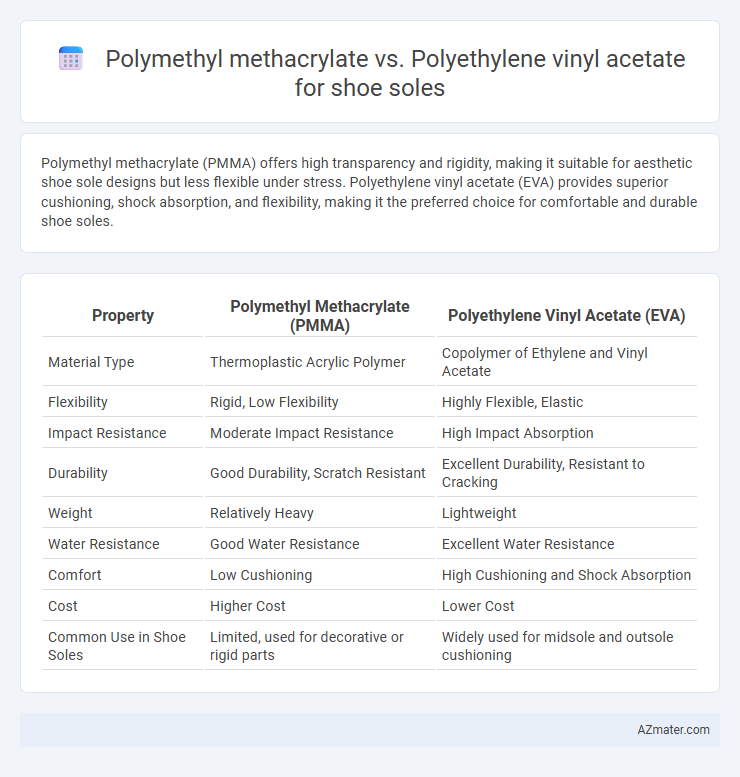
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers high transparency and rigidity, making it suitable for aesthetic shoe sole designs but less flexible under stress. Polyethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) provides superior cushioning, shock absorption, and flexibility, making it the preferred choice for comfortable and durable shoe soles.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) | Polyethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Acrylic Polymer | Copolymer of Ethylene and Vinyl Acetate |
| Flexibility | Rigid, Low Flexibility | Highly Flexible, Elastic |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate Impact Resistance | High Impact Absorption |
| Durability | Good Durability, Scratch Resistant | Excellent Durability, Resistant to Cracking |
| Weight | Relatively Heavy | Lightweight |
| Water Resistance | Good Water Resistance | Excellent Water Resistance |
| Comfort | Low Cushioning | High Cushioning and Shock Absorption |
| Cost | Higher Cost | Lower Cost |
| Common Use in Shoe Soles | Limited, used for decorative or rigid parts | Widely used for midsole and outsole cushioning |
Introduction to Shoe Sole Materials
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and Polyethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) are widely utilized materials in shoe sole manufacturing, each offering distinct properties beneficial for footwear performance. PMMA is known for its rigidity, optical clarity, and resistance to UV light, making it suitable for durable, transparent components in shoe soles. EVA provides exceptional flexibility, lightweight cushioning, and excellent shock absorption, commonly used in athletic and comfort-oriented shoe soles to enhance wearer comfort and reduce foot fatigue.
Overview of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) is a lightweight, transparent thermoplastic commonly used in shoe soles for its excellent durability and high impact resistance. It offers superior abrasion resistance and maintains stability under various environmental conditions, making it ideal for long-lasting footwear. PMMA's rigidity and clarity distinguish it from more flexible materials like Polyethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), often resulting in a firmer sole structure.
Overview of Polyethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA)
Polyethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is a lightweight, flexible, and shock-absorbing material widely used in shoe soles for enhanced comfort and durability. Compared to Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), EVA offers superior cushioning and resilience, making it ideal for athletic and casual footwear. Its excellent compression set resistance and water-repellent properties contribute to long-lasting performance in various environmental conditions.
Mechanical Properties: PMMA vs EVA
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers high rigidity, excellent scratch resistance, and superior tensile strength, making it durable but less flexible for shoe sole applications. Polyethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) provides exceptional elasticity, lightweight cushioning, and better impact absorption, enhancing comfort and shock resistance in footwear. While PMMA excels in hardness and structural integrity, EVA outperforms in flexibility and resilience crucial for dynamic movements.
Cushioning and Comfort Comparison
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent rigidity and impact resistance but lacks the softness required for prolonged cushioning and comfort in shoe soles. Polyethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) provides superior flexibility and shock absorption, enhancing foot cushioning and long-term comfort during extended wear. EVA's lightweight and elastic properties make it the preferred material for shoe soles needing optimal cushioning performance.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers higher durability and superior wear resistance compared to Polyethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) in shoe soles, making it ideal for applications requiring long-lasting performance. PMMA's rigid structure provides excellent abrasion resistance and maintains its integrity under frequent mechanical stress. In contrast, EVA is softer and more flexible but tends to wear down faster, reducing its lifespan under heavy or prolonged use.
Flexibility and Lightweight Features
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers moderate flexibility but excels in rigidity and transparency, making it less ideal for flexible shoe soles compared to polyethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), which provides superior elasticity and cushioning. EVA is renowned for its lightweight properties and excellent shock absorption, enhancing comfort and flexibility in footwear applications. The choice between PMMA and EVA significantly impacts the shoe sole's flexibility, with EVA preferred for lightweight, flexible, and durable soles.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers higher transparency and rigidity in shoe soles but comes with increased material and processing costs compared to Polyethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), which is favored for its flexibility and cost-efficiency in mass production. EVA's lower melting point enables simpler mold fabrication and faster cycle times, reducing manufacturing expenses significantly. Cost analysis must also consider PMMA's durability and aesthetic appeal against EVA's lightweight comfort and affordability in large-scale footwear manufacturing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and Polyethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability in shoe sole applications. PMMA, derived from petrochemicals, has limited biodegradability and produces microplastics, contributing to long-term ecological concerns, whereas EVA offers better recyclability and lower carbon footprint due to its partial bio-based formulations. The choice between PMMA and EVA for shoe soles hinges on prioritizing durability versus eco-friendly disposal, with EVA emerging as the more sustainable option in eco-conscious footwear design.
Choosing the Right Material for Shoe Soles
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent rigidity, transparency, and resistance to UV degradation, making it suitable for stylish shoe soles where durability and appearance are priorities. Polyethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) provides superior flexibility, lightweight cushioning, and shock absorption, ideal for athletic and comfort-focused footwear. Selecting the right material depends on the balance between desired sole stiffness, impact resistance, and wearer comfort requirements.
Infographic: Polymethyl methacrylate vs Polyethylene vinyl acetate for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com