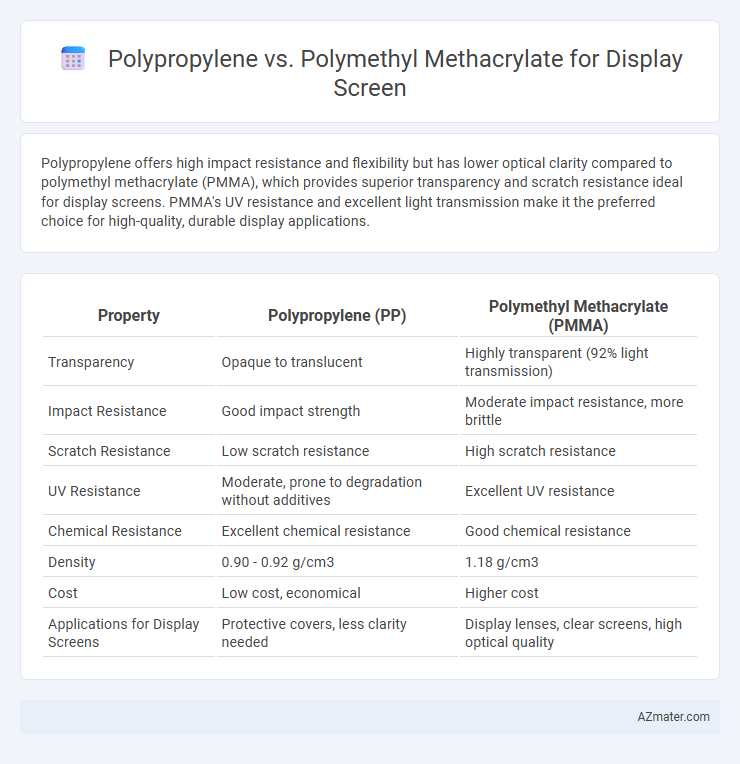
Polypropylene offers high impact resistance and flexibility but has lower optical clarity compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), which provides superior transparency and scratch resistance ideal for display screens. PMMA's UV resistance and excellent light transmission make it the preferred choice for high-quality, durable display applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene (PP) | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | Opaque to translucent | Highly transparent (92% light transmission) |
| Impact Resistance | Good impact strength | Moderate impact resistance, more brittle |
| Scratch Resistance | Low scratch resistance | High scratch resistance |
| UV Resistance | Moderate, prone to degradation without additives | Excellent UV resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent chemical resistance | Good chemical resistance |
| Density | 0.90 - 0.92 g/cm3 | 1.18 g/cm3 |
| Cost | Low cost, economical | Higher cost |
| Applications for Display Screens | Protective covers, less clarity needed | Display lenses, clear screens, high optical quality |
Introduction to Display Screen Materials
Polypropylene and polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) are key materials used in display screen manufacturing due to their distinct optical and mechanical properties. PMMA offers superior clarity and high light transmittance of approximately 92%, making it ideal for high-resolution displays that demand crisp image quality. Polypropylene provides enhanced impact resistance and chemical stability, suited for durable and flexible screen covers in portable electronic devices.
Overview of Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its excellent chemical resistance, low density (approximately 0.90 g/cm3), and high impact strength, making it a cost-effective material for display screens. It offers good fatigue resistance and flexibility but has lower optical clarity compared to Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), with light transmittance typically around 90%. Polypropylene's thermal resistance ranges between 160-170degC, suitable for durable yet lightweight display components where transparency is less critical.
Overview of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), commonly known as acrylic glass, offers superior optical clarity and UV resistance compared to polypropylene, making it a preferred material for high-quality display screens. Its excellent light transmittance of approximately 92% ensures vibrant color reproduction and sharp image quality, crucial for advanced electronic displays. PMMA's inherent rigidity and scratch resistance enhance screen durability, although it is less impact-resistant than polypropylene.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior optical clarity with light transmission rates up to 92%, making it ideal for high-quality display screens requiring sharp and vivid visuals. Polypropylene (PP) provides lower optical clarity and light transmission, typically around 85%, due to its semi-crystalline structure, which can cause slight haze and reduced image sharpness. Choosing PMMA ensures enhanced brightness and color accuracy in display applications, while PP is more suitable for cost-sensitive or impact-resistant solutions.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polypropylene offers high impact resistance and flexibility, making it suitable for displays requiring durability under stress and bending, while polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) provides superior hardness and scratch resistance, ensuring long-lasting clarity and surface protection. PMMA exhibits greater tensile strength (about 70 MPa) compared to polypropylene (around 30 MPa), contributing to its rigidity but reduced flexibility. For applications demanding mechanical strength combined with durability against wear, PMMA is preferred, whereas polypropylene excels in environments where impact resistance and deformation tolerance are critical.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Stability
Polypropylene exhibits superior chemical resistance against acids, bases, and solvents, making it highly durable for display screen applications exposed to harsh environments. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent environmental stability with high resistance to UV radiation and weathering, ensuring long-lasting optical clarity in outdoor or fluctuating conditions. The choice between polypropylene and PMMA depends on application-specific requirements, balancing chemical resistance and environmental durability.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Polypropylene offers a lower cost alternative for display screens compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), making it suitable for budget-sensitive applications. PMMA, while more expensive, provides superior optical clarity and scratch resistance, often justifying its higher price in premium display markets. Availability for polypropylene is more widespread due to its extensive industrial use, whereas PMMA supply can be more limited and subject to higher demand fluctuations.
Ease of Fabrication and Processing
Polypropylene offers excellent ease of fabrication due to its low melting point and high melt flow index, enabling efficient injection molding and extrusion for display screens. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) provides superior optical clarity but requires careful processing at higher temperatures to avoid warping, making fabrication more complex. The choice impacts manufacturing speed and cost, with polypropylene favoring rapid production and PMMA demanding precision in thermal management.
Applications in Display Technology
Polypropylene offers excellent impact resistance and flexibility, making it suitable for protective coatings and lightweight display casings in consumer electronics, while polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) provides superior optical clarity and UV resistance, ideal for high-quality screen covers and transparent panels in LCD and OLED displays. PMMA's rigidity and scratch resistance enhance touchscreen durability and visual performance, whereas polypropylene's chemical resistance supports ruggedized and outdoor display applications. Both polymers contribute uniquely to display technology by balancing durability, transparency, and environmental resistance depending on device requirements.
Choosing the Right Material for Display Screens
Polypropylene offers excellent impact resistance and flexibility for display screen housings, making it ideal for durable and lightweight applications, while polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) provides superior optical clarity and UV resistance essential for high-quality screen covers. PMMA's scratch resistance and translucency support vibrant display visibility, whereas polypropylene excels in thermal stability and chemical resistance, crucial for demanding environments. Selecting between polypropylene and PMMA depends on the priority of optical performance versus mechanical durability in the display screen design.
Infographic: Polypropylene vs Polymethyl methacrylate for Display screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com