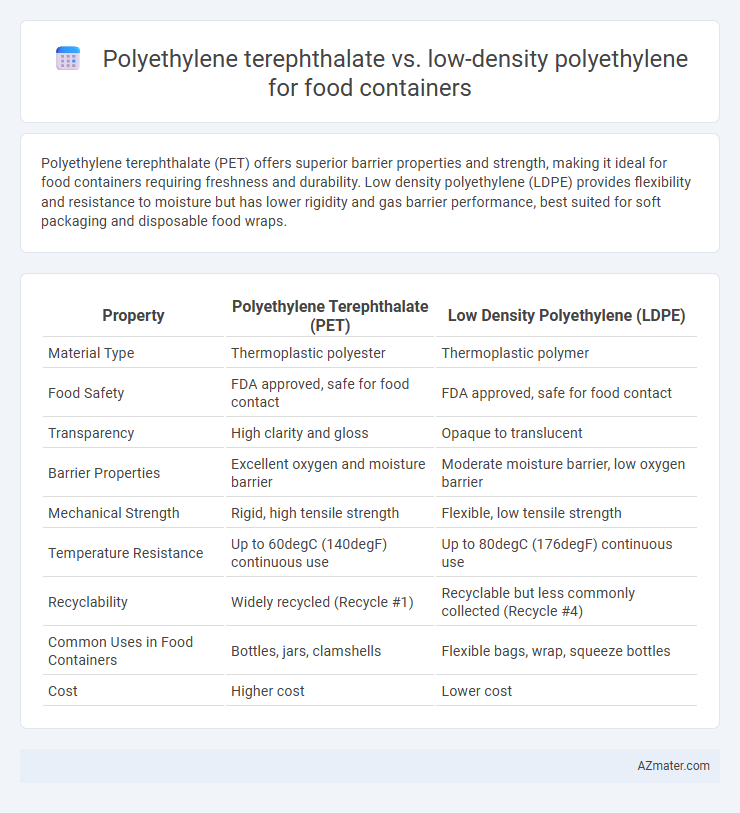
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior barrier properties and strength, making it ideal for food containers requiring freshness and durability. Low density polyethylene (LDPE) provides flexibility and resistance to moisture but has lower rigidity and gas barrier performance, best suited for soft packaging and disposable food wraps.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polyester | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Food Safety | FDA approved, safe for food contact | FDA approved, safe for food contact |
| Transparency | High clarity and gloss | Opaque to translucent |
| Barrier Properties | Excellent oxygen and moisture barrier | Moderate moisture barrier, low oxygen barrier |
| Mechanical Strength | Rigid, high tensile strength | Flexible, low tensile strength |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 60degC (140degF) continuous use | Up to 80degC (176degF) continuous use |
| Recyclability | Widely recycled (Recycle #1) | Recyclable but less commonly collected (Recycle #4) |
| Common Uses in Food Containers | Bottles, jars, clamshells | Flexible bags, wrap, squeeze bottles |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
Introduction to Food-Grade Plastics
Food-grade plastics like polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE) are widely used in food packaging due to their safety and chemical resistance. PET offers high strength, clarity, and excellent barrier properties against moisture and gases, making it ideal for beverages and perishable foods. LDPE provides flexibility, impact resistance, and good moisture barrier performance, commonly used for bags, wraps, and squeezable containers.
Overview of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a widely used polyester resin known for its excellent strength, clarity, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for food containers requiring durability and transparency. PET offers superior barrier properties against oxygen and moisture compared to low density polyethylene (LDPE), which helps preserve food freshness and extend shelf life. Its recyclability and compliance with food safety standards enhance its preference over LDPE in packaging applications demanding high hygiene and product protection.
Key Properties of PET for Food Containers
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior clarity, high strength, and excellent gas barrier properties compared to low density polyethylene (LDPE), making it ideal for food containers that require product visibility and extended shelf life. PET's resistance to moisture and ability to withstand higher temperatures during hot filling or sterilization processes ensure food safety and quality retention. Unlike LDPE, PET provides a rigid structure that enhances stackability and prevents deformation under pressure, which is crucial for efficient packaging and transport.
Understanding Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a flexible, lightweight polymer commonly used in food containers due to its excellent moisture resistance and impact strength. Compared to Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), LDPE offers better flexibility and is less prone to cracking, making it ideal for squeezable or flexible food packaging. Its lower melting point and chemical inertness contribute to safe food storage without compromising container integrity.
Essential Characteristics of LDPE in Food Packaging
Low density polyethylene (LDPE) offers excellent flexibility, moisture resistance, and a good balance of strength and transparency, making it ideal for food packaging that requires airtight sealing and protection against contamination. Its low melting point allows for easy heat sealing, contributing to efficient manufacturing processes and reliable package integrity. Compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), LDPE provides superior flexibility and impact resistance but generally lower barrier properties against oxygen and carbon dioxide.
PET vs LDPE: Barrier Performance and Food Safety
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) exhibits superior barrier performance compared to low-density polyethylene (LDPE), providing enhanced resistance to oxygen, moisture, and carbon dioxide, which significantly prolongs food freshness and shelf life. PET's high clarity, rigidity, and strong chemical resistance make it a preferred choice for packaging perishable food items requiring stringent hygiene and safety standards. LDPE, while more flexible and impact-resistant, offers lower barrier properties and is generally less effective in preventing microbial contamination or preserving food quality over extended periods.
Durability and Temperature Resistance Comparison
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior durability with high impact resistance and maintains structural integrity at temperatures up to 70degC, making it ideal for hot food packaging. Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) exhibits greater flexibility but lower tensile strength, and its temperature resistance is limited to around 65degC, increasing the risk of deformation under heat. PET's enhanced thermal stability and mechanical strength favor long-term food storage and reheating compared to LDPE in food container applications.
Environmental Impact: PET vs LDPE Recyclability
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is highly recyclable with established infrastructure, allowing it to be processed into new bottles and containers efficiently, reducing environmental waste. Low-density polyethylene (LDPE), while recyclable, faces challenges due to limited recycling facilities and lower market demand for recycled products, often resulting in landfill disposal. PET's recyclability contributes significantly to its lower environmental impact compared to LDPE in food container applications.
Common Applications: Choosing Between PET and LDPE
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is commonly used for rigid food containers such as water bottles, salad trays, and microwaveable meal trays due to its excellent strength, clarity, and barrier properties against moisture and gases. Low density polyethylene (LDPE) is favored for flexible packaging applications like squeeze bottles, plastic wraps, and grocery bags because of its softer, more flexible texture and good moisture resistance. Choosing between PET and LDPE depends on the desired container rigidity, transparency, and barrier requirements for preserving food quality.
Conclusion: Selecting the Best Plastic for Food Containers
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior strength, clarity, and barrier properties against moisture and gases, making it ideal for food containers requiring high durability and extended shelf life. Low density polyethylene (LDPE) provides excellent flexibility, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for products needing soft packaging or resealable options. Selecting the best plastic depends on specific food protection needs, with PET favored for rigid, transparent containers and LDPE chosen for flexible, lightweight applications.
Infographic: Polyethylene terephthalate vs Low density polyethylene for Food Container
 azmater.com
azmater.com