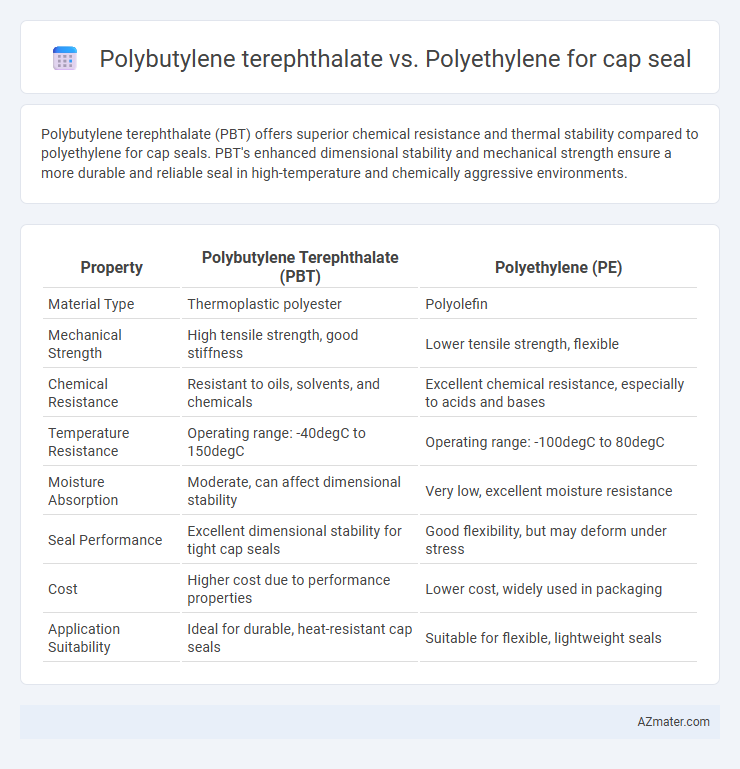
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to polyethylene for cap seals. PBT's enhanced dimensional stability and mechanical strength ensure a more durable and reliable seal in high-temperature and chemically aggressive environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polyester | Polyolefin |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, good stiffness | Lower tensile strength, flexible |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to oils, solvents, and chemicals | Excellent chemical resistance, especially to acids and bases |
| Temperature Resistance | Operating range: -40degC to 150degC | Operating range: -100degC to 80degC |
| Moisture Absorption | Moderate, can affect dimensional stability | Very low, excellent moisture resistance |
| Seal Performance | Excellent dimensional stability for tight cap seals | Good flexibility, but may deform under stress |
| Cost | Higher cost due to performance properties | Lower cost, widely used in packaging |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for durable, heat-resistant cap seals | Suitable for flexible, lightweight seals |
Introduction to Cap Seal Materials
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior chemical resistance, high tensile strength, and excellent dimensional stability compared to polyethylene (PE) in cap seal applications. PBT's thermal resistance up to 150degC ensures retention of seal integrity under high-temperature conditions, whereas polyethylene typically softens at lower temperatures. Polyethylene provides cost-effective flexibility and good moisture barrier properties but lacks the mechanical robustness and heat resistance needed for long-term durable cap seals.
Overview of Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic polyester known for its strong chemical resistance, high dimensional stability, and excellent electrical insulation properties, making it ideal for cap seal applications. PBT exhibits superior mechanical strength and thermal resistance compared to Polyethylene (PE), ensuring enhanced durability and performance under stress and elevated temperatures. Its low moisture absorption and resistance to solvents contribute to reliable sealing and long-term integrity in packaging uses.
Overview of Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene (PE) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer known for its excellent chemical resistance, flexibility, and durability, making it ideal for cap seals in the packaging industry. PE variants such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE) provide superior moisture barrier properties and impact resistance, ensuring secure sealing and protection of contents. Its low cost and ease of processing contribute to PE's popularity in producing reliable, lightweight, and efficient cap seals.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior mechanical strength, higher tensile modulus, and better dimensional stability compared to polyethylene (PE), making it ideal for cap seals requiring durability and resistance to deformation. PBT exhibits excellent impact resistance and maintains rigidity under high temperatures, whereas polyethylene tends to have lower tensile strength and greater flexibility, which may lead to easier wear and less effective sealing under stress. For applications demanding prolonged mechanical performance and thermal endurance, PBT outperforms PE in maintaining consistent seal integrity.
Chemical Resistance and Compatibility
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for cap seals exposed to aggressive solvents and oils. PBT maintains structural integrity in the presence of acids and alkalis, whereas polyethylene may degrade or swell under similar chemical conditions. Compatibility with diverse chemical formulations ensures PBT cap seals provide enhanced durability and performance in demanding packaging applications.
Thermal Stability and Performance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior thermal stability compared to polyethylene (PE), maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 220degC, while PE typically softens around 110degC. This enhanced thermal resistance allows PBT cap seals to perform reliably in high-temperature applications, preventing deformation and leakage. The crystallinity and chemical resistance of PBT further contribute to its durability and long-term performance under thermal stress, making it ideal for demanding sealing environments.
Seal Integrity and Leak Prevention
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior seal integrity and enhanced leak prevention compared to polyethylene (PE) in cap seals due to its higher chemical resistance and dimensional stability under temperature variations. PBT's rigidity and low moisture absorption minimize seal deformation, ensuring consistent closure and effective barrier properties. Polyethylene, while flexible and cost-effective, may experience deformation and compromised sealing under stress, increasing the risk of leaks in demanding applications.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior mechanical strength and thermal stability for cap seals but tends to be more expensive and less widely available compared to polyethylene (PE). Polyethylene is highly cost-effective and readily available, making it a popular choice for mass-produced cap seals despite its lower heat resistance and durability. Selecting between PBT and PE depends on balancing the desired seal performance with budget constraints and supply chain considerations.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers a lower environmental impact than polyethylene (PE) due to its higher durability and resistance to chemical degradation, which extends the lifespan of cap seals and reduces waste. PBT is more compatible with recycling processes that enable closed-loop recovery, whereas polyethylene, although widely recyclable, often faces contamination issues that lower its recyclability grade in cap seal applications. Choosing PBT for cap seals supports improved resource efficiency and reduced carbon footprint in packaging sustainability efforts.
Application Suitability: Choosing the Right Material for Cap Seals
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior chemical resistance, thermal stability, and dimensional accuracy, making it highly suitable for durable and high-performance cap seals in the automotive and electronics industries. Polyethylene (PE), with its excellent flexibility, impact resistance, and cost-effectiveness, is ideal for consumer packaging applications where lightweight and sealing integrity are critical. Selecting the right material depends on the application environment, with PBT preferred for high-temperature and chemically aggressive conditions, while PE suits applications requiring elasticity and moisture resistance.
Infographic: Polybutylene terephthalate vs Polyethylene for Cap seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com