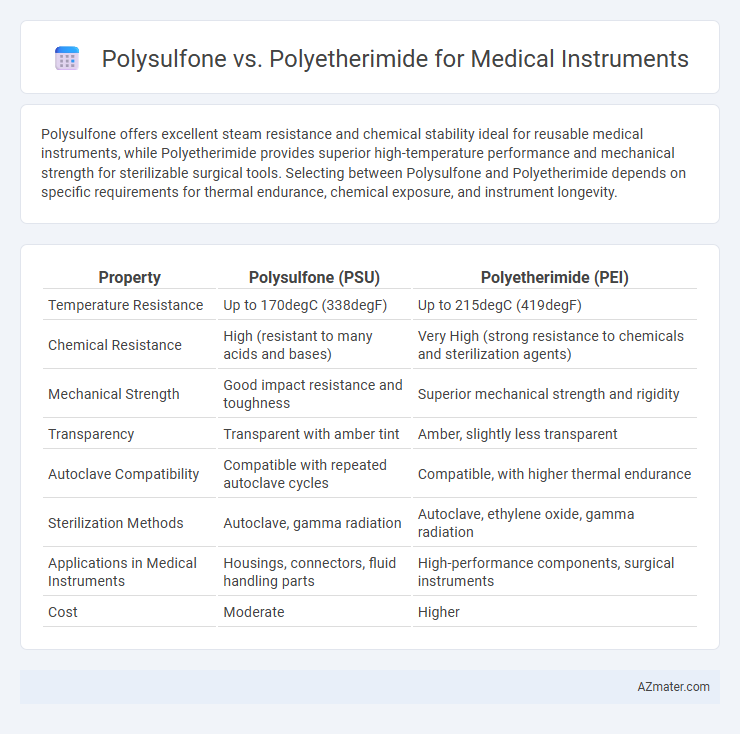
Polysulfone offers excellent steam resistance and chemical stability ideal for reusable medical instruments, while Polyetherimide provides superior high-temperature performance and mechanical strength for sterilizable surgical tools. Selecting between Polysulfone and Polyetherimide depends on specific requirements for thermal endurance, chemical exposure, and instrument longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfone (PSU) | Polyetherimide (PEI) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 170degC (338degF) | Up to 215degC (419degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | High (resistant to many acids and bases) | Very High (strong resistance to chemicals and sterilization agents) |
| Mechanical Strength | Good impact resistance and toughness | Superior mechanical strength and rigidity |
| Transparency | Transparent with amber tint | Amber, slightly less transparent |
| Autoclave Compatibility | Compatible with repeated autoclave cycles | Compatible, with higher thermal endurance |
| Sterilization Methods | Autoclave, gamma radiation | Autoclave, ethylene oxide, gamma radiation |
| Applications in Medical Instruments | Housings, connectors, fluid handling parts | High-performance components, surgical instruments |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
Introduction to Polysulfone and Polyetherimide
Polysulfone (PSU) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent heat resistance, chemical stability, and transparency, making it ideal for medical instruments requiring sterilization and durability. Polyetherimide (PEI) offers superior mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and resistance to hydrolysis, suited for complex medical device components exposed to repeated autoclaving. Both polymers meet stringent FDA biocompatibility standards, supporting their widespread use in medical instrument manufacturing.
Material Composition and Chemical Structure
Polysulfone (PSU) is a thermoplastic polymer characterized by its aromatic backbone containing sulfone groups, lending it exceptional thermal stability and resistance to hydrolysis, making it ideal for medical instruments requiring sterilization. Polyetherimide (PEI) features a rigid molecular structure comprising imide groups and ether linkages, delivering superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance in demanding medical environments. The distinct chemical structures of PSU and PEI govern their performance, with PSU excelling in steam sterilization resistance and PEI offering higher tensile strength and dimensional stability for precise medical applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polysulfone exhibits high impact resistance and excellent dimensional stability under heat, making it suitable for medical instruments requiring durability and sterilization tolerance. Polyetherimide offers superior tensile strength and higher glass transition temperature, enhancing performance in demanding environments with elevated thermal and mechanical stress. Comparing mechanical properties, polyetherimide generally outperforms polysulfone in stiffness and heat deflection temperature, while polysulfone provides better clarity and chemical resistance for certain medical applications.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polysulfone (PSU) and Polyetherimide (PEI) both exhibit excellent thermal stability and heat resistance crucial for medical instruments, with PEI typically offering higher continuous use temperatures up to 170degC compared to PSU's range around 150degC. PEI's superior glass transition temperature (Tg) near 217degC provides enhanced dimensional stability under sterilization conditions such as autoclaving and repeated exposure to high temperatures. PSU maintains good thermal resistance but may experience accelerated degradation under extreme heat, making PEI more suitable for applications demanding prolonged heat exposure and stringent sterilization protocols.
Biocompatibility for Medical Applications
Polysulfone and polyetherimide are both high-performance polymers widely used in medical instruments, with polysulfone recognized for its excellent biocompatibility and long-term stability in sterilization processes such as autoclaving and gamma radiation. Polyetherimide offers superior mechanical strength and heat resistance, but its biocompatibility is also well-established, particularly for devices requiring sustained blood contact or implantable applications. Selecting between these polymers depends on the specific medical application requirements, balancing biocompatibility with thermal and mechanical performance under sterilization conditions.
Sterilization Compatibility and Resistance
Polysulfone (PSU) and Polyetherimide (PEI) both exhibit excellent sterilization compatibility, with PSU maintaining structural integrity under repeated steam autoclaving cycles up to 150degC and PEI offering superior resistance to gamma radiation and ethylene oxide sterilization methods. PSU provides high hydrolytic stability, making it ideal for medical instruments subjected to moist heat sterilization, while PEI's higher glass transition temperature (around 217degC) ensures greater thermal stability and chemical resistance in aggressive sterilization environments. The choice between PSU and PEI hinges on specific sterilization processes, with PSU favored for steam sterilization and PEI preferred for radiation or chemical sterilization requiring enhanced mechanical and thermal endurance.
Transparency and Optical Clarity
Polysulfone exhibits excellent transparency and maintains optical clarity under high-temperature sterilization, making it suitable for reusable medical instruments requiring clear visibility. Polyetherimide offers superior optical clarity with higher heat resistance and chemical durability, ensuring long-term transparency without yellowing or degradation. Both polymers provide reliable transparency, but Polyetherimide's enhanced thermal and chemical stability delivers better optical performance for demanding medical applications.
Processability and Fabrication Methods
Polysulfone (PSU) offers excellent processability with good thermal stability and ease of thermoforming, making it suitable for injection molding and extrusion in medical instrument fabrication. Polyetherimide (PEI) exhibits higher heat resistance and dimensional stability but requires more precise temperature control during processing, often favoring techniques like injection molding and advanced machining. Both polymers allow sterilization compatibility, yet PSU's superior transparency and chemical resistance enhance its use in complex medical device components.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Polysulfone offers a lower initial material cost and easier processing compared to polyetherimide, making it cost-effective for high-volume medical instrument production. Polyetherimide provides superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, which reduces long-term maintenance and replacement expenses despite a higher upfront price. Economic considerations favor polysulfone for budget-sensitive projects, while polyetherimide is ideal for applications requiring durability and extended lifecycle performance.
Application Suitability: Choosing the Right Polymer
Polysulfone (PSU) and Polyetherimide (PEI) both offer excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, making them ideal for medical instruments requiring sterilization and exposure to aggressive cleaning agents. PSU is favored for applications needing good flexural strength and transparency, such as surgical trays and endoscope components, while PEI excels in high-performance devices demanding superior mechanical strength and dimensional stability, like electrical connectors and housings. Selecting the right polymer hinges on balancing PSU's transparency and flexibility with PEI's enhanced heat resistance and rigidity to ensure optimal performance and safety in medical environments.
Infographic: Polysulfone vs Polyetherimide for Medical Instrument
 azmater.com
azmater.com