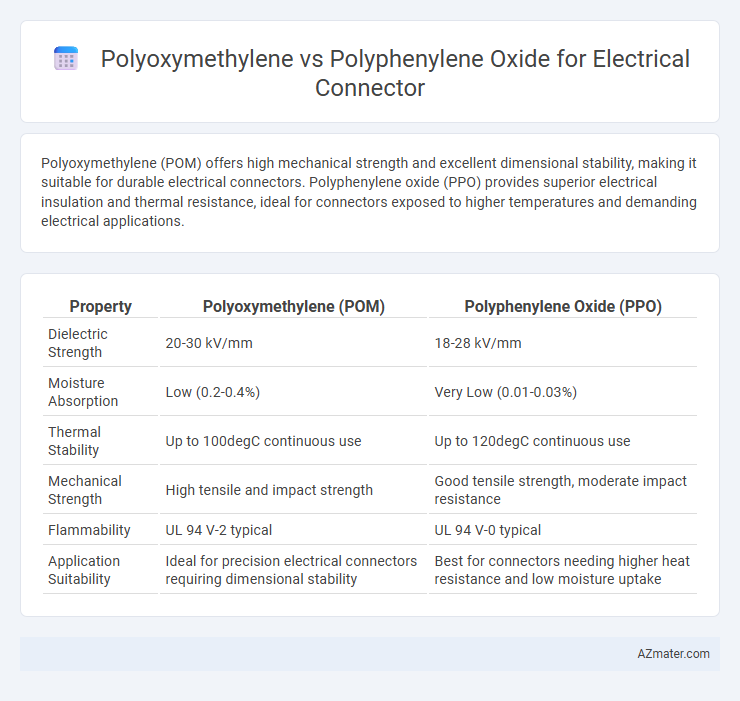
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high mechanical strength and excellent dimensional stability, making it suitable for durable electrical connectors. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) provides superior electrical insulation and thermal resistance, ideal for connectors exposed to higher temperatures and demanding electrical applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyoxymethylene (POM) | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Strength | 20-30 kV/mm | 18-28 kV/mm |
| Moisture Absorption | Low (0.2-0.4%) | Very Low (0.01-0.03%) |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 100degC continuous use | Up to 120degC continuous use |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile and impact strength | Good tensile strength, moderate impact resistance |
| Flammability | UL 94 V-2 typical | UL 94 V-0 typical |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for precision electrical connectors requiring dimensional stability | Best for connectors needing higher heat resistance and low moisture uptake |
Introduction to Polyoxymethylene and Polyphenylene Oxide
Polyoxymethylene (POM) is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic known for its excellent mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and low friction properties, making it ideal for precise electrical connector components requiring durability and wear resistance. Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) offers superior heat resistance, electrical insulation, and chemical stability, which are critical for electrical connectors operating in high-temperature or chemically aggressive environments. Both materials provide unique advantages in electrical connector manufacturing, with POM favored for mechanical robustness and PPO for thermal and electrical performance.
Key Properties of Polyoxymethylene in Electrical Connectors
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits exceptional dimensional stability, high tensile strength, and excellent wear resistance, making it ideal for electrical connector housings. Its low electrical conductivity combined with superior dielectric properties ensures reliable insulation and minimal signal loss. POM's resistance to moisture, solvents, and temperature variations enhances connector durability in demanding electrical applications.
Core Characteristics of Polyphenylene Oxide for Electrical Applications
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers excellent dimensional stability, high heat resistance, and superior electrical insulation properties crucial for electrical connectors. Its low moisture absorption and strong dielectric strength ensure reliable performance in harsh environments. Compared to polyoxymethylene, PPO provides better thermal endurance and maintains mechanical integrity at elevated temperatures, making it ideal for demanding electrical applications.
Mechanical Strength Comparison: POM vs. PPO
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits superior mechanical strength and stiffness compared to Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO), making it more suitable for electrical connectors requiring high durability and resistance to deformation under mechanical stress. POM's tensile strength typically ranges between 60-70 MPa, significantly outperforming PPO's average tensile strength of around 50 MPa. While PPO offers better thermal stability and electrical insulating properties, POM's enhanced impact resistance and fatigue strength make it the preferred choice for connectors subjected to rigorous mechanical loading conditions.
Electrical Insulation Performance: Polyoxymethylene vs. Polyphenylene Oxide
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior electrical insulation performance compared to polyoxymethylene (POM) due to its higher dielectric strength and lower dielectric constant, ensuring minimal energy loss in electrical connectors. PPO's inherent thermal stability and resistance to moisture absorption enhance its insulating properties, making it ideal for high-frequency and high-voltage applications. In contrast, POM has moderate electrical insulation capabilities but is more susceptible to deterioration under prolonged electrical stress and humidity exposure, limiting its use in critical electrical connector components.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance Analysis
Polyoxymethylene (POM) demonstrates excellent dimensional stability and low moisture absorption, but its thermal stability peaks around 90-100degC, limiting its use in high-temperature electrical connectors. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior heat resistance with a continuous use temperature often above 150degC and maintains mechanical properties under thermal stress, making it more suitable for demanding electrical connector applications. The thermal degradation onset of PPO occurs at higher temperatures compared to POM, ensuring enhanced long-term performance and reliability in elevated thermal environments.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Suitability
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers excellent chemical resistance against fuels, solvents, and dilute acids, making it suitable for electrical connectors exposed to harsh chemical environments. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior thermal stability and resistance to oxidation, maintaining performance in high-temperature and high-humidity conditions commonly found in automotive and industrial electrical applications. PPO's dimensional stability and low moisture absorption enhance environmental suitability, whereas POM may degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure or extreme humidity.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers a cost-effective solution with widespread availability, making it a preferred choice for electrical connectors in budget-sensitive applications. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO), while typically more expensive, provides superior thermal stability and dielectric properties, justifying its higher cost in high-performance electrical connector systems. The decision between POM and PPO hinges on balancing upfront material cost against long-term reliability and availability in the supply chain.
Typical Applications in Electrical Connectors
Polyoxymethylene (POM) is widely used in electrical connectors for its excellent dimensional stability, low friction, and high mechanical strength, making it ideal for precision components such as terminal blocks and housings. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal resistance and electrical insulation properties, often chosen for connectors requiring high heat endurance and flame retardancy, including automotive and industrial applications. Both materials provide reliable performance in harsh environments, with POM favored for mechanical durability and PPO preferred for thermal and electrical insulation.
Conclusion: Selecting the Best Material for Electrical Connectors
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior mechanical strength and excellent dimensional stability, making it ideal for electrical connectors requiring durability and precision. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits outstanding thermal stability and electrical insulating properties, suitable for high-temperature applications and enhanced dielectric performance. Choosing the best material depends on balancing mechanical demands and thermal-electrical requirements, with POM preferred for structural integrity and PPO for thermal resilience and insulation.
Infographic: Polyoxymethylene vs Polyphenylene oxide for Electrical connector
 azmater.com
azmater.com