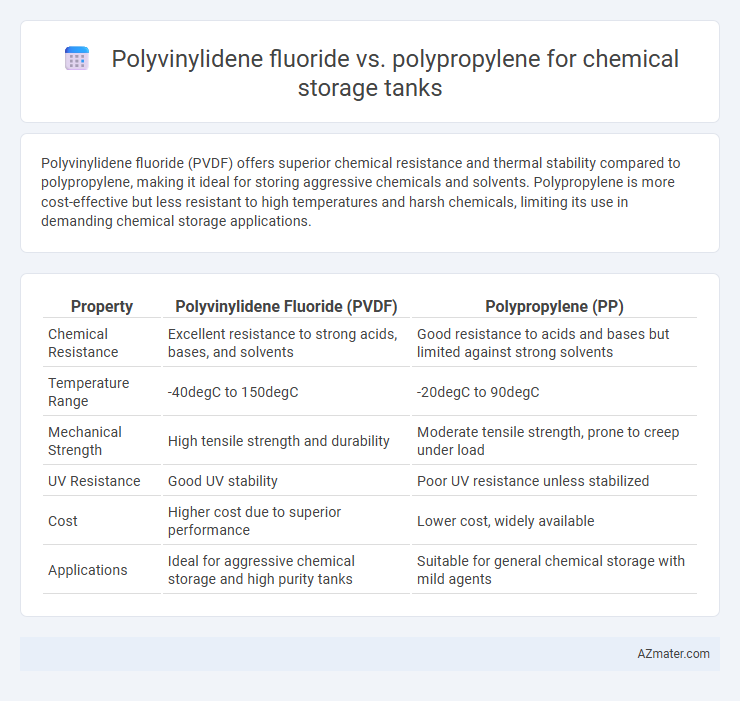
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for storing aggressive chemicals and solvents. Polypropylene is more cost-effective but less resistant to high temperatures and harsh chemicals, limiting its use in demanding chemical storage applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to strong acids, bases, and solvents | Good resistance to acids and bases but limited against strong solvents |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC | -20degC to 90degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and durability | Moderate tensile strength, prone to creep under load |
| UV Resistance | Good UV stability | Poor UV resistance unless stabilized |
| Cost | Higher cost due to superior performance | Lower cost, widely available |
| Applications | Ideal for aggressive chemical storage and high purity tanks | Suitable for general chemical storage with mild agents |
Introduction to Chemical Storage Tank Materials
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and polypropylene (PP) are widely used materials for chemical storage tanks due to their excellent chemical resistance and durability. PVDF offers superior resistance to strong acids, bases, and solvents, making it ideal for aggressive chemical environments, while polypropylene excels in handling less corrosive substances at a lower cost. Both materials provide good mechanical strength and thermal stability, but PVDF's higher temperature tolerance and inertness make it preferable for demanding chemical storage applications.
Overview of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is a high-performance fluoropolymer known for its exceptional chemical resistance, making it ideal for chemical storage tanks handling aggressive acids and solvents. PVDF offers superior mechanical strength, UV resistance, and thermal stability compared to polypropylene, ensuring long-term durability in harsh environments. Its low permeability and outstanding resistance to oxidation and abrasion provide enhanced safety and reliability for storing highly corrosive chemicals.
Key Properties of Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) offers excellent chemical resistance, making it suitable for storing a wide range of acids, bases, and solvents commonly handled in industrial applications. Its high impact strength and resistance to fatigue enhance the durability of chemical storage tanks under mechanical stress and temperature fluctuations. Moreover, PP's low density and cost-effectiveness provide a lightweight and economical solution compared to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), which is typically reserved for more aggressive chemical environments.
Chemical Resistance Comparison: PVDF vs. PP
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polypropylene (PP), withstanding strong acids, bases, and solvents such as hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, and ketones without degradation. Polypropylene, while cost-effective and resistant to many alkalis and mild acids, tends to degrade faster when exposed to aggressive chemicals like aromatic hydrocarbons and strong oxidizers. PVDF's higher temperature tolerance and resistance to permeation make it the preferred choice for long-term chemical storage of highly corrosive substances.
Temperature Tolerance and Performance
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior temperature tolerance for chemical storage tanks, withstanding continuous use temperatures up to 150degC, compared to polypropylene's limit of around 90degC. PVDF also demonstrates enhanced chemical resistance and mechanical strength at elevated temperatures, making it ideal for aggressive chemical storage environments. Polypropylene remains a cost-effective option for lower temperature applications but may degrade or deform under high thermal stress and prolonged chemical exposure.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance compared to polypropylene (PP), making it more suitable for demanding chemical storage tank applications. PVDF exhibits higher tensile strength, impact resistance, and long-term durability under exposure to aggressive chemicals and UV radiation. Polypropylene, while cost-effective and resistant to many chemicals, has lower mechanical strength and can degrade faster under harsh environmental conditions.
Cost Analysis: PVDF vs. PP Tanks
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) tanks generally have higher upfront costs than polypropylene (PP) tanks due to PVDF's superior chemical resistance and thermal stability. While PP tanks offer a lower initial investment, they may incur higher maintenance and replacement expenses in aggressive chemical environments. Long-term cost analysis favors PVDF tanks for handling corrosive chemicals, reducing total cost of ownership despite the premium price.
Safety and Regulatory Compliance Considerations
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and flame retardancy compared to polypropylene (PP), making it a safer choice for chemical storage tanks handling aggressive solvents and acids. PVDF complies with stringent regulatory standards such as FDA, USP Class VI, and FDA CFR Title 21, ensuring it meets food and pharmaceutical industry safety requirements, whereas PP may fall short in high-temperature and high-pressure applications. Selecting PVDF enhances tank durability and compliance with OSHA and EPA regulations, minimizing risks of chemical leaks and contamination.
Typical Applications in Chemical Storage
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is highly resistant to strong acids, bases, and organic solvents, making it ideal for storing aggressive chemicals such as hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, and solvents in chemical storage tanks. Polypropylene (PP) offers excellent chemical resistance for less aggressive substances, including diluted acids, alkalis, and water-based solutions, commonly used in pharmaceutical, food processing, and light chemical industries. PVDF is preferred for high-purity and high-temperature applications, whereas polypropylene is favored for cost-effective storage of general-purpose chemicals at moderate temperatures.
Selecting the Optimal Material for Chemical Storage Tanks
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers exceptional chemical resistance and high mechanical strength, making it ideal for storing aggressive chemicals and solvents. Polypropylene (PP) provides cost-effective corrosion resistance and good durability but may degrade with strong acids or high temperatures. Selecting the optimal material depends on the specific chemical composition, operating temperature, and budget constraints to ensure long-term tank integrity and safety.
Infographic: Polyvinylidene fluoride vs Polypropylene for Chemical storage tank
 azmater.com
azmater.com