Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior rigidity and durability for shoe insoles, enhancing long-term support and impact resistance. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) provides excellent cushioning and flexibility, making it ideal for shock absorption and comfort in athletic footwear.
Table of Comparison
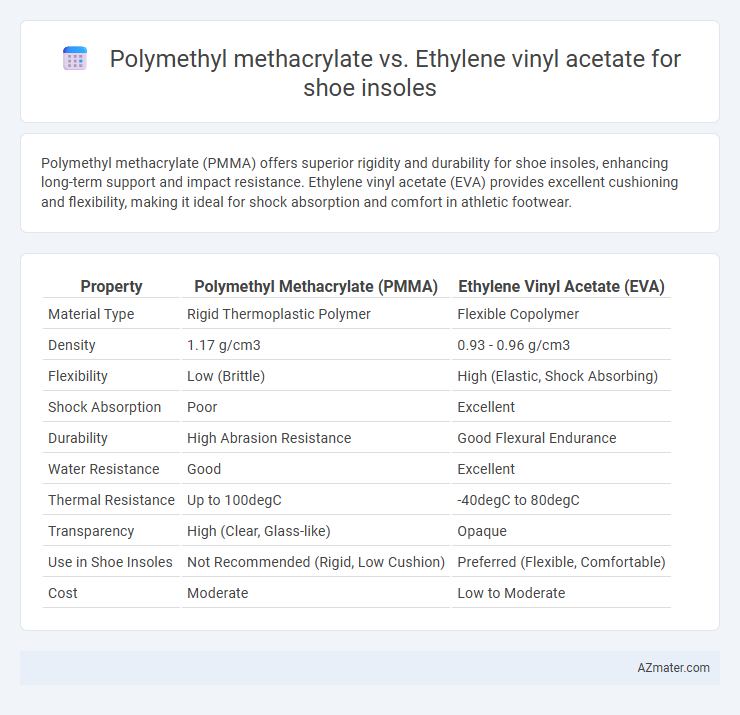
| Property | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Rigid Thermoplastic Polymer | Flexible Copolymer |
| Density | 1.17 g/cm3 | 0.93 - 0.96 g/cm3 |
| Flexibility | Low (Brittle) | High (Elastic, Shock Absorbing) |
| Shock Absorption | Poor | Excellent |
| Durability | High Abrasion Resistance | Good Flexural Endurance |
| Water Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 100degC | -40degC to 80degC |
| Transparency | High (Clear, Glass-like) | Opaque |
| Use in Shoe Insoles | Not Recommended (Rigid, Low Cushion) | Preferred (Flexible, Comfortable) |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to Moderate |
Introduction to Shoe Insole Materials
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers rigidity and durability, making it ideal for structural support in shoe insoles, whereas Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) provides superior cushioning and flexibility due to its elastomeric properties. EVA's lightweight nature and excellent shock absorption make it preferred for athletic and comfort-focused insoles, while PMMA is often used in applications requiring firm arch support and abrasion resistance. Choosing between PMMA and EVA depends on balancing stiffness for stability against softness for impact mitigation in footwear design.
Overview of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) is a transparent thermoplastic known for its rigidity, lightweight nature, and excellent resistance to UV light and weathering, making it suitable for durable shoe insoles. Its high tensile strength and clarity provide structural support and aesthetic appeal in footwear applications. Compared to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA), PMMA offers greater hardness and dimensional stability but lacks EVA's flexibility and cushioning properties.
Overview of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA)
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is a lightweight, flexible, and cushioning material extensively used in shoe insoles for its excellent shock absorption and durability. Unlike Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), which offers rigidity and transparency, EVA provides superior comfort and resilience, making it ideal for athletic and casual footwear. Its capability to withstand compression and maintain cushioning properties under repetitive stress ensures enhanced foot support and fatigue reduction.
Mechanical Properties: PMMA vs EVA
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior hardness and rigidity compared to Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), providing enhanced structural support for shoe insoles. EVA is known for its excellent flexibility, shock absorption, and cushioning properties, making it ideal for comfort in footwear applications. While PMMA ensures durability and resistance to deformation under stress, EVA outperforms in energy return and impact attenuation for prolonged wear.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior durability with high resistance to wear, scratches, and environmental degradation, making it ideal for long-lasting shoe insoles. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) provides excellent flexibility and cushioning but tends to compress and degrade faster under prolonged stress compared to PMMA, resulting in a shorter lifespan. When comparing lifespan, PMMA insoles maintain structural integrity over extended use, while EVA insoles require more frequent replacement due to material fatigue and loss of resilience.
Comfort and Shock Absorption Analysis
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers high rigidity and excellent impact resistance but lacks the cushioning properties essential for prolonged comfort in shoe insoles. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) provides superior shock absorption due to its lightweight, flexible structure and ability to compress under pressure, reducing foot fatigue and enhancing comfort during extended wear. Comparative studies show EVA insoles outperform PMMA in energy return and pressure distribution, making EVA the preferred material for comfort-focused footwear applications.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is significantly denser and heavier than ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), making EVA the preferred choice for lightweight shoe insoles. EVA excels in flexibility due to its elastic polymer structure, providing superior cushioning and shock absorption compared to the rigid and brittle nature of PMMA. Consequently, EVA insoles offer enhanced comfort for prolonged wear, while PMMA is better suited for applications requiring higher durability but less flexibility.
Biocompatibility and Skin Sensitivity
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) provides excellent biocompatibility with minimal risk of skin irritation, making it suitable for shoe insoles, especially for users with sensitive skin. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is also biocompatible but tends to offer better cushioning and flexibility, which can reduce pressure points and enhance comfort for extended wear. EVA's hypoallergenic properties further minimize the chance of skin sensitivity reactions, making it a preferred choice in insoles designed for sensitive or compromised skin conditions.
Cost and Accessibility Considerations
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers high durability and excellent cushioning for shoe insoles but tends to be more expensive and less widely available compared to Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA). EVA is favored for its cost-effectiveness, lightweight properties, and ease of manufacturing, making it more accessible for mass-market footwear production. The affordability and broad distribution of EVA materials often drive its preference in budget-conscious shoe insole applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Shoe Insoles
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior rigidity and durability, making it ideal for high-impact and structural shoe insoles that demand firm support. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) provides exceptional cushioning, flexibility, and shock absorption, enhancing comfort for everyday wear and activities involving prolonged standing or walking. Selecting the right material depends on the balance between rigidity for support (PMMA) and softness for comfort (EVA) based on the user's specific foot health needs and activity levels.
Infographic: Polymethyl methacrylate vs Ethylene vinyl acetate for Shoe Insole
 azmater.com
azmater.com