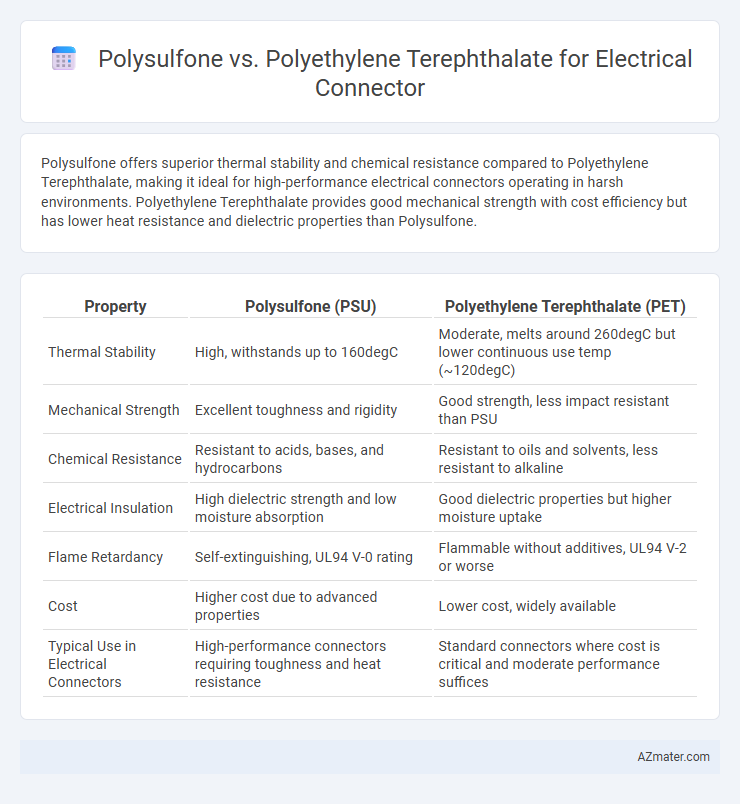
Polysulfone offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to Polyethylene Terephthalate, making it ideal for high-performance electrical connectors operating in harsh environments. Polyethylene Terephthalate provides good mechanical strength with cost efficiency but has lower heat resistance and dielectric properties than Polysulfone.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfone (PSU) | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | High, withstands up to 160degC | Moderate, melts around 260degC but lower continuous use temp (~120degC) |
| Mechanical Strength | Excellent toughness and rigidity | Good strength, less impact resistant than PSU |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids, bases, and hydrocarbons | Resistant to oils and solvents, less resistant to alkaline |
| Electrical Insulation | High dielectric strength and low moisture absorption | Good dielectric properties but higher moisture uptake |
| Flame Retardancy | Self-extinguishing, UL94 V-0 rating | Flammable without additives, UL94 V-2 or worse |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Lower cost, widely available |
| Typical Use in Electrical Connectors | High-performance connectors requiring toughness and heat resistance | Standard connectors where cost is critical and moderate performance suffices |
Introduction to Polysulfone and Polyethylene Terephthalate
Polysulfone (PSU) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent thermal stability, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance, making it suitable for demanding electrical connector applications exposed to high temperatures. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) offers good electrical insulation properties, dimensional stability, and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in connectors requiring moderate heat resistance and rigidity. The choice between Polysulfone and PET hinges on balancing high-temperature endurance and mechanical robustness with budget considerations for electrical connector manufacturing.
Material Properties Comparison
Polysulfone exhibits high thermal stability with a continuous operating temperature of up to 150degC, superior mechanical strength, and excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for electrical connectors exposed to harsh environments. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers good dimensional stability, moderate thermal resistance up to 120degC, and excellent electrical insulation properties but is less resistant to chemical exposure compared to polysulfone. The choice between polysulfone and PET depends on the required thermal endurance, mechanical robustness, and environmental exposure conditions in electrical connector applications.
Electrical Insulation Performance
Polysulfone offers superior electrical insulation performance compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET) due to its high dielectric strength and excellent thermal stability, making it ideal for demanding electrical connector applications. Its inherent resistance to moisture and chemical degradation enhances long-term insulation reliability, surpassing PET's moderate dielectric properties and lower temperature resistance. Thus, polysulfone ensures consistent, high-performance electrical insulation in harsh environments where PET might fail.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polysulfone exhibits superior thermal stability and heat resistance compared to Polyethylene Terephthalate, maintaining mechanical integrity at temperatures up to 190degC, making it ideal for high-temperature electrical connector applications. Polyethylene Terephthalate typically withstands temperatures up to 120degC before deformation occurs, limiting its use in environments with elevated heat exposure. The enhanced heat resistance of Polysulfone ensures reliable electrical performance and durability under continuous thermal stress.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polysulfone exhibits superior mechanical strength and thermal stability compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), making it highly suitable for electrical connectors subjected to high stress and elevated temperatures. PET offers good toughness and chemical resistance but falls short in long-term durability and dimensional stability under continuous mechanical load. In demanding electrical connector applications, polysulfone ensures enhanced durability and sustained performance, especially in environments involving heat and mechanical strain.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Suitability
Polysulfone (PSU) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), with high tolerance to acids, bases, and organic solvents, making it ideal for electrical connectors exposed to harsh chemical environments. PET offers good resistance to water and moderate chemicals but is more prone to hydrolysis and degradation under prolonged exposure to high temperatures and aggressive chemicals. Environmentally, PSU withstands elevated temperatures up to 150degC and maintains mechanical integrity, suitable for demanding electrical applications, while PET, with a lower maximum service temperature around 120degC, is better suited for less extreme conditions.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Polysulfone offers higher thermal resistance and chemical stability but comes at a significantly higher cost compared to Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), which is more affordable and widely accessible due to its extensive industrial production. PET's abundant availability ensures lower lead times and supply chain reliability for electrical connector manufacturing, whereas polysulfone's specialized production leads to limited supply and potential cost variability. When analyzing overall expenses, PET presents a cost-effective solution for large-scale applications, while polysulfone is preferred in high-performance scenarios where material durability justifies the premium price.
Applications in Electrical Connectors
Polysulfone exhibits superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, making it ideal for high-performance electrical connectors used in aerospace and automotive industries. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers excellent mechanical strength and electrical insulation properties, suitable for connectors in consumer electronics and general electrical applications. The choice between Polysulfone and PET depends on the required operating temperature, environmental exposure, and electrical performance criteria of the connector.
Pros and Cons of Each Material
Polysulfone (PSU) offers excellent thermal stability up to 150degC, superior chemical resistance, and robust mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-performance electrical connectors in harsh environments; however, its higher cost and lower dimensional stability compared to some alternatives can be drawbacks. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) provides good electrical insulation, dimensional stability, and cost-effectiveness with decent thermal resistance up to about 120degC, but it is more susceptible to hydrolysis and less resistant to high-temperature aging than polysulfone. Choosing between PSU and PET depends on the balance of required thermal endurance, chemical exposure, mechanical demands, and budget constraints for specific electrical connector applications.
Selecting the Right Polymer for Connector Design
Polysulfone (PSU) offers excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for electrical connectors exposed to high temperatures and harsh environments. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) provides superior mechanical strength and dimensional stability, suitable for connectors requiring rigidity and precision. Selecting the right polymer depends on balancing thermal performance, mechanical properties, and environmental exposure specific to the connector application.
Infographic: Polysulfone vs Polyethylene Terephthalate for Electrical Connector
 azmater.com
azmater.com