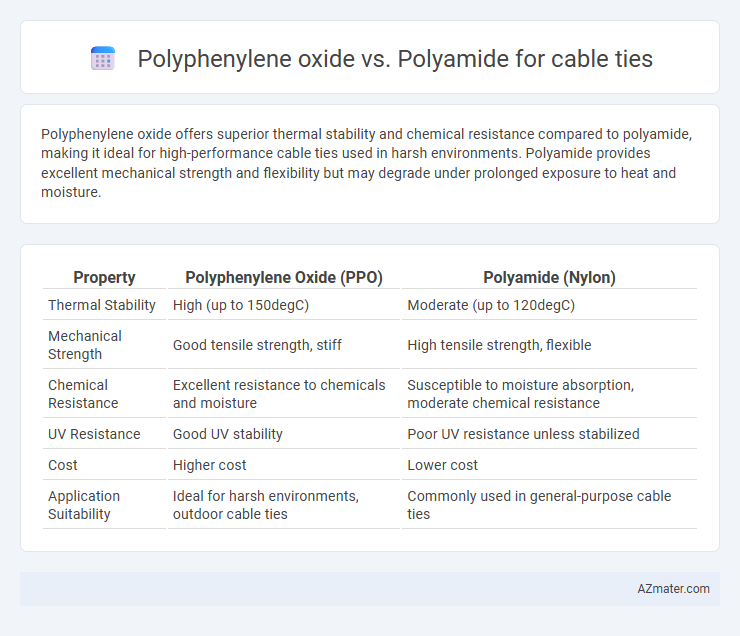
Polyphenylene oxide offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polyamide, making it ideal for high-performance cable ties used in harsh environments. Polyamide provides excellent mechanical strength and flexibility but may degrade under prolonged exposure to heat and moisture.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) | Polyamide (Nylon) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | High (up to 150degC) | Moderate (up to 120degC) |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile strength, stiff | High tensile strength, flexible |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to chemicals and moisture | Susceptible to moisture absorption, moderate chemical resistance |
| UV Resistance | Good UV stability | Poor UV resistance unless stabilized |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for harsh environments, outdoor cable ties | Commonly used in general-purpose cable ties |
Introduction to Polyphenylene Oxide and Polyamide
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent dimensional stability, high heat resistance, and strong electrical insulating properties, making it suitable for cable tie applications in demanding environments. Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, offers superior mechanical strength, flexibility, and abrasion resistance, which enhances its durability in cable tie manufacturing. Both materials provide unique advantages, with PPO excelling in thermal stability and electrical insulation, while polyamide delivers exceptional toughness and wear resistance.
Material Composition and Structure
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) features a rigid aromatic backbone that offers excellent thermal stability and dimensional retention, making it resistant to deformation under high temperatures. Polyamide (PA), composed of repeating amide linkages, provides superior mechanical strength and flexibility due to its semi-crystalline structure, which enhances impact resistance and toughness. PPO's amorphous structure results in better electrical insulation and chemical resistance, whereas polyamide's crystalline regions improve moisture absorption resistance and durability in harsh environmental conditions.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers excellent mechanical strength and high tensile modulus, making it ideal for robust cable tie applications requiring resistance to deformation and high impact. Polyamide (PA), commonly known as nylon, provides superior elongation at break and impact resistance but tends to exhibit more variability in mechanical strength depending on moisture absorption and environmental conditions. In critical cable tie applications where consistent mechanical strength and rigidity are essential, PPO outperforms polyamide by maintaining structural integrity under stress and temperature variations.
Thermal Resistance and Operating Temperatures
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal resistance compared to polyamide, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 210degC, while polyamide typically withstands continuous use around 120-150degC. PPO's higher glass transition temperature ensures better performance in high-heat environments, making it ideal for cable ties exposed to elevated temperatures. Polyamide's lower thermal stability limits its application where prolonged heat exposure is expected, although it provides excellent flexibility and mechanical strength at moderate temperatures.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Stability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior chemical resistance compared to polyamide, excelling in exposure to oils, acids, and alkaline solutions without degrading. PPO maintains excellent environmental stability, including UV resistance and low moisture absorption, ensuring durability in outdoor or harsh environments. Polyamide, while strong mechanically, is more prone to hydrolysis and UV damage, making PPO the preferred choice for chemically aggressive and environmentally demanding cable tie applications.
Electrical Insulation Properties
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers excellent electrical insulation properties due to its high dielectric strength and low moisture absorption, making it ideal for cable tie applications in electrical environments. Polyamide (PA), while strong and flexible, tends to absorb more moisture, which can reduce its insulating performance over time. Therefore, PPO provides more stable and reliable electrical insulation for cable ties used in demanding electrical and electronic applications.
Moisture Absorption and Durability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits significantly lower moisture absorption compared to polyamide (PA), enhancing its dimensional stability and electrical insulation properties in humid environments. Polyamide tends to absorb moisture, which can lead to swelling, reduced mechanical strength, and premature failure in cable tie applications. PPO's superior durability and resistance to environmental stress cracking make it a preferred choice for cable ties exposed to moisture and harsh conditions.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) cable ties generally offer a higher initial cost than polyamide (nylon) ties due to superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making them suitable for demanding environments. Polyamide ties dominate the market because of their lower price, ease of molding, and adequate performance in most standard applications, driving cost efficiency in large-scale production. Selecting between PPO and polyamide hinges on balancing upfront investment with long-term durability and environmental exposure, influencing overall economic viability.
Typical Applications in Cable Ties
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is commonly used in cable ties for electrical and electronic applications due to its excellent thermal stability, dimensional accuracy, and resistance to chemicals and UV exposure. Polyamide (PA), particularly Nylon 6 and Nylon 6/6, is favored for heavy-duty cable ties requiring high tensile strength, flexibility, and abrasion resistance in automotive, construction, and industrial environments. Both materials enable reliable securing of cables, but PPO suits environments with elevated temperatures and exposure, while polyamide excels under mechanical stress and harsh physical conditions.
Choosing the Right Material for Cable Tie Needs
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers excellent thermal stability and electrical insulation, making it ideal for high-temperature environments and electronic applications in cable ties. Polyamide (PA), commonly known as nylon, provides superior mechanical strength, flexibility, and chemical resistance, suitable for outdoor and heavy-duty cable tie uses. Selecting the right cable tie material depends on specific requirements such as operating temperature, environmental exposure, and mechanical stress to ensure durability and performance.
Infographic: Polyphenylene oxide vs Polyamide for Cable Tie
 azmater.com
azmater.com