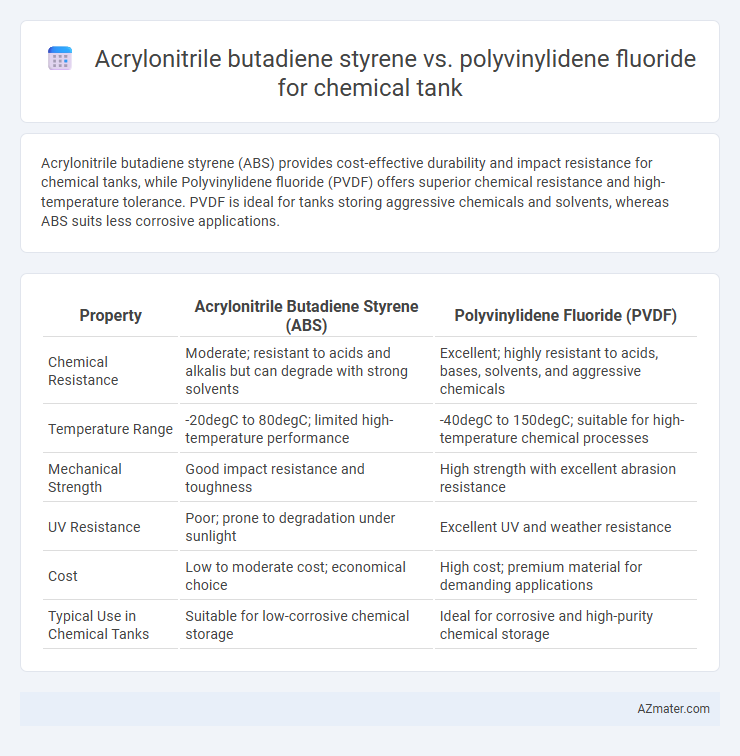
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides cost-effective durability and impact resistance for chemical tanks, while Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and high-temperature tolerance. PVDF is ideal for tanks storing aggressive chemicals and solvents, whereas ABS suits less corrosive applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate; resistant to acids and alkalis but can degrade with strong solvents | Excellent; highly resistant to acids, bases, solvents, and aggressive chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -20degC to 80degC; limited high-temperature performance | -40degC to 150degC; suitable for high-temperature chemical processes |
| Mechanical Strength | Good impact resistance and toughness | High strength with excellent abrasion resistance |
| UV Resistance | Poor; prone to degradation under sunlight | Excellent UV and weather resistance |
| Cost | Low to moderate cost; economical choice | High cost; premium material for demanding applications |
| Typical Use in Chemical Tanks | Suitable for low-corrosive chemical storage | Ideal for corrosive and high-purity chemical storage |
Introduction: ABS vs PVDF for Chemical Tank Applications
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers cost-effective durability and impact resistance, making it suitable for chemical tanks exposed to moderate corrosive environments. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) provides superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, ideal for tanks handling aggressive chemicals and high-temperature fluids. Selection between ABS and PVDF depends on specific chemical compatibility, temperature range, and budget considerations in chemical storage applications.
Chemical Resistance: Comparing ABS and PVDF
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) when used for chemical tanks, effectively withstanding strong acids, bases, and organic solvents without degradation. ABS, while durable and impact-resistant, tends to degrade or swell in the presence of aggressive chemicals, limiting its use in highly corrosive environments. PVDF's exceptional resistance to chemicals such as hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, and solvents makes it the preferred choice for long-term chemical storage applications.
Temperature Tolerance: Performance Under Various Conditions
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate temperature tolerance, performing well between -20degC and 80degC but degrading rapidly above this range, which limits its use in high-temperature chemical tanks. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) demonstrates superior thermal stability, maintaining structural integrity and chemical resistance up to 150degC, making it ideal for tanks exposed to elevated temperatures or aggressive chemical environments. PVDF's high melting point and UV resistance contribute to its reliability under various thermal conditions, surpassing ABS in long-term durability for chemical storage.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent mechanical strength with high impact resistance and moderate tensile strength, making it suitable for chemical tanks requiring toughness under physical stress. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) provides superior durability through exceptional chemical resistance, UV stability, and mechanical strength, particularly in harsh chemical environments where long-term performance is critical. PVDF outperforms ABS in resistance to corrosive chemicals and maintains structural integrity over extended periods, making it the preferred choice for highly demanding chemical storage applications.
Cost Analysis: ABS vs PVDF
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers a significantly lower initial cost compared to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), making it a budget-friendly option for chemical tanks with less aggressive chemical exposure. PVDF, despite its higher upfront price, provides superior chemical resistance and durability, reducing long-term maintenance and replacement costs in harsh environments. Cost analysis favors ABS for cost-sensitive applications with mild chemicals, while PVDF ensures cost-effectiveness through longevity and minimal downtime in highly corrosive conditions.
Fabrication and Installation Considerations
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers easier fabrication due to its lower melting point and excellent weldability, making it suitable for complex chemical tank designs requiring precise fittings. In contrast, Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) demands higher processing temperatures and specialized welding techniques to maintain chemical resistance and mechanical integrity, often increasing installation time and costs. The choice between ABS and PVDF significantly impacts fabrication workflows and installation efficiency based on the chemical tank's operational environment and required durability.
Maintenance and Longevity
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate chemical resistance and requires routine maintenance to prevent degradation from aggressive chemicals, primarily in acidic environments, whereas Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior chemical inertness, significantly reducing maintenance frequency. PVDF's high resistance to UV, oxidation, and many corrosive substances extends tank longevity beyond ABS, making it ideal for long-term chemical storage applications. The durability of PVDF ensures fewer repairs and replacements, thus optimizing lifecycle costs compared to ABS.
Safety and Environmental Impacts
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate chemical resistance and impact strength ideal for general chemical tanks but can release toxic fumes like styrene and acrylonitrile during combustion, posing health hazards. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior chemical resistance, especially to acids and solvents, along with excellent UV stability and low permeability, enhancing environmental safety by reducing chemical leakage risks. PVDF's inert nature and recyclability contribute to a lower environmental footprint compared to ABS, which has limited chemical durability and potential for harmful emissions during degradation.
Industry-Specific Recommendations
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance, ease of fabrication, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for light-duty chemical tanks used with non-corrosive substances in industries like water treatment and agriculture. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) excels in chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and durability, preferred for aggressive chemical storage in pharmaceutical, semiconductor, and chemical manufacturing sectors. Industry recommendations favor PVDF for tanks handling strong acids, bases, and solvents, while ABS suits applications with milder chemical exposure and budget constraints.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Material for Chemical Tanks
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for chemical tanks exposed to mechanical stress but limited chemical aggressiveness. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) provides superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, ideal for aggressive chemicals and high-temperature environments. Selecting the best material depends on the chemical compatibility, temperature conditions, and budget constraints, with PVDF preferred for harsh and corrosive substances, while ABS fits less demanding applications.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polyvinylidene fluoride for Chemical tank
 azmater.com
azmater.com