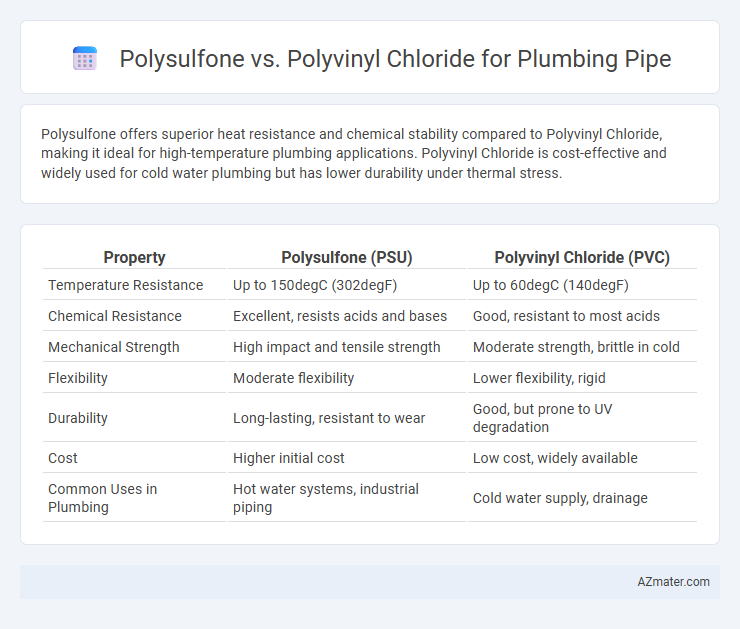
Polysulfone offers superior heat resistance and chemical stability compared to Polyvinyl Chloride, making it ideal for high-temperature plumbing applications. Polyvinyl Chloride is cost-effective and widely used for cold water plumbing but has lower durability under thermal stress.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfone (PSU) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 150degC (302degF) | Up to 60degC (140degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, resists acids and bases | Good, resistant to most acids |
| Mechanical Strength | High impact and tensile strength | Moderate strength, brittle in cold |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | Lower flexibility, rigid |
| Durability | Long-lasting, resistant to wear | Good, but prone to UV degradation |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Low cost, widely available |
| Common Uses in Plumbing | Hot water systems, industrial piping | Cold water supply, drainage |
Introduction to Polysulfone and Polyvinyl Chloride
Polysulfone (PSU) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for demanding plumbing applications requiring durability and longevity. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer characterized by excellent corrosion resistance, ease of installation, and cost-effectiveness, commonly employed in residential and commercial plumbing systems. Both materials offer distinct advantages in terms of chemical durability and mechanical properties, influencing their suitability for specific plumbing environments and pressure conditions.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Polysulfone (PSU) is a high-performance thermoplastic characterized by aromatic rings linked by sulfone (-SO2-) groups, providing excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance in plumbing applications. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), a widely used polymer in plumbing, is composed of vinyl chloride monomers with a linear, semi-rigid structure containing chlorine atoms that impart corrosion resistance but lower thermal tolerance compared to polysulfone. The molecular structure of polysulfone offers superior resistance to hydrolysis and elevated temperatures, while PVC's chlorinated backbone ensures cost-effective durability and chemical resistance suitable for standard water supply systems.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polysulfone exhibits higher mechanical strength and superior impact resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it more suitable for high-pressure plumbing applications. Its tensile strength typically ranges from 55 to 75 MPa, whereas PVC generally measures between 40 and 60 MPa. The enhanced thermal stability of polysulfone also contributes to maintaining mechanical integrity under fluctuating temperatures in plumbing systems.
Thermal Resistance and Temperature Tolerance
Polysulfone pipes exhibit superior thermal resistance and can withstand continuous exposure to temperatures up to 150degC, making them ideal for hot water plumbing applications. In contrast, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes have a lower temperature tolerance, typically up to 60degC, which limits their use in high-temperature environments. The enhanced temperature resilience of polysulfone ensures long-term durability and stability under harsh thermal conditions compared to PVC.
Durability and Longevity
Polysulfone pipes exhibit superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making them more durable in high-temperature and corrosive plumbing environments. PVC pipes tend to degrade under prolonged exposure to UV light and extreme temperatures, which can reduce their lifespan. Polysulfone's resistance to hydrolysis and mechanical stress ensures longer-lasting performance and lower maintenance costs in demanding plumbing applications.
Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
Polysulfone (PSU) exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), maintaining structural integrity in highly acidic and alkaline environments. PVC, while cost-effective and widely used, is prone to chemical degradation from strong solvents and oxidizers, leading to potential pipe failure over time. The high thermal stability and chemical inertness of polysulfone make it ideal for plumbing systems exposed to aggressive chemicals and harsh operating conditions.
Installation and Handling Considerations
Polysulfone pipes offer superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making them suitable for high-temperature plumbing applications, although their higher rigidity requires precise alignment during installation. PVC pipes are lightweight and flexible, facilitating easier cutting and fitting, but demand careful handling to prevent crack formation under stress or UV exposure. Installation of polysulfone systems often involves solvent welding or mechanical joints that withstand extreme conditions, while PVC pipes typically use solvent cement or push-fit connectors allowing for faster, more cost-effective assembly.
Cost Analysis and Economic Factors
Polysulfone pipes typically have a higher initial cost compared to Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) pipes due to their superior heat resistance and durability, making them suitable for specialized plumbing applications. PVC pipes are more economically viable for large-scale projects because of their lower material and installation costs, as well as widespread availability. Long-term maintenance and replacement expenses tend to be lower for polysulfone pipes, potentially offsetting the upfront investment in environments requiring chemical resistance and higher temperatures.
Common Applications in Plumbing
Polysulfone pipes are commonly used in hot water plumbing systems and industrial wastewater applications due to their high heat resistance and chemical stability. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) pipes dominate cold water distribution and irrigation systems because of their affordability, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation. Both materials serve distinct roles in plumbing, with Polysulfone preferred for temperature-sensitive environments and PVC favored for general-purpose water conveyance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polysulfone (PSU) plumbing pipes exhibit superior environmental performance compared to Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), as PSU is more chemically stable and resists degradation, reducing microplastic pollution. PVC production and disposal release hazardous chlorine-based compounds such as dioxins, posing significant environmental and health risks. PSU's higher durability and recyclability contribute to greater sustainability by extending pipe lifespan and minimizing landfill waste.
Infographic: Polysulfone vs Polyvinyl Chloride for Plumbing Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com