Ocean-bound plastic shampoo bottles reduce marine pollution by repurposing waste collected near coastlines, while high-density polyethylene (HDPE) offers durability and recyclability with a lower environmental impact during production. Choosing ocean-bound plastic supports circular economy efforts, whereas HDPE provides consistent performance and widespread recycling infrastructure.
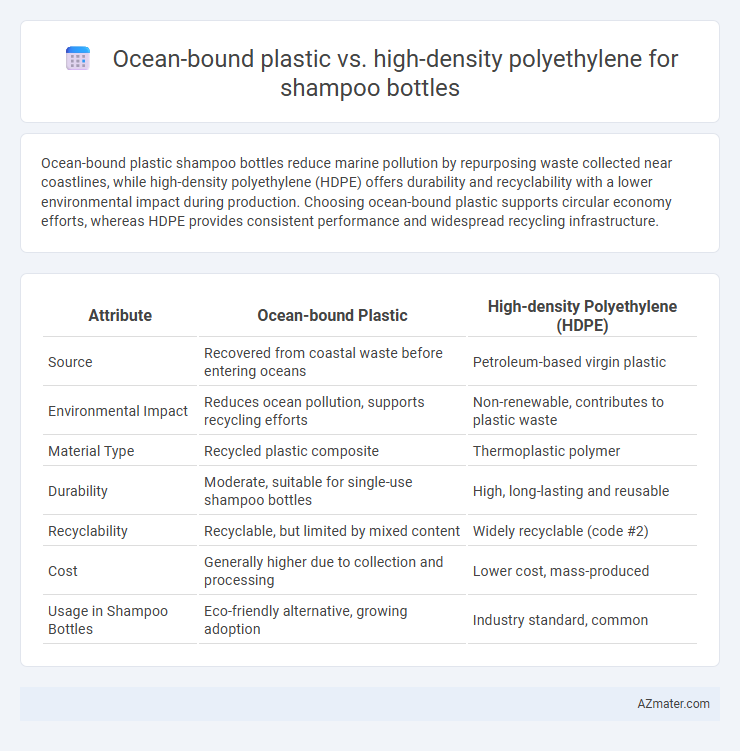
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Ocean-bound Plastic | High-density Polyethylene (HDPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Recovered from coastal waste before entering oceans | Petroleum-based virgin plastic |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces ocean pollution, supports recycling efforts | Non-renewable, contributes to plastic waste |
| Material Type | Recycled plastic composite | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Durability | Moderate, suitable for single-use shampoo bottles | High, long-lasting and reusable |
| Recyclability | Recyclable, but limited by mixed content | Widely recyclable (code #2) |
| Cost | Generally higher due to collection and processing | Lower cost, mass-produced |
| Usage in Shampoo Bottles | Eco-friendly alternative, growing adoption | Industry standard, common |
Introduction: The Environmental Impact of Shampoo Bottle Materials
Ocean-bound plastic in shampoo bottles reduces marine pollution by repurposing waste destined for oceans, significantly lowering environmental harm compared to virgin High-density Polyethylene (HDPE). HDPE, although recyclable and widely used for durability, relies on fossil fuels and contributes to greenhouse gas emissions during production. Prioritizing ocean-bound plastic supports circular economy initiatives and mitigates landfill overflow while maintaining the functional integrity required for shampoo packaging.
Understanding Ocean-Bound Plastic: Definition and Sourcing
Ocean-bound plastic refers to waste material collected within 50 kilometers of coastlines, preventing it from polluting marine environments and is sourced primarily from coastal communities vulnerable to inadequate waste management systems. High-density polyethylene (HDPE), a widely used plastic for shampoo bottles, is typically derived from virgin or recycled materials but lacks the specific environmental focus of ocean-bound plastic sourcing. Understanding ocean-bound plastic involves recognizing its role in mitigating ocean pollution by intercepting plastic waste before it enters waterways, making it a sustainable raw material alternative for packaging like shampoo bottles.
Overview of High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE): Properties and Uses
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is a versatile thermoplastic polymer known for its strength, durability, and resistance to impact and moisture, making it an ideal material for shampoo bottles. HDPE's chemical inertness and ability to withstand varying temperatures ensure effective protection and preservation of shampoo products. Its recyclability and widespread availability contribute to its dominance in packaging, contrasting with ocean-bound plastic, which emphasizes environmental remediation by repurposing waste collected near coastlines.
Sustainability Comparison: Ocean-Bound Plastic vs HDPE
Ocean-bound plastic used for shampoo bottles reduces marine pollution by repurposing waste collected near shorelines, significantly lowering environmental impact compared to virgin High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE). While HDPE offers durability and recyclability, ocean-bound plastic contributes to a circular economy by diverting plastic debris from oceans and minimizing reliance on fossil fuels. Sustainable packaging decisions favor ocean-bound plastic for its role in enhancing marine ecosystem health and promoting responsible plastic waste management.
Recycling Processes: Ocean-Bound Plastic vs HDPE
Ocean-bound plastic undergoes thorough cleaning and sterilization to remove salt, sand, and organic contaminants before being processed into flakes or pellets for recycling, ensuring minimal environmental pollutants remain. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is mechanically recycled through shredding, washing, melting, and remolding, benefiting from its uniform polymer structure that allows for efficient recycling with high material recovery rates. While HDPE recycling infrastructure is well-established and yields consistent quality for shampoo bottles, ocean-bound plastic recycling requires more intensive preprocessing to address contamination but contributes significantly to reducing marine pollution by repurposing waste collected near waterways.
Durability and Performance in Shampoo Packaging
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) offers superior durability and chemical resistance compared to ocean-bound plastic, making it a preferred choice for shampoo bottles that require long-term storage and repeated handling. Ocean-bound plastic, derived from recycled waste close to waterways, provides an eco-friendly alternative but may have variable quality and mechanical strength, potentially impacting shelf life and product protection. HDPE's consistent performance ensures optimal containment of shampoo ingredients, while ocean-bound plastic contributes to sustainability goals with some compromise on durability.
Consumer Perception and Market Trends
Consumers increasingly favor shampoo bottles made from ocean-bound plastic due to growing environmental awareness and demand for sustainable packaging. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) remains popular for its durability and recyclability, but brands incorporating ocean-bound plastic capitalize on the eco-friendly narrative, enhancing brand loyalty and market differentiation. Market trends indicate a rising shift towards eco-conscious materials, with ocean-bound plastic gaining traction as a symbol of corporate responsibility and circular economy principles.
Cost Analysis: Production and Supply Chain Considerations
Ocean-bound plastic generally incurs higher production costs due to the complex collection, cleaning, and sorting processes required to ensure material quality, whereas high-density polyethylene (HDPE) benefits from established, large-scale manufacturing systems that reduce unit costs. The supply chain for ocean-bound plastic involves additional logistics expenses linked to sourcing from coastal collection points, impacting overall cost-effectiveness compared to the more streamlined, globally integrated HDPE supply networks. However, ocean-bound plastic presents potential savings through waste diversion incentives and sustainability branding, which may offset higher upfront costs in long-term supply chain strategies for shampoo bottle production.
Regulatory and Certification Standards
Ocean-bound plastic used in shampoo bottles must comply with environmental certifications such as the Global Recycled Standard (GRS) and the Ocean Bound Plastic Certification to ensure traceability and sustainable sourcing. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) bottles are regulated under FDA Title 21 CFR for food-grade and cosmetic packaging safety, requiring compliance with migration limits and material purity standards. Both materials must adhere to regional regulations like EU's REACH and the US Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) to meet safety and environmental impact criteria in personal care product packaging.
Future Directions: Innovations in Sustainable Shampoo Bottles
Future innovations in sustainable shampoo bottles emphasize the use of ocean-bound plastic and high-density polyethylene (HDPE) with enhanced recyclability and eco-friendly additives. Advances in bio-based HDPE and improved sorting technologies support circular economy goals by reducing carbon footprint and ocean pollution. Emerging biodegradable coatings and composite materials offer promising solutions for durable, yet environmentally responsible shampoo packaging.
Infographic: Ocean-bound plastic vs High-density Polyethylene for Shampoo bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com