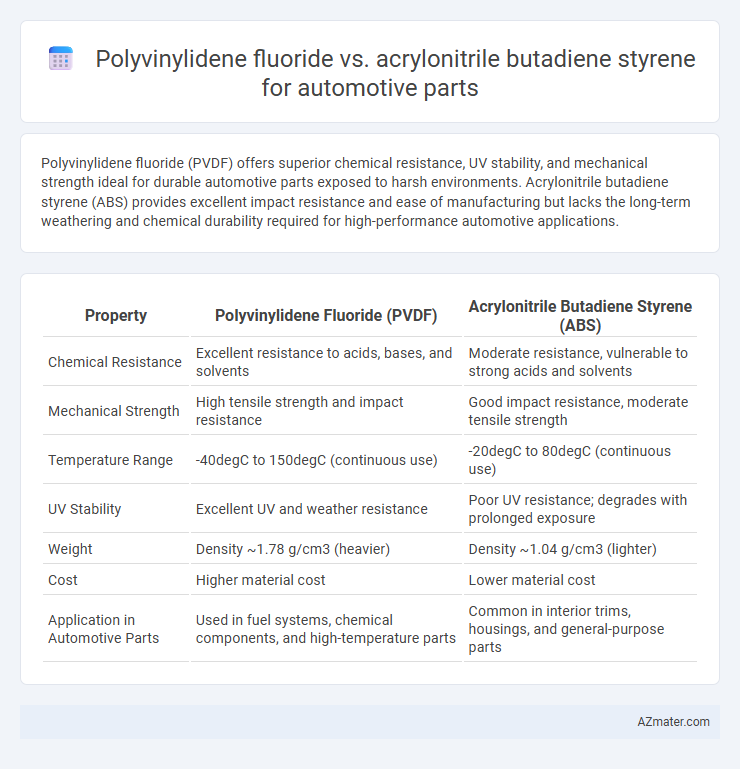
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance, UV stability, and mechanical strength ideal for durable automotive parts exposed to harsh environments. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides excellent impact resistance and ease of manufacturing but lacks the long-term weathering and chemical durability required for high-performance automotive applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids, bases, and solvents | Moderate resistance, vulnerable to strong acids and solvents |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and impact resistance | Good impact resistance, moderate tensile strength |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC (continuous use) | -20degC to 80degC (continuous use) |
| UV Stability | Excellent UV and weather resistance | Poor UV resistance; degrades with prolonged exposure |
| Weight | Density ~1.78 g/cm3 (heavier) | Density ~1.04 g/cm3 (lighter) |
| Cost | Higher material cost | Lower material cost |
| Application in Automotive Parts | Used in fuel systems, chemical components, and high-temperature parts | Common in interior trims, housings, and general-purpose parts |
Introduction to Automotive Plastics
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) are critical polymers used in automotive parts due to their distinct properties. PVDF offers superior chemical resistance, UV stability, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for exterior components exposed to harsh environments. ABS is valued for its impact resistance, ease of molding, and cost-effectiveness, often utilized for interior trim and non-structural parts in automotive manufacturing.
Overview of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is a high-performance fluoropolymer known for its exceptional chemical resistance, thermal stability up to 150degC, and excellent mechanical properties, making it ideal for demanding automotive parts exposed to harsh environments. PVDF offers outstanding UV resistance and low permeability to gases and liquids, which enhances durability and longevity in fuel system components and sensor housings. Compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), PVDF delivers superior corrosion resistance and dimensional stability, essential for automotive applications requiring both robustness and precision.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer renowned for its impact resistance, toughness, and ease of fabrication, making it a preferred material for automotive parts such as interior panels, dashboards, and protective housings. Its chemical structure, combining acrylonitrile for chemical resistance, butadiene for toughness, and styrene for rigidity, offers a balanced performance in varying temperature and environmental conditions commonly encountered in automotive applications. Compared to Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF), ABS provides superior mechanical properties and cost-effectiveness while sacrificing some chemical and UV resistance, which can be critical factors depending on the specific automotive component requirements.
Mechanical Properties: PVDF vs ABS
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and higher tensile strength compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), making it ideal for automotive parts exposed to harsh environments. PVDF exhibits excellent impact resistance and maintains mechanical stability at elevated temperatures up to 150degC, whereas ABS typically softens above 100degC and has lower chemical durability. The fatigue resistance and UV stability of PVDF surpass ABS, supporting longer service life in demanding automotive applications.
Chemical Resistance in Automotive Environments
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior chemical resistance in automotive environments compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), particularly against fuels, oils, and solvents commonly encountered in engines and fuel systems. PVDF maintains mechanical integrity and resists degradation under exposure to automotive fluids, making it ideal for fuel lines, seals, and components requiring long-term chemical stability. ABS, while offering good impact resistance, tends to degrade faster when exposed to aggressive chemicals, limiting its use in high-exposure applications within vehicles.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior thermal stability with continuous service temperatures up to 150degC, making it highly suitable for automotive parts exposed to high heat. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), by contrast, has a lower heat resistance, typically withstanding temperatures around 80-100degC before deformation occurs. PVDF's exceptional resistance to thermal degradation ensures enhanced durability and performance in engine components and under-the-hood applications compared to ABS.
Weight and Design Flexibility
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and durability but generally has a higher density compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), impacting the overall weight of automotive parts. ABS provides greater design flexibility due to its excellent impact resistance and ease of molding, making it ideal for complex shapes and lightweight components. Choosing between PVDF and ABS depends on balancing the need for lightweight construction with specific performance requirements in automotive applications.
Cost Comparison for Automotive Manufacturing
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) generally incurs higher material and processing costs compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) due to its superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, which are critical in demanding automotive applications. ABS offers a more cost-effective solution for automotive parts manufacturing, with lower raw material expenses and easier moldability, enhancing production efficiency. The choice between PVDF and ABS heavily depends on the specific performance requirements and budget constraints within the automotive manufacturing process.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and durability, making it more environmentally favorable due to its longer lifespan in automotive parts, thereby reducing waste generation. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is widely recycled and has established recycling streams, but its shorter service life contributes to more frequent replacement and higher environmental burden. The choice between PVDF and ABS significantly impacts automotive sustainability strategies, with PVDF enhancing durability and ABS facilitating recyclability.
Applications and Case Studies in Automotives
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is favored in automotive applications requiring high chemical resistance, UV stability, and exceptional durability for fuel system components, wire insulation, and under-the-hood parts. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance, aesthetic surface finish, and ease of processing, making it ideal for interior trims, instrument panels, and bumper covers. Case studies highlight PVDF's superior performance in harsh chemical environments and ABS's cost-effectiveness and versatility in structural and aesthetic automotive parts.
Infographic: Polyvinylidene fluoride vs Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene for Automotive Part
 azmater.com
azmater.com