Biodegradable plastics, such as Polybutylene Succinate (PBS), offer excellent compostability and durability for food trays, making them an eco-friendly alternative to conventional plastics. PBS provides strong heat resistance and high transparency, ensuring safety and functionality in food packaging applications.
Table of Comparison
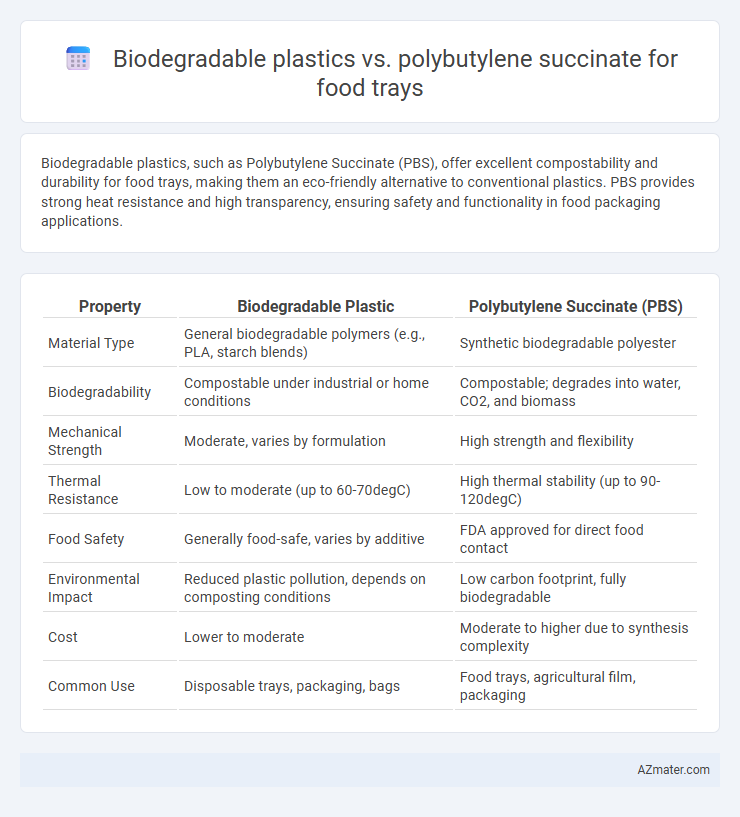
| Property | Biodegradable Plastic | Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | General biodegradable polymers (e.g., PLA, starch blends) | Synthetic biodegradable polyester |
| Biodegradability | Compostable under industrial or home conditions | Compostable; degrades into water, CO2, and biomass |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, varies by formulation | High strength and flexibility |
| Thermal Resistance | Low to moderate (up to 60-70degC) | High thermal stability (up to 90-120degC) |
| Food Safety | Generally food-safe, varies by additive | FDA approved for direct food contact |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced plastic pollution, depends on composting conditions | Low carbon footprint, fully biodegradable |
| Cost | Lower to moderate | Moderate to higher due to synthesis complexity |
| Common Use | Disposable trays, packaging, bags | Food trays, agricultural film, packaging |
Overview of Food Tray Materials
Biodegradable plastics, such as polylactic acid (PLA) and starch-based compounds, are designed to break down under specific conditions, reducing environmental impact compared to conventional plastics. Polybutylene succinate (PBS) is a biodegradable aliphatic polyester known for its excellent mechanical properties, heat resistance, and compostability, making it a suitable material for durable and eco-friendly food trays. Food trays made from PBS offer enhanced performance in terms of strength and thermal stability, while maintaining the environmental benefits of biodegradability.
What is Biodegradable Plastic?
Biodegradable plastic refers to materials capable of breaking down naturally through microbial action into water, carbon dioxide, and biomass, reducing environmental impact compared to conventional plastics. Polybutylene succinate (PBS) is a type of biodegradable plastic derived from renewable resources, offering excellent heat resistance and mechanical properties suitable for food trays. Unlike general biodegradable plastics, PBS provides stronger durability and better moisture resistance, making it ideal for sustainable food packaging solutions.
Polybutylene Succinate (PBS): An Introduction
Polybutylene succinate (PBS) is a biodegradable plastic derived from renewable resources, offering excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength ideal for food tray applications. Compared to conventional biodegradable plastics, PBS provides superior heat resistance up to 115degC, making it suitable for hot food packaging while maintaining compostability within 6 months under industrial conditions. Its balanced blend of flexibility and rigidity ensures durability during handling and transportation, positioning PBS as a sustainable alternative for environmentally conscious food packaging solutions.
Environmental Impact: Degradation and Compostability
Biodegradable plastic and polybutylene succinate (PBS) differ significantly in environmental impact, particularly in degradation and compostability. PBS demonstrates superior biodegradability, breaking down efficiently in industrial composting conditions within 60 to 90 days, producing non-toxic byproducts that enhance soil quality. In contrast, many conventional biodegradable plastics require specific conditions and extended timeframes for decomposition, often limiting their environmental benefits in typical disposal environments.
Food Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Biodegradable plastics for food trays must meet strict food safety standards such as FDA 21 CFR 177.1520 and EU Regulation No 10/2011 to ensure non-toxicity and prevent contamination. Polybutylene succinate (PBS) offers excellent biodegradability and complies with food contact legislation due to its high thermal stability and low migration rates of harmful substances. Regulatory compliance for PBS includes certifications like ASTM D6400 and EN 13432, making it a safer and eco-friendly alternative for food packaging applications.
Mechanical and Thermal Properties Comparison
Biodegradable plastics such as polylactic acid (PLA) and polybutylene succinate (PBS) both offer favorable mechanical properties for food tray applications, with PBS typically exhibiting higher tensile strength (up to 40 MPa) and better elongation at break (over 200%) compared to PLA. Thermal properties also favor PBS, which has a melting point around 115degC and a glass transition temperature near -32degC, allowing better heat resistance and flexibility under varying temperature conditions, unlike PLA's lower heat distortion temperature (~60degC). The superior thermal stability and toughness of PBS enhance its suitability for hot food packaging, while maintaining biodegradability and compostability standards.
Cost Analysis: Production and Market Pricing
Biodegradable plastics generally incur higher production costs due to the complexity of raw materials and processing technologies compared to traditional plastics like Polybutylene Succinate (PBS), which is valued for its cost-efficient scalability in food tray manufacturing. Market pricing for PBS food trays tends to be more competitive, benefiting from established supply chains and economies of scale, whereas biodegradable plastics command premium prices influenced by consumer demand for sustainable packaging. Cost analysis reveals that while biodegradable plastics offer environmental advantages, PBS provides a balanced cost-performance profile suitable for mass-market food tray applications.
Biodegradable Plastic vs PBS: Shelf Life & Performance
Biodegradable plastics generally offer moderate shelf life and performance for food trays, breaking down under composting conditions but may lack heat resistance and mechanical strength compared to Polybutylene Succinate (PBS). PBS exhibits superior thermal stability and durability, extending shelf life by maintaining structural integrity under various temperature ranges and increasing resistance to moisture and grease. Choosing PBS enhances food tray performance by balancing biodegradability with higher mechanical properties, making it ideal for demanding food packaging applications.
Consumer Perception and Market Trends
Consumer perception of biodegradable plastic food trays centers on eco-friendliness and sustainability, driving growing demand in markets prioritizing environmental impact. Polybutylene succinate (PBS) offers a competitive advantage with its superior biodegradability and compostability, aligning well with consumer preferences for fully degradable packaging solutions. Market trends indicate increasing adoption of PBS in food trays due to regulatory support and the shift towards circular economy principles in packaging industries.
Future Prospects and Innovations in Food Tray Materials
Biodegradable plastics and polybutylene succinate (PBS) present promising future prospects as sustainable alternatives for food tray materials due to their eco-friendly degradation and comparable mechanical properties. Innovations in blending PBS with natural fibers and enhancing its thermal resistance enable improved performance and broader application in food packaging. Advanced research focuses on refining biodegradation rates and compostability standards, positioning PBS as a frontrunner in next-generation food trays that minimize environmental impact without compromising food safety or quality.
Infographic: Biodegradable plastic vs Polybutylene succinate for Food tray
 azmater.com
azmater.com