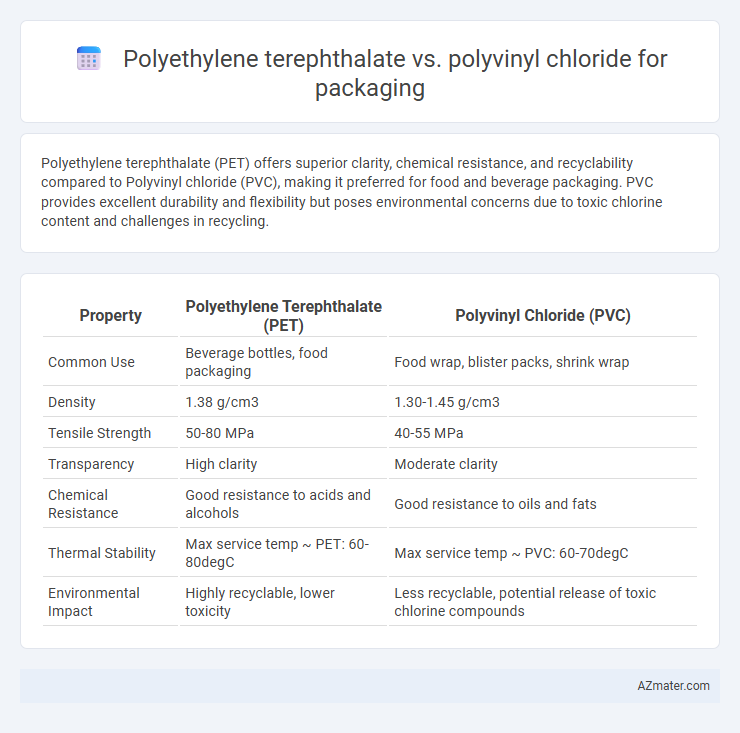
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior clarity, chemical resistance, and recyclability compared to Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it preferred for food and beverage packaging. PVC provides excellent durability and flexibility but poses environmental concerns due to toxic chlorine content and challenges in recycling.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Common Use | Beverage bottles, food packaging | Food wrap, blister packs, shrink wrap |
| Density | 1.38 g/cm3 | 1.30-1.45 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 50-80 MPa | 40-55 MPa |
| Transparency | High clarity | Moderate clarity |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and alcohols | Good resistance to oils and fats |
| Thermal Stability | Max service temp ~ PET: 60-80degC | Max service temp ~ PVC: 60-70degC |
| Environmental Impact | Highly recyclable, lower toxicity | Less recyclable, potential release of toxic chlorine compounds |
Overview of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) is a lightweight, transparent thermoplastic polymer widely used in beverage bottles and food packaging due to its excellent strength, chemical resistance, and recyclability. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) offers superior flexibility and durability with good barrier properties against moisture and gases, making it suitable for packaging applications like shrink wraps and blister packs. While PET provides better clarity and is more environmentally friendly, PVC's chemical resistance and versatility make it ideal for specialized packaging needs.
Chemical Structure and Physical Properties Comparison
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) features a repeating ester functional group linking aromatic rings, contributing to its high tensile strength and excellent clarity, making it ideal for transparent packaging. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) consists of repeating vinyl chloride units, which provide greater chemical resistance and flexibility but result in an opaque, more rigid material compared to PET. PET's higher melting point and superior gas barrier properties contrast with PVC's lower thermal stability and broader chemical compatibility, influencing their specific applications in food and industrial packaging.
Barrier Properties: Moisture, Gas, and Light Resistance
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior moisture and gas barrier properties compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it more effective for packaging applications requiring extended shelf life. PET exhibits excellent resistance to oxygen and carbon dioxide permeability, ensuring better product freshness and reduced spoilage. While PVC provides moderate barrier protection, PET's superior clarity and light resistance further enhance its suitability for packaging sensitive products.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Analysis
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) exhibits superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it ideal for packaging applications requiring durability and mechanical robustness. PET's higher crystallinity contributes to better dimensional stability and resistance to deformation under stress, enhancing its performance in protecting contents during transportation. In contrast, PVC demonstrates lower mechanical strength and is more prone to brittleness over time, limiting its effectiveness in high-stress packaging environments.
Cost Efficiency and Material Availability
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior cost efficiency due to its lower production costs and widespread recyclability, making it a preferred choice for sustainable packaging solutions. In contrast, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) tends to be more expensive to produce and recycle, with limited material availability stemming from environmental and regulatory restrictions. PET's abundant availability and cost-effective manufacturing make it a more practical option for large-scale packaging applications.
Safety and Food Contact Regulations
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely preferred in food packaging due to its inert chemical properties and compliance with FDA and EU food contact regulations, ensuring safety against leaching or contamination. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), while durable, often contains additives like phthalates that raise concerns over potential migration into food, leading to restrictions and stricter regulatory scrutiny in many countries. Regulatory agencies favor PET for its stability and recyclability, making it a safer and more sustainable choice for consumer food packaging applications.
Environmental Impact: Recycling and Biodegradability
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior recyclability with established global systems enabling efficient recovery and reuse, reducing landfill accumulation and conserving resources. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) presents challenges in recycling due to its chlorine content, which can release harmful chemicals during processing and limits its circular lifecycle. Biodegradability for both plastics is minimal, but PET's safer recycling profile makes it a more environmentally sustainable choice for packaging applications.
Processing and Manufacturing Considerations
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior clarity and chemical resistance, making it ideal for food and beverage packaging, while its thermoforming properties allow efficient molding and recycling. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) provides excellent rigidity and barrier qualities but requires careful handling during processing due to the release of hazardous gases when heated. Manufacturing with PET involves higher processing temperatures and more energy consumption compared to PVC, which benefits from lower processing temperatures and versatility in producing flexible or rigid packaging forms.
Typical Packaging Applications for PET vs PVC
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely used in packaging for beverages, food containers, and cosmetic bottles due to its high clarity, excellent barrier properties, and recyclability. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is commonly employed in packaging for blister packs, shrink wraps, and cling films because of its durability, chemical resistance, and flexibility. PET's application emphasis is on lightweight, transparent containers, while PVC is preferred for protective, form-fitting packaging solutions.
Future Trends in Packaging Material Selection
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is gaining prominence in packaging due to its recyclability, lightweight nature, and clarity, making it ideal for sustainable consumer goods packaging. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is gradually being phased out in many applications because of environmental concerns and limited recyclability, driving a shift towards eco-friendly alternatives like PET and bio-based plastics. Future trends emphasize material innovations that combine performance with reduced carbon footprint, promoting circular economy principles in packaging material selection.
Infographic: Polyethylene terephthalate vs Polyvinyl chloride for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com