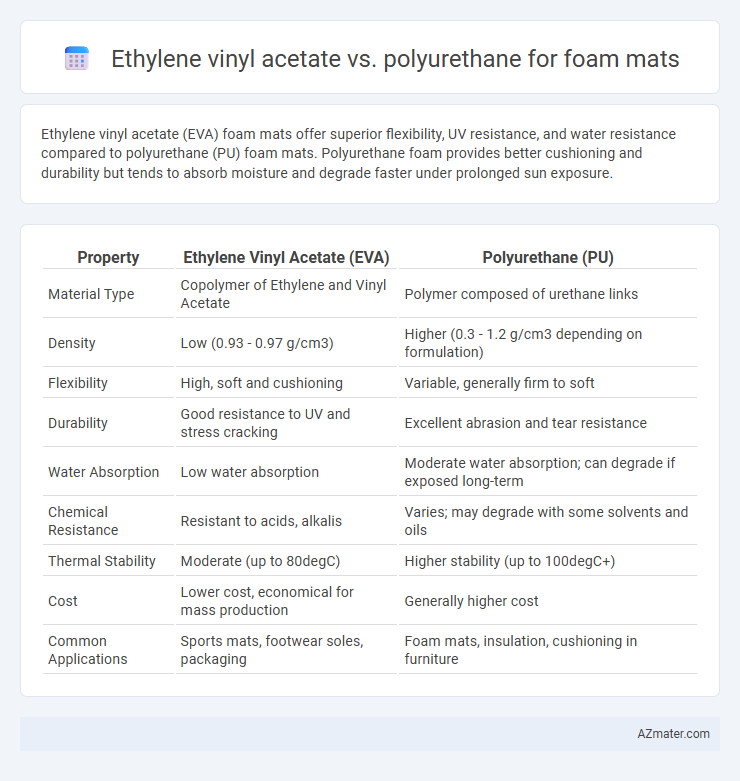
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam mats offer superior flexibility, UV resistance, and water resistance compared to polyurethane (PU) foam mats. Polyurethane foam provides better cushioning and durability but tends to absorb moisture and degrade faster under prolonged sun exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Copolymer of Ethylene and Vinyl Acetate | Polymer composed of urethane links |
| Density | Low (0.93 - 0.97 g/cm3) | Higher (0.3 - 1.2 g/cm3 depending on formulation) |
| Flexibility | High, soft and cushioning | Variable, generally firm to soft |
| Durability | Good resistance to UV and stress cracking | Excellent abrasion and tear resistance |
| Water Absorption | Low water absorption | Moderate water absorption; can degrade if exposed long-term |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids, alkalis | Varies; may degrade with some solvents and oils |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate (up to 80degC) | Higher stability (up to 100degC+) |
| Cost | Lower cost, economical for mass production | Generally higher cost |
| Common Applications | Sports mats, footwear soles, packaging | Foam mats, insulation, cushioning in furniture |
Introduction to EVA and PU Foam Mats
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam mats offer excellent flexibility, lightweight cushioning, and water resistance, making them ideal for exercise and outdoor activities. Polyurethane (PU) foam mats provide superior durability, denser structure, and higher resilience, suitable for heavy-duty applications and prolonged comfort. Both materials excel in shock absorption and thermal insulation but differ significantly in texture, lifespan, and environmental resistance.
Chemical Composition: EVA vs Polyurethane
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam consists of a copolymer made from ethylene and vinyl acetate monomers, providing a flexible, lightweight, and chemically stable structure ideal for cushioning applications. Polyurethane foam is synthesized through the reaction of polyols and diisocyanates, resulting in a versatile polymer with variable density and resilience, often used for high-impact and durable foam mats. The chemical composition of EVA emphasizes elasticity and water resistance, while polyurethane offers enhanced durability and resistance to abrasion due to its urethane linkages.
Physical Properties Comparison
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam mats exhibit excellent flexibility, low-temperature toughness, and high impact resistance, making them ideal for cushioning and shock absorption. Polyurethane (PU) foam mats offer superior abrasion resistance, higher tensile strength, and greater durability under mechanical stress, often used in applications requiring long-term resilience. Both materials differ significantly in density and hardness, with EVA generally lighter and softer, while PU tends to be denser and firmer, affecting comfort and wear performance in foam mat applications.
Comfort and Cushioning Performance
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam mats offer excellent shock absorption and a soft, cushioned feel, making them ideal for activities requiring prolonged comfort and impact reduction. Polyurethane (PU) foam provides superior resilience and higher density, delivering enhanced support and durability under repeated pressure, which is beneficial for intensive use and long-term cushioning performance. When comparing comfort, EVA excels in lightweight softness and flexibility, while PU outperforms in firmness and energy return, influencing user preference based on cushioning needs.
Durability and Longevity
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam mats are known for their excellent resistance to cracking and UV damage, providing long-lasting durability ideal for outdoor use. Polyurethane (PU) foam mats offer superior abrasion resistance and cushioning but tend to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to moisture and heat. EVA mats generally outperform PU in terms of longevity, especially in environments requiring consistent durability and weather resistance.
Safety and Environmental Impact
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam mats are non-toxic, free of phthalates and heavy metals, and feature excellent biodegradability compared to polyurethane (PU), which often contains isocyanates linked to respiratory issues and slower degradation rates. EVA foam exhibits higher resistance to UV radiation and chemical leaching, reducing environmental pollution during disposal, while PU foam's breakdown contributes to persistent microplastic contamination. Choosing EVA over PU enhances indoor air quality and minimizes ecological footprint, making it preferable for safety-conscious and eco-friendly mat applications.
Water Resistance and Maintenance
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam mats exhibit superior water resistance due to their closed-cell structure, making them less prone to water absorption and mold growth compared to polyurethane (PU) foam mats, which have a more open-cell composition. EVA foam is easier to maintain, requiring simple cleaning with mild soap and water, while PU foam demands careful drying to prevent mildew and deterioration. For environments with frequent moisture exposure, EVA foam offers enhanced durability and lower maintenance costs.
Cost and Affordability
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam mats generally offer greater cost-effectiveness and affordability compared to polyurethane (PU) foam mats due to lower material and manufacturing expenses. EVA foam's lightweight and flexible properties reduce shipping and handling costs, making it an economical choice for budget-conscious consumers. Polyurethane foam mats, while providing superior cushioning and durability, often come with higher price points that reflect their enhanced performance characteristics.
Popular Applications of EVA and PU Foam Mats
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam mats are widely used in yoga, gym flooring, and children's play areas due to their lightweight, shock-absorbing properties, and non-toxic materials. Polyurethane (PU) foam mats find popular applications in automotive seating, medical mattresses, and furniture padding because of their higher durability, superior cushioning, and resistance to wear and tear. Both EVA and PU foams are favored in sports and fitness equipment, but EVA is preferred for water-resistant and outdoor uses, while PU is chosen for comfort and long-term support.
Choosing the Right Foam Mat: Key Considerations
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam mats offer lightweight durability, excellent shock absorption, and water resistance, making them ideal for yoga and fitness activities requiring flexibility and moisture control. Polyurethane (PU) foam mats provide superior cushioning and long-term resilience, with higher density and firmness suitable for heavy-impact exercises or prolonged use where support is crucial. When choosing the right foam mat, prioritize factors like activity type, desired comfort level, moisture exposure, and durability to ensure optimal performance and lifespan.
Infographic: Ethylene vinyl acetate vs Polyurethane for Foam mat
 azmater.com
azmater.com