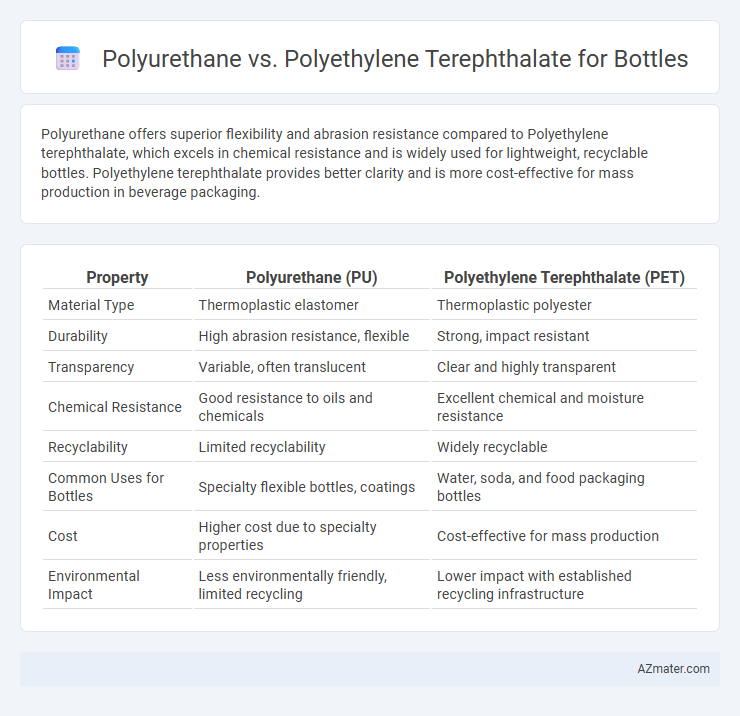
Polyurethane offers superior flexibility and abrasion resistance compared to Polyethylene terephthalate, which excels in chemical resistance and is widely used for lightweight, recyclable bottles. Polyethylene terephthalate provides better clarity and is more cost-effective for mass production in beverage packaging.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane (PU) | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic elastomer | Thermoplastic polyester |
| Durability | High abrasion resistance, flexible | Strong, impact resistant |
| Transparency | Variable, often translucent | Clear and highly transparent |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and chemicals | Excellent chemical and moisture resistance |
| Recyclability | Limited recyclability | Widely recyclable |
| Common Uses for Bottles | Specialty flexible bottles, coatings | Water, soda, and food packaging bottles |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialty properties | Cost-effective for mass production |
| Environmental Impact | Less environmentally friendly, limited recycling | Lower impact with established recycling infrastructure |
Introduction to Polyurethane and Polyethylene Terephthalate
Polyurethane is a versatile polymer known for its elasticity, durability, and resistance to impact, making it suitable for flexible bottle applications and protective coatings. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a strong, lightweight thermoplastic widely used in beverage bottles due to its excellent gas barrier properties and recyclability. Both materials serve distinct functions in bottle manufacturing, with polyurethane offering enhanced flexibility and PET providing structural rigidity and transparency.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Polyurethane (PU) consists of repeating urethane linkages formed by the reaction of diisocyanates with polyols, providing flexibility and durability in bottle applications. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a polyester made from terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol, featuring ester functional groups that offer excellent rigidity and chemical resistance. The chemical structure of polyurethane allows for variable hardness and elasticity, while PET's aromatic rings and ester bonds deliver superior barrier properties and thermal stability in bottles.
Manufacturing Processes of Polyurethane vs PET Bottles
Polyurethane bottles are typically manufactured using a chemical reaction between polyols and isocyanates through a process called reactive casting or molding, allowing for flexible, customizable shapes and enhanced durability. In contrast, polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles are produced via a blow molding process, where PET resin pellets are melted, formed into a preform, and then blown into the final bottle shape, offering high clarity and excellent barrier properties. The PET manufacturing process is highly automated and optimized for mass production, while polyurethane production allows for more tailored applications with variable mechanical properties.
Physical Properties and Performance
Polyurethane offers superior flexibility and impact resistance compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), making it ideal for applications requiring durability and abrasion resistance, while PET excels in clarity and chemical resistance, which are crucial for food and beverage bottles. PET provides excellent tensile strength and dimensional stability under various temperatures, whereas polyurethane demonstrates enhanced elasticity and resilience to wear and tear. Both materials differ in barrier properties; PET has better gas barrier performance, crucial for preserving carbonation and freshness, whereas polyurethane's moisture barrier is less effective but provides better resistance to oils and solvents.
Barrier Properties: Oxygen and Moisture Resistance
Polyurethane (PU) offers moderate oxygen barrier properties but excels in moisture resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring flexibility and water vapor protection. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) demonstrates superior oxygen barrier capabilities due to its dense polymer structure, which significantly reduces oxygen transmission rates, ideal for preserving the freshness of beverages. However, PET has lower moisture barrier efficiency compared to PU, which can be mitigated by coating or multilayer packaging technologies to enhance overall performance.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Polyurethane offers superior durability with high abrasion resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for impact-prone bottle applications. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) exhibits excellent environmental resistance, including strong chemical stability, UV resistance, and moisture barrier properties essential for beverage packaging. PET bottles also provide efficient recyclability compared to polyurethane, which is less commonly recycled and more prone to environmental degradation.
Applications and Common Uses in Bottling
Polyurethane offers excellent flexibility and impact resistance, making it suitable for protective coatings and seals in specialized bottling applications, especially for products requiring enhanced durability. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) dominates the beverage industry due to its lightweight, clarity, and strong barrier properties, ideal for carbonated drinks, water, and juices. PET bottles are widely recycled, contributing to sustainability efforts, whereas polyurethane is less common in primary container production but valuable in auxiliary components like liners and adhesives.
Recyclability and Environmental Impact
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles are widely favored for recyclability due to their clear recycling streams and high recovery rates, significantly reducing plastic waste in landfills. Polyurethane (PU) bottles, however, face challenges in recyclability because of their chemical complexity and limited recycling infrastructure, leading to greater environmental persistence. The environmental impact of PET is generally lower, supported by extensive recycling networks that enable reuse and reduce carbon footprints, whereas PU's environmental footprint remains higher due to difficulties in processing and disposal.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles dominate the market due to their low production costs and widespread recycling infrastructure, making them the most cost-efficient option for mass production. Polyurethane bottles, while offering superior flexibility and durability, present higher manufacturing costs and limited market availability, restricting their use to niche applications. PET's well-established supply chain and economies of scale provide significant cost advantages over polyurethane in bottle manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Material: Polyurethane or PET?
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior clarity, lightweight properties, and excellent barrier resistance, making it ideal for beverage bottles requiring durability and food safety compliance. Polyurethane (PU) provides enhanced flexibility, impact resistance, and chemical durability, suitable for specialized packaging needing high abrasion resistance and prolonged lifespan. Selecting between PET and PU hinges on application-specific requirements such as transparency, mechanical strength, environmental stress resistance, and recyclability preferences.
Infographic: Polyurethane vs Polyethylene terephthalate for Bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com