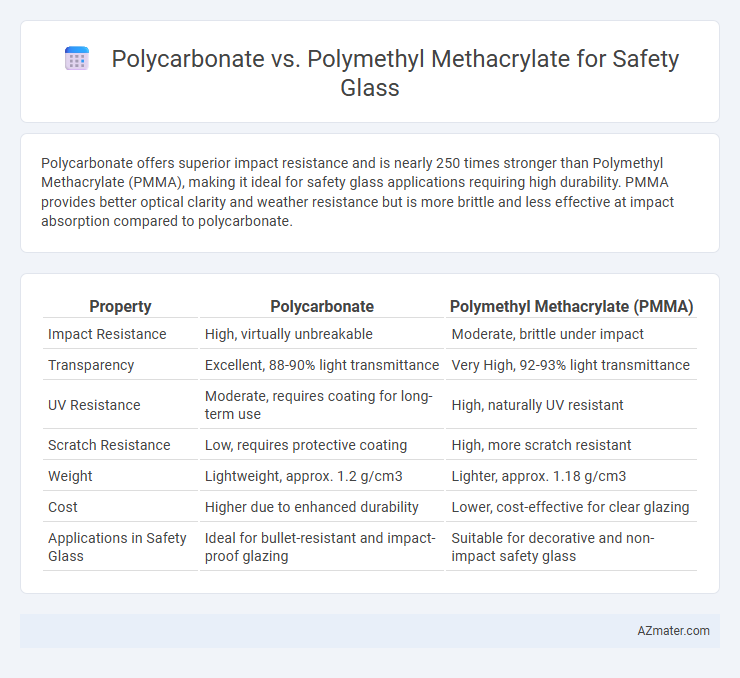
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and is nearly 250 times stronger than Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), making it ideal for safety glass applications requiring high durability. PMMA provides better optical clarity and weather resistance but is more brittle and less effective at impact absorption compared to polycarbonate.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polycarbonate | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Resistance | High, virtually unbreakable | Moderate, brittle under impact |
| Transparency | Excellent, 88-90% light transmittance | Very High, 92-93% light transmittance |
| UV Resistance | Moderate, requires coating for long-term use | High, naturally UV resistant |
| Scratch Resistance | Low, requires protective coating | High, more scratch resistant |
| Weight | Lightweight, approx. 1.2 g/cm3 | Lighter, approx. 1.18 g/cm3 |
| Cost | Higher due to enhanced durability | Lower, cost-effective for clear glazing |
| Applications in Safety Glass | Ideal for bullet-resistant and impact-proof glazing | Suitable for decorative and non-impact safety glass |
Introduction to Safety Glass Materials
Polycarbonate and Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) are prominent materials used in safety glass applications due to their impact resistance and clarity. Polycarbonate offers superior toughness and shatter resistance, making it ideal for environments requiring maximum protection. PMMA provides excellent optical clarity and UV resistance but lacks the high impact strength of polycarbonate, influencing material selection based on specific safety and performance requirements.
Overview of Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate (PC) is a durable, impact-resistant thermoplastic commonly used in safety glass applications due to its exceptional toughness and high optical clarity. It offers superior resistance to shattering compared to Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), making it ideal for protective barriers, vehicle windshields, and security windows. Polycarbonate's lightweight nature combined with its ability to withstand extreme temperatures and UV radiation enhances safety and longevity in demanding environments.
Overview of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) is a transparent thermoplastic often chosen for safety glass applications due to its high optical clarity and resistance to UV light. It offers superior scratch resistance compared to polycarbonate, making it ideal for environments where surface durability is critical. Although PMMA is less impact-resistant than polycarbonate, it provides excellent weatherability and chemical resistance, ensuring long-term performance in outdoor safety glazing.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polycarbonate exhibits significantly higher impact resistance and tensile strength compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), making it more suitable for safety glass applications where mechanical durability is crucial. While PMMA offers good clarity and weather resistance, its lower fracture toughness and brittleness reduce its effectiveness in high-impact scenarios. The superior toughness and flexibility of polycarbonate provide enhanced protection against mechanical stresses, ensuring greater safety performance.
Impact Resistance and Durability
Polycarbonate exhibits superior impact resistance compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), with the ability to withstand high-velocity impacts without cracking or shattering, making it ideal for safety glass applications. PMMA offers excellent optical clarity and UV resistance but is more prone to scratches and impact damage, reducing its durability under harsh conditions. Polycarbonate's high tensile strength and flexibility contribute to its long-lasting performance in environments requiring enhanced safety and impact protection.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance but has slightly lower optical clarity and light transmission, typically around 88-92%, compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), which provides excellent optical clarity with light transmission up to 92-93%. PMMA is favored for applications where high transparency and minimal light distortion are critical, maintaining better color fidelity and haze resistance under prolonged UV exposure. While polycarbonate is more durable against impact and weathering, PMMA's optical properties make it the preferred choice for safety glass when maximum visual clarity and precise light transmission are required.
UV Resistance and Weatherability
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance but tends to yellow and degrade faster under UV exposure compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), which provides excellent clarity and better UV stability for prolonged outdoor use. PMMA maintains its optical properties and resists weathering effectively, making it ideal for safety glass applications in environments with high sun exposure. Both materials benefit from UV-resistant coatings, but PMMA inherently delivers longer-lasting weatherability without significant loss of transparency.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Considerations
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and durability compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), making it more cost-efficient for long-term safety glass applications despite its higher initial price. PMMA is generally less expensive upfront but has lower resistance to cracking and weathering, potentially increasing maintenance and replacement costs over time. Economic considerations favor polycarbonate for environments requiring enhanced safety and longevity, while PMMA suits budget-sensitive projects with moderate durability demands.
Application Suitability in Various Industries
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and optical clarity, making it ideal for safety glass applications in industries like automotive, aerospace, and construction where high durability and shatterproof properties are critical. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) provides excellent UV resistance and weatherability, suited for outdoor displays, signage, and architectural glazing where transparency and scratch resistance are prioritized. Both materials serve distinct industry needs based on mechanical strength, environmental exposure, and cost efficiency requirements.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Safety Glass
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and higher durability, making it ideal for safety glass in high-risk environments like automotive and security applications. Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) provides better optical clarity and scratch resistance, suitable for indoor or low-impact safety glass uses. Selecting the right material depends on balancing impact strength, optical properties, and environmental exposure to ensure optimal safety performance.
Infographic: Polycarbonate vs Polymethyl Methacrylate for Safety Glass
 azmater.com
azmater.com