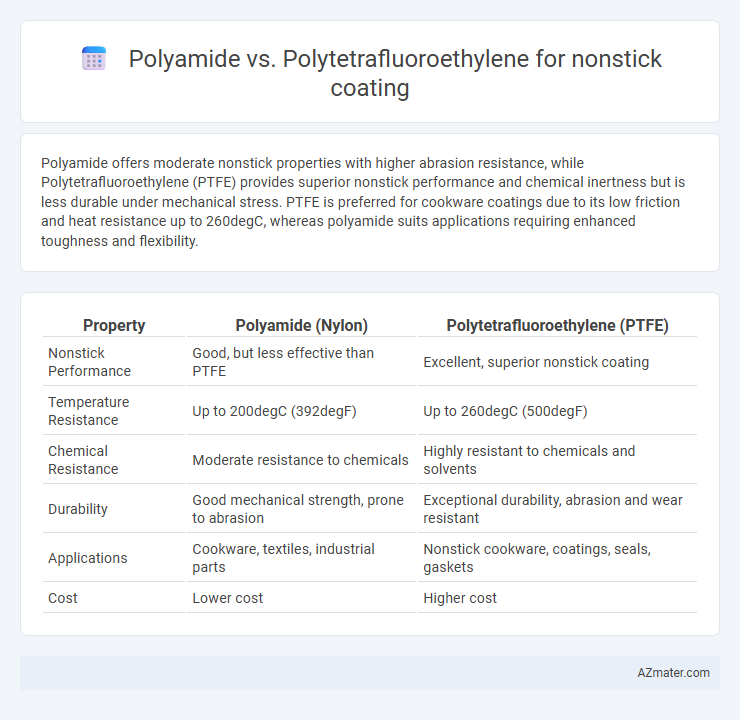
Polyamide offers moderate nonstick properties with higher abrasion resistance, while Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides superior nonstick performance and chemical inertness but is less durable under mechanical stress. PTFE is preferred for cookware coatings due to its low friction and heat resistance up to 260degC, whereas polyamide suits applications requiring enhanced toughness and flexibility.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyamide (Nylon) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Nonstick Performance | Good, but less effective than PTFE | Excellent, superior nonstick coating |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 200degC (392degF) | Up to 260degC (500degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance to chemicals | Highly resistant to chemicals and solvents |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength, prone to abrasion | Exceptional durability, abrasion and wear resistant |
| Applications | Cookware, textiles, industrial parts | Nonstick cookware, coatings, seals, gaskets |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Nonstick Coating Materials
Nonstick coating materials primarily include polyamide and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), each offering distinct performance characteristics. Polyamide coatings provide excellent abrasion resistance and durability, making them suitable for various cookware applications. PTFE, known for its superior nonstick properties and chemical inertness, is widely used for high-performance nonstick surfaces in kitchen utensils and industrial equipment.
What is Polyamide?
Polyamide is a synthetic polymer known for its strong, durable, and heat-resistant properties, often utilized in nonstick coatings for cookware due to its ability to withstand high temperatures without degrading. It provides good mechanical strength and chemical resistance, making it suitable for applications where durability and long-term performance are essential. Unlike polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), polyamide offers excellent abrasion resistance but may have lower nonstick efficiency.
What is Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)?
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer renowned for its superior nonstick properties, chemical resistance, and high-temperature stability, making it a preferred choice for cookware coatings. PTFE's molecular structure creates a low-friction surface that prevents food from adhering during cooking, enhancing ease of cleaning and durability. Compared to polyamide, PTFE offers better resistance to heat and chemical exposure, optimizing nonstick performance in demanding culinary applications.
Physical and Chemical Properties Comparison
Polyamide exhibits high tensile strength, flexibility, and moderate chemical resistance, making it suitable for heat-resistant nonstick coatings, while Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers exceptional chemical inertness, extremely low friction, and a higher melting point around 327degC. Polyamide's water absorption can affect durability, whereas PTFE's hydrophobic nature prevents moisture absorption, enhancing longevity. PTFE generally outperforms polyamide in thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it the preferred choice for demanding nonstick applications.
Nonstick Performance: Polyamide vs PTFE
Polyamide offers moderate nonstick performance suitable for light cooking tasks but tends to degrade faster under high heat compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which provides superior nonstick properties with excellent food release and durability. PTFE coatings resist abrasion and chemical damage, maintaining slick surfaces for extended use, making them the preferred choice in high-performance nonstick cookware. Polyamide's nonstick layer is more prone to wear and may require more frequent recoating, whereas PTFE ensures consistent nonstick efficiency and easy cleanup over time.
Durability and Lifespan
Polyamide coatings exhibit moderate durability with good resistance to abrasion and impact but tend to degrade faster under high heat compared to Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which maintains nonstick properties and structural integrity at temperatures up to 260degC. PTFE's exceptional chemical inertness and low coefficient of friction contribute to a longer lifespan, often exceeding that of polyamide in cookware applications. Despite polyamide's flexibility and initial toughness, PTFE remains the superior choice for nonstick surfaces demanding extended durability and thermal stability.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Stability
Polyamide exhibits moderate heat resistance, typically enduring temperatures up to 260degC, suitable for general cookware applications, while Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) boasts superior thermal stability with heat resistance up to 327degC, making it ideal for high-temperature nonstick coatings. PTFE's exceptional chemical inertness and low surface energy contribute to its ability to maintain nonstick properties under prolonged heat exposure, unlike Polyamide which can degrade faster under thermal stress. The choice between Polyamide and PTFE for nonstick coatings primarily hinges on required operating temperature and durability, with PTFE favored for its enhanced heat resistance and longevity.
Safety and Food Contact Considerations
Polyamide coatings offer excellent heat resistance and durability but may release harmful substances at very high temperatures, making compliance with FDA and EFSA food contact regulations essential. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is widely recognized for its superior nonstick properties and inertness, with safety ensured under typical cooking conditions; however, overheating above 260degC can emit toxic fumes, requiring careful temperature control. Both materials must meet strict migration limits and manufacturing standards to guarantee safe use in cookware applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is derived from perfluorinated compounds, which are persistent in the environment and can degrade into toxic substances like PFOA, raising long-term concerns about bioaccumulation and pollution. Polyamide coatings, being nylon-based, are generally more biodegradable and produced from less hazardous raw materials, making them a more sustainable option with lower environmental toxicity. The lifecycle assessment of polyamide shows reduced greenhouse gas emissions and improved recyclability compared to PTFE, positioning it as a preferable material for eco-friendly nonstick coatings.
Choosing the Right Coating: Polyamide or PTFE?
Polyamide coatings offer excellent durability and heat resistance for nonstick cookware, making them suitable for moderate cooking temperatures and frequent use. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides superior nonstick performance and chemical inertness, ideal for high-heat cooking and preventing food adhesion. Selecting the right coating depends on the specific cooking needs, with polyamide favored for durability and PTFE preferred for premium nonstick efficiency and ease of cleaning.
Infographic: Polyamide vs Polytetrafluoroethylene for Nonstick coating
 azmater.com
azmater.com