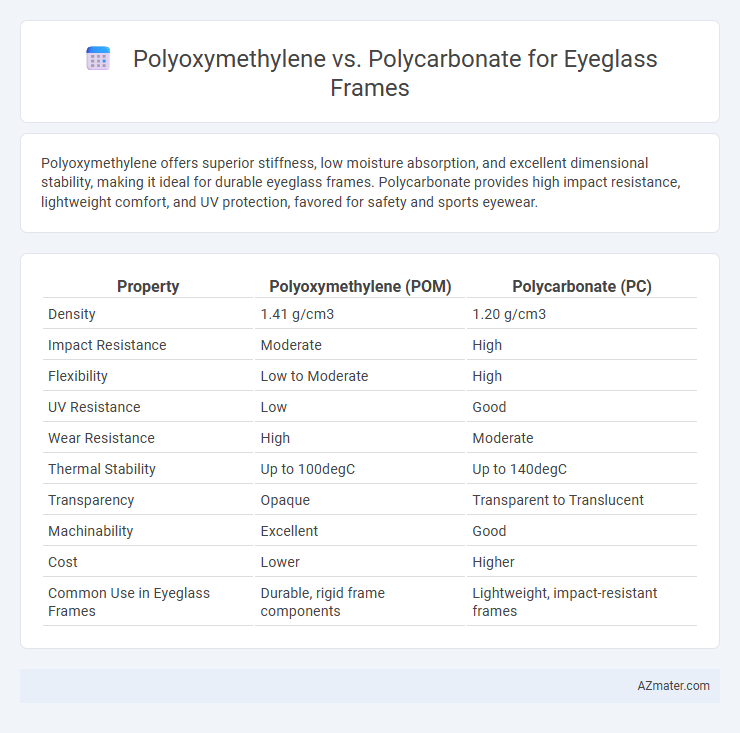
Polyoxymethylene offers superior stiffness, low moisture absorption, and excellent dimensional stability, making it ideal for durable eyeglass frames. Polycarbonate provides high impact resistance, lightweight comfort, and UV protection, favored for safety and sports eyewear.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyoxymethylene (POM) | Polycarbonate (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1.41 g/cm3 | 1.20 g/cm3 |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Flexibility | Low to Moderate | High |
| UV Resistance | Low | Good |
| Wear Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 100degC | Up to 140degC |
| Transparency | Opaque | Transparent to Translucent |
| Machinability | Excellent | Good |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Common Use in Eyeglass Frames | Durable, rigid frame components | Lightweight, impact-resistant frames |
Introduction to Eyeglass Frame Materials
Polyoxymethylene (POM) and polycarbonate (PC) stand out as advanced materials for eyeglass frames due to their remarkable strength and lightweight properties. POM is known for its excellent dimensional stability, chemical resistance, and high tensile strength, making it ideal for durable and flexible frames. Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and optical clarity with inherent UV protection, commonly used in sports and safety eyewear frames for enhanced performance and comfort.
What is Polyoxymethylene (POM)?
Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, is a high-performance thermoplastic polymer characterized by its exceptional stiffness, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability, making it highly suitable for eyeglass frames. Compared to polycarbonate, POM offers superior resistance to wear and chemical degradation, ensuring long-lasting durability under daily use. Its lightweight nature and ability to maintain structural integrity under mechanical stress allow eyeglass frames to deliver both comfort and robustness.
What is Polycarbonate (PC)?
Polycarbonate (PC) is a durable, lightweight thermoplastic polymer commonly used in eyeglass frames due to its high impact resistance and optical clarity. It offers superior flexibility compared to polyoxymethylene (POM), reducing the risk of frame breakage during regular use. The inherent UV protection and scratch resistance of polycarbonate make it an ideal material for eyewear applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits high tensile strength and excellent fatigue resistance, making it durable and resilient for eyeglass frames subjected to frequent bending or stress. Polycarbonate (PC) offers superior impact resistance and higher fracture toughness, providing enhanced protection against drops and accidental impacts. While POM excels in stiffness and dimensional stability, PC outperforms in flexibility and UV resistance, crucial for long-term wear comfort and frame longevity.
Durability and Impact Resistance
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers exceptional durability and high impact resistance, making it ideal for eyeglass frames that require long-lasting wear and resistance to deformation. Polycarbonate frames provide superior impact resistance and flexibility, particularly excelling in shock absorption and resistance to cracking upon impact. Both materials deliver robust performance, but polycarbonate's lightweight nature and better impact energy dispersion often make it the preferred choice for high-impact applications in eyewear.
Weight and Comfort in Eyewear
Polyoxymethylene (POM) eyeglass frames weigh significantly less than polycarbonate frames, offering enhanced comfort for prolonged wear due to their lightweight and flexible properties. Polyoxymethylene provides excellent dimensional stability and resistance to fatigue, reducing pressure on the nose and ears, which is crucial for all-day use. Polycarbonate frames, while impact-resistant and durable, are typically heavier and can cause discomfort during extended periods of wear.
Aesthetics and Color Options
Polyoxymethylene eyeglass frames offer a sleek, matte finish with limited color options primarily in neutral tones, emphasizing durability over vibrant appearance. Polycarbonate frames provide a wide array of colors and translucent styles, allowing for more personalized and trendy aesthetic choices. The versatility of polycarbonate in color and finish makes it preferable for fashion-forward and expressive eyewear designs.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers lower material costs and easier injection molding compared to polycarbonate (PC), making it a cost-effective choice for mass-producing eyeglass frames. Polycarbonate provides superior impact resistance and optical clarity but requires more complex manufacturing processes, increasing production expenses. Manufacturers often balance POM's affordability against PC's durability when selecting materials for eyewear frames.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high durability and impact resistance for eyeglass frames but poses environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradable nature and limited recycling options. Polycarbonate (PC) frames provide excellent lightweight strength with better recyclability through established mechanical and chemical processes, reducing landfill waste. Choosing polycarbonate can significantly lower environmental impact by supporting circular economy practices and minimizing persistent plastic pollution.
Which is Better: Polyoxymethylene or Polycarbonate for Eyeglass Frames?
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior rigidity and excellent dimensional stability, making it highly resistant to wear and deformation in eyeglass frames compared to polycarbonate. Polycarbonate provides enhanced impact resistance and lightweight comfort, ideal for active lifestyles or sports eyewear. Choosing between POM and polycarbonate depends on prioritizing either durability and stiffness (POM) or impact resistance and flexibility (polycarbonate) for eyeglass frame applications.
Infographic: Polyoxymethylene vs Polycarbonate for Eyeglass Frame
 azmater.com
azmater.com