, breaking down efficiently under industrial composting conditions and reducing long-term environmental pollution. Polyisoprene gloves, while flexible and durable, are synthetic polymers derived from petrochemicals that resist natural degradation, contributing to persistent plastic waste in ecosystems. PLA's production from renewable resources like corn starch enhances its environmental impact profile, whereas polyisoprene relies on non-renewable sources with higher carbon footprints.
Allergenicity and Skin Sensitivity
Polylactic acid (PLA) gloves offer a biodegradable alternative with minimal allergenicity, making them suitable for individuals with sensitive skin or latex allergies. Polyisoprene gloves mimic natural latex properties but are specifically processed to remove allergenic proteins, significantly reducing the risk of allergic reactions compared to traditional latex gloves. Studies highlight that polyisoprene gloves maintain favorable tactile sensitivity while minimizing skin irritation, whereas PLA gloves provide a hypoallergenic option with lower environmental impact but may lack the elasticity and fit preferred in medical settings.
Barrier Protection and Chemical Resistance
Polylactic acid (PLA) gloves offer moderate barrier protection primarily against biological contaminants but exhibit limited chemical resistance, making them less suitable for handling aggressive chemicals. Polyisoprene gloves provide superior barrier protection with excellent elasticity and high resistance to a broad range of chemicals, including acids, alcohols, and oils, ensuring durability in industrial and medical applications. The enhanced chemical resistance of polyisoprene gloves makes them a preferred choice for environments requiring robust protection against hazardous substances.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Polylactic acid (PLA) gloves generally offer lower production costs due to their biodegradable nature and use of renewable resources, while polyisoprene gloves have higher manufacturing expenses related to synthetic rubber processing and polymerization. Market availability favors polyisoprene gloves because of their established demand in the medical and industrial sectors, whereas PLA gloves are emerging products with limited distribution primarily in eco-friendly niche markets. Cost efficiency and widespread supply chains make polyisoprene gloves more accessible, but increasing environmental regulations could shift demand toward cost-competitive PLA alternatives.
Applications in Medical and Industrial Sectors
Polylactic acid (PLA) gloves are biodegradable and commonly used in medical settings requiring disposable, eco-friendly options for short-term protection, such as examination and surgical gloves. Polyisoprene gloves offer superior elasticity, durability, and tactile sensitivity, making them ideal for both medical procedures requiring precision and industrial applications involving chemical handling or mechanical tasks. The choice between PLA and polyisoprene depends on the specific requirements for biodegradability, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals or physical stress in medical and industrial environments.
Future Trends and Innovations in Glove Materials
Polylactic acid (PLA) gloves are gaining traction due to their biodegradability and renewable sourcing, aligning with increasing environmental regulations and consumer demand for sustainable products. Polyisoprene gloves maintain superior elasticity and tactile sensitivity, positioning them as a preferred choice for medical and examination uses, yet ongoing research aims to enhance their biodegradability through advanced polymer blending techniques. Future innovations focus on hybrid materials combining PLA's eco-friendliness with polyisoprene's performance, driven by advances in nanocomposites and bio-based additives to improve durability, flexibility, and antimicrobial properties.
Infographic: Polylactic acid vs Polyisoprene for Glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com