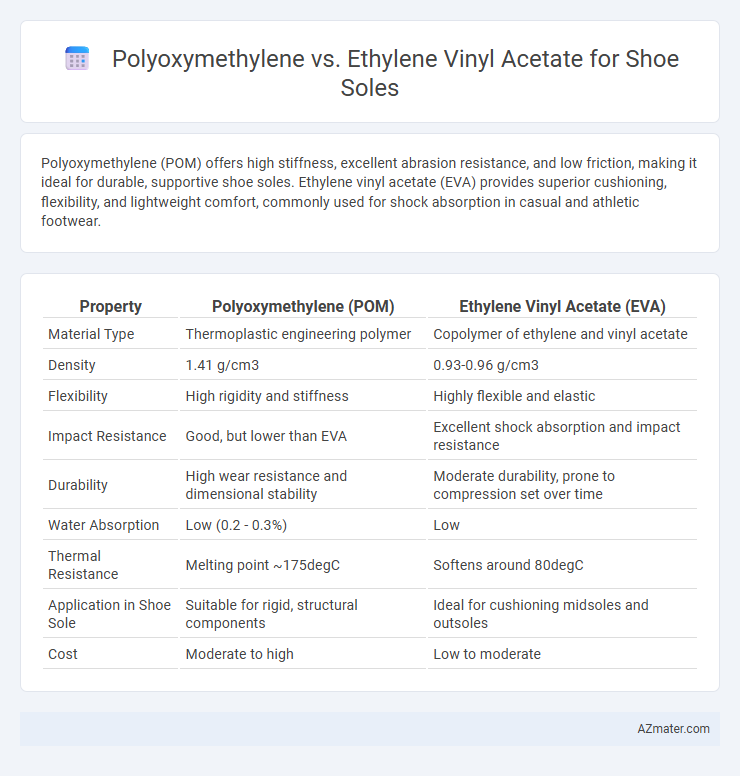
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high stiffness, excellent abrasion resistance, and low friction, making it ideal for durable, supportive shoe soles. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) provides superior cushioning, flexibility, and lightweight comfort, commonly used for shock absorption in casual and athletic footwear.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyoxymethylene (POM) | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic engineering polymer | Copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate |
| Density | 1.41 g/cm3 | 0.93-0.96 g/cm3 |
| Flexibility | High rigidity and stiffness | Highly flexible and elastic |
| Impact Resistance | Good, but lower than EVA | Excellent shock absorption and impact resistance |
| Durability | High wear resistance and dimensional stability | Moderate durability, prone to compression set over time |
| Water Absorption | Low (0.2 - 0.3%) | Low |
| Thermal Resistance | Melting point ~175degC | Softens around 80degC |
| Application in Shoe Sole | Suitable for rigid, structural components | Ideal for cushioning midsoles and outsoles |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
Introduction to Polyoxymethylene and Ethylene Vinyl Acetate
Polyoxymethylene (POM) is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic known for its excellent dimensional stability, low friction, and high mechanical strength, making it suitable for durable shoe soles requiring rigidity and wear resistance. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is a lightweight, flexible polymer characterized by its superior cushioning, shock absorption, and elasticity, commonly used in athletic shoe soles for enhanced comfort and flexibility. The distinct material properties of POM and EVA align with different performance needs, with POM optimized for structural durability and EVA for impact mitigation in footwear applications.
Material Composition and Structure Comparison
Polyoxymethylene (POM) is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic characterized by a crystalline structure with excellent stiffness, low friction, and high dimensional stability, making it suitable for durable shoe sole applications requiring rigidity and wear resistance. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is a copolymer composed of ethylene and vinyl acetate units, featuring an amorphous, foam-like structure that provides lightweight cushioning, flexibility, and shock absorption in midsoles and outsoles. The crystalline, dense molecular arrangement of POM contrasts with the soft, porous structure of EVA, directly influencing their mechanical properties and suitability for different shoe sole performance demands.
Mechanical Properties: Strength, Flexibility, and Durability
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior mechanical strength and rigidity, making it highly resistant to wear and deformation in shoe soles, ideal for high-performance footwear requiring durability. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) excels in flexibility and cushioning, providing excellent shock absorption and comfort but with lower tensile strength compared to POM. EVA's enhanced elasticity supports prolonged flexibility, while POM's durability ensures long-term structural integrity under mechanical stress.
Weight and Density Differences
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits a higher density around 1.41 g/cm3 compared to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA), which typically ranges from 0.93 to 0.96 g/cm3, making POM denser and consequently heavier for shoe sole applications. This density difference directly impacts the overall weight of the footwear, with EVA offering a lighter and more flexible sole suitable for comfort and athletic performance. Choosing between POM and EVA depends on the balance between durability requirements and weight considerations in the shoe design.
Comfort and Cushioning in Shoe Soles
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high rigidity and durability but provides limited cushioning, making it less comfortable for prolonged wear in shoe soles. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) excels in comfort and cushioning due to its lightweight, flexible, and shock-absorbing properties, which reduce foot fatigue and enhance overall comfort. EVA is widely preferred in athletic and casual footwear for its superior energy return and adaptability to foot movements.
Wear Resistance and Lifespan
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior wear resistance and a longer lifespan compared to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) when used for shoe soles due to its high mechanical strength and low friction properties. EVA provides excellent cushioning and flexibility but tends to wear out faster under high abrasion conditions, reducing its durability. POM's rigid molecular structure enhances its resistance to deformation and abrasion, making it ideal for footwear requiring extended durability and performance.
Manufacturing Process and Cost Implications
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high dimensional stability and wear resistance in shoe sole manufacturing, utilizing injection molding processes that require precise temperature control and tooling investment, resulting in higher upfront costs. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is processed through compression or injection molding with lower temperature requirements, enabling faster cycle times and reduced energy consumption, which translates to lower manufacturing costs. EVA's cost-effectiveness and ease of processing make it suitable for mass production, whereas POM's durability justifies its higher production expenses in premium footwear applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyoxymethylene (POM) and Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability for shoe soles. POM is a thermoplastic polymer with higher durability and recyclability but relies on fossil fuel-derived raw materials, resulting in substantial carbon emissions. EVA, while less durable and harder to recycle, often contains bio-based ethylene components and is favored for its lower energy consumption during production, contributing to a reduced overall environmental footprint.
Suitability for Different Types of Footwear
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high stiffness, durability, and excellent wear resistance, making it suitable for rigid footwear like formal shoes and work boots that require structural support. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) provides superior cushioning, flexibility, and lightweight comfort, ideal for athletic shoes, casual footwear, and running shoes demanding shock absorption and flexibility. The choice between POM and EVA depends on the required balance of firmness versus comfort and the specific performance needs of different shoe types.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Best Material for Shoe Soles
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior mechanical strength, excellent wear resistance, and dimensional stability, making it ideal for durable shoe soles requiring rigidity and longevity. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) provides lightweight flexibility, high cushioning, and shock absorption, favoring comfort-focused footwear with enhanced energy return. Selecting between POM and EVA depends on the specific shoe sole application, prioritizing either robust structural support with POM or adaptive comfort and flexibility with EVA.
Infographic: Polyoxymethylene vs Ethylene vinyl acetate for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com