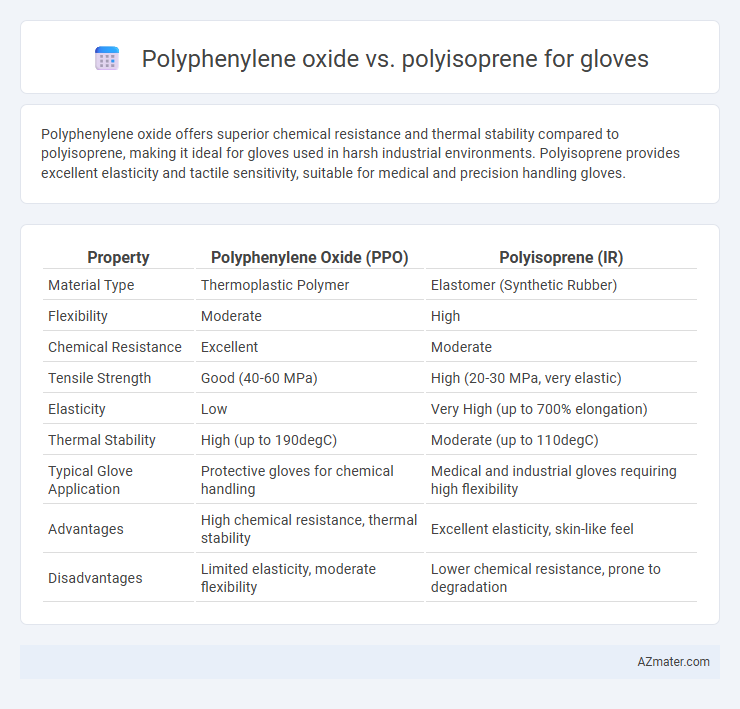
Polyphenylene oxide offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to polyisoprene, making it ideal for gloves used in harsh industrial environments. Polyisoprene provides excellent elasticity and tactile sensitivity, suitable for medical and precision handling gloves.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) | Polyisoprene (IR) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polymer | Elastomer (Synthetic Rubber) |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Tensile Strength | Good (40-60 MPa) | High (20-30 MPa, very elastic) |
| Elasticity | Low | Very High (up to 700% elongation) |
| Thermal Stability | High (up to 190degC) | Moderate (up to 110degC) |
| Typical Glove Application | Protective gloves for chemical handling | Medical and industrial gloves requiring high flexibility |
| Advantages | High chemical resistance, thermal stability | Excellent elasticity, skin-like feel |
| Disadvantages | Limited elasticity, moderate flexibility | Lower chemical resistance, prone to degradation |
Introduction to Glove Material Selection
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) and polyisoprene are two distinct materials used in glove manufacturing, each offering unique properties impacting glove performance and application suitability. PPO provides excellent chemical resistance and thermal stability, making it ideal for environments requiring durability against solvents and heat. Polyisoprene, a natural elastomer, delivers superior elasticity and tactile sensitivity, commonly chosen for medical or laboratory gloves where flexibility and comfort are critical.
Overview of Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO)
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent dimensional stability, chemical resistance, and thermal properties, making it suitable for protective glove applications requiring durability and heat resistance. Unlike polyisoprene, which offers superior elasticity and comfort due to its natural rubber-like properties, PPO gloves provide enhanced resistance to oils, solvents, and abrasion. PPO's inherent flame retardancy and low moisture absorption further contribute to its functionality in industrial glove manufacturing where chemical exposure and mechanical wear are concerns.
Overview of Polyisoprene
Polyisoprene is a synthetic elastomer that closely mimics the properties of natural rubber, offering excellent elasticity, flexibility, and comfort for glove applications. It provides superior tactile sensitivity and durability, making it ideal for medical and laboratory gloves requiring high dexterity and resistance to tearing. Unlike polyphenylene oxide, polyisoprene gloves exhibit lower chemical resistance but excel in hypoallergenic performance and fit.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to polyisoprene in glove applications due to its high tensile strength and excellent dimensional stability under stress. PPO's inherent rigidity and resistance to deformation contribute to enhanced durability and puncture resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty protective gloves. In contrast, polyisoprene offers greater elasticity but lower tensile strength, resulting in gloves that prioritize flexibility over mechanical robustness.
Chemical Resistance Properties
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) gloves exhibit superior chemical resistance against a wide range of organic solvents, oils, and acids, making them highly suitable for industrial applications involving aggressive chemicals. In contrast, polyisoprene gloves offer excellent resistance to aqueous chemicals and moderate protection against alcohols but are less effective against hydrocarbons, oils, and solvents. The molecular structure of PPO provides enhanced barrier properties and durability compared to the elastomeric nature of polyisoprene, which limits its chemical resistance primarily to water-based substances.
Comfort and Wearability
Polyisoprene gloves offer superior comfort and flexibility due to their excellent elasticity and soft texture, closely mimicking natural rubber. Polyphenylene oxide gloves, while durable and resistant to heat and chemicals, tend to be stiffer and less breathable, potentially reducing long-term wearability. For applications prioritizing tactile sensitivity and comfort, polyisoprene is generally preferred over polyphenylene oxide.
Allergenicity and Skin Sensitivity
Polyphenylene oxide gloves exhibit low allergenicity and minimal skin sensitivity, making them suitable for users with latex allergies or sensitive skin. Polyisoprene gloves closely mimic natural rubber latex but contain fewer proteins that typically trigger allergic reactions, reducing the risk of allergenic responses. Both materials provide hypoallergenic alternatives, but polyphenylene oxide is often preferred for its superior chemical resistance and non-latex composition in medical and industrial gloves.
Cost and Availability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) gloves generally have higher production costs due to complex synthesis and limited raw material availability, making them less cost-effective for mass production. Polyisoprene gloves are widely available and more affordable, benefiting from established production processes and abundant natural rubber sources. The cost-efficiency and accessibility of polyisoprene make it a preferred choice for disposable and medical glove applications compared to PPO.
Typical Applications in Industry
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) gloves are widely used in electronics and chemical industries due to their excellent thermal stability, electrical insulation, and chemical resistance properties. Polyisoprene gloves, favored in healthcare and food processing sectors, offer superior elasticity and tactile sensitivity, making them ideal for precision tasks and protection against biological contaminants. Both materials fulfill critical roles in industrial safety, with PPO suited for protective applications in hazardous chemical handling, while polyisoprene excels in environments requiring dexterity and allergen-free protection.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Glove Material
Polyisoprene offers superior elasticity and comfort for gloves requiring high tactile sensitivity, making it ideal for medical and delicate tasks, while polyphenylene oxide provides enhanced chemical resistance and thermal stability suitable for industrial applications. Selecting the right glove material depends on specific use cases, balancing flexibility, chemical exposure, and durability requirements. For environments demanding both protection and precision, polyisoprene gloves are preferred, whereas polyphenylene oxide gloves excel in harsh or high-temperature conditions.
Infographic: Polyphenylene oxide vs Polyisoprene for Glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com