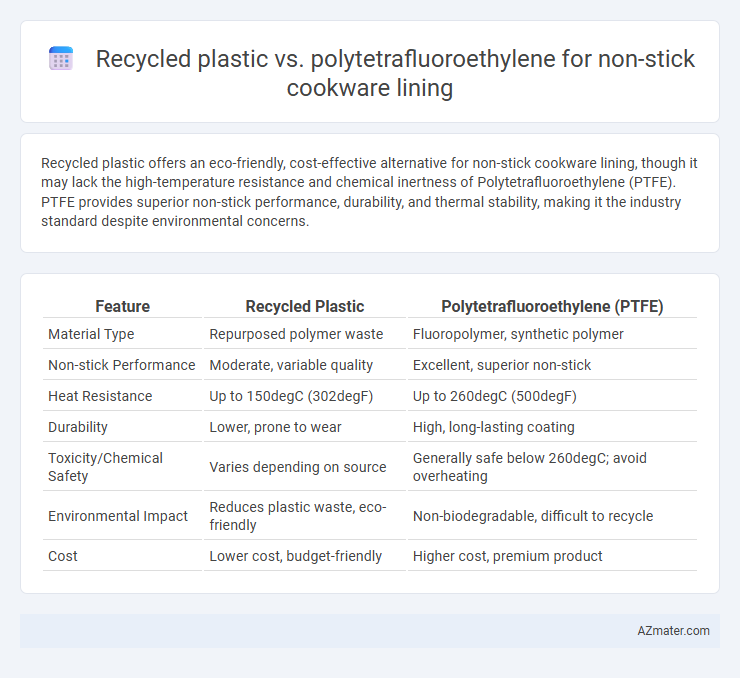
Recycled plastic offers an eco-friendly, cost-effective alternative for non-stick cookware lining, though it may lack the high-temperature resistance and chemical inertness of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). PTFE provides superior non-stick performance, durability, and thermal stability, making it the industry standard despite environmental concerns.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled Plastic | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Repurposed polymer waste | Fluoropolymer, synthetic polymer |
| Non-stick Performance | Moderate, variable quality | Excellent, superior non-stick |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 150degC (302degF) | Up to 260degC (500degF) |
| Durability | Lower, prone to wear | High, long-lasting coating |
| Toxicity/Chemical Safety | Varies depending on source | Generally safe below 260degC; avoid overheating |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces plastic waste, eco-friendly | Non-biodegradable, difficult to recycle |
| Cost | Lower cost, budget-friendly | Higher cost, premium product |
Introduction to Non-Stick Cookware Linings
Non-stick cookware linings commonly utilize materials such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and recycled plastics to enhance cooking convenience by preventing food adhesion. PTFE offers superior heat resistance and chemical stability, making it a preferred choice for durability and low friction during cooking. Recycled plastic linings provide an eco-friendly alternative but often lack the thermal resilience and non-stick efficiency of PTFE, impacting performance and longevity.
Overview of Recycled Plastic as Cookware Lining
Recycled plastic as cookware lining offers an eco-friendly alternative by repurposing waste materials to reduce environmental impact and conserve resources. This material provides effective non-stick properties, though it may have lower heat resistance and durability compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon. Innovations in recycled plastic composites aim to enhance thermal stability and safety, making them increasingly viable for sustainable non-stick cookware applications.
What is Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)?
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer known for its exceptional non-stick properties, chemical resistance, and high melting point, commonly used in cookware linings. Unlike recycled plastic, PTFE provides a durable, heat-resistant coating that prevents food from sticking and facilitates easy cleaning. Its molecular structure creates a smooth, low-friction surface, making it a preferred choice for high-performance non-stick cookware.
Manufacturing Process: Recycled Plastic vs PTFE
Recycled plastic non-stick coatings undergo a melting and reforming process that reduces plastic waste by repurposing existing materials, emphasizing eco-friendly manufacturing with lower energy consumption compared to virgin polymers. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) coatings are created through polymerization of tetrafluoroethylene monomers and require precise high-temperature sintering and curing to achieve the desired non-stick properties, involving energy-intensive chemical processes and strict controls to ensure coating durability. The manufacturing of recycled plastic linings supports sustainability goals with reduced carbon footprint, whereas PTFE production prioritizes high-performance material characteristics through complex synthetic pathways.
Non-Stick Performance Comparison
Recycled plastic liners in non-stick cookware often offer variable non-stick performance due to inconsistencies in material composition and durability, which can lead to faster wear and reduced coating effectiveness. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides superior non-stick properties, featuring high resistance to sticking and excellent durability under typical cooking temperatures up to 260degC (500degF). PTFE-coated surfaces maintain easy food release and ease of cleaning longer than recycled plastic alternatives, making PTFE the preferred choice for reliable, high-performance non-stick cookware lining.
Health and Safety Considerations
Recycled plastic cookware lining raises concerns due to potential contaminants and chemical leaching, which can pose health risks when exposed to high cooking temperatures. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, is valued for its non-stick properties and chemical stability but can release toxic fumes if overheated above 260degC (500degF), posing respiratory hazards. Choosing PTFE coatings with proper temperature management or exploring high-quality, food-safe recycled plastics with verified non-toxicity is crucial for ensuring safe cookware use.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Recycled plastic used in non-stick cookware lining reduces landfill waste and lowers carbon emissions by repurposing existing materials, yet often lacks the high heat resistance and durability of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). PTFE, while offering excellent non-stick performance and longevity, poses significant environmental concerns due to its production process involving perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), a persistent pollutant linked to ecological and health risks. Sustainable alternatives increasingly prioritize recycled plastics with improved heat tolerance or bio-based coatings to mitigate the ecological footprint associated with traditional PTFE linings.
Durability and Longevity of Each Material
Recycled plastic cookware linings typically show lower durability compared to Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), as they are prone to scratching and degradation under high heat. PTFE is renowned for its exceptional heat resistance and chemical stability, enabling non-stick surfaces to maintain integrity and functionality for years without peeling or chipping. The longevity of PTFE significantly surpasses recycled plastics, making it a preferred material in premium non-stick cookware for sustained performance.
Cost Analysis: Recycled Plastic vs PTFE
Recycled plastic offers a cost-effective alternative to Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) for non-stick cookware lining, with production expenses significantly lower due to simpler manufacturing processes and reduced raw material costs. PTFE, known for its superior non-stick properties and durability, commands a higher price point driven by complex chemical synthesis and stricter quality controls. Evaluating long-term cost efficiency, recycled plastic may require more frequent replacement, whereas PTFE's longevity can offset its initial higher investment.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Consumer preferences show a growing demand for eco-friendly non-stick cookware with recycled plastic gaining traction due to its sustainable appeal, whereas polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) remains popular for its superior non-stick performance and durability. Market trends indicate an increasing shift toward recycled plastic linings driven by environmental concerns and regulatory pressures, while PTFE coatings continue to dominate premium segments for their high heat resistance and ease of cleaning. Brands leveraging recycled materials emphasize transparency and health safety to capture environmentally conscious consumers, whereas PTFE products highlight long-lasting, efficient cooking experiences.
Infographic: Recycled plastic vs Polytetrafluoroethylene for Non-stick cookware lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com