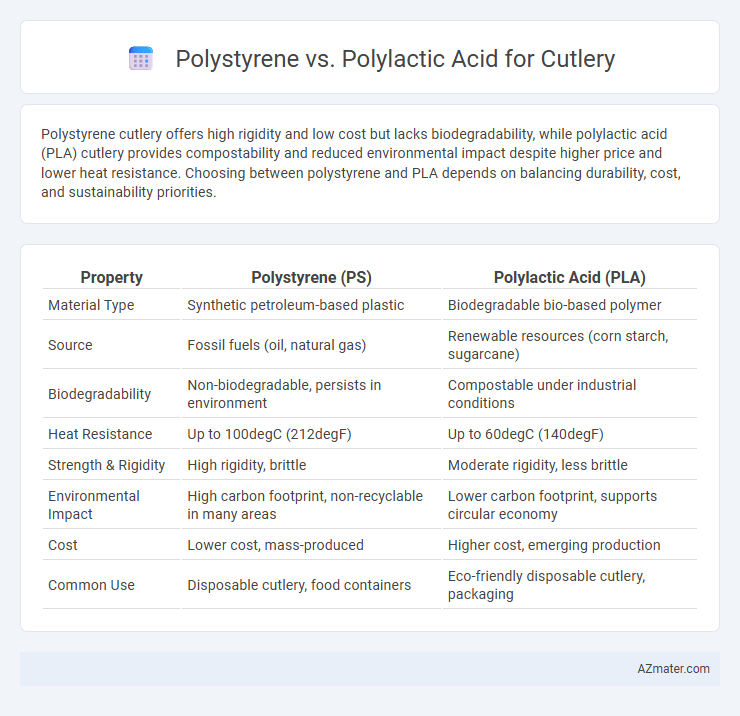
Polystyrene cutlery offers high rigidity and low cost but lacks biodegradability, while polylactic acid (PLA) cutlery provides compostability and reduced environmental impact despite higher price and lower heat resistance. Choosing between polystyrene and PLA depends on balancing durability, cost, and sustainability priorities.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polystyrene (PS) | Polylactic Acid (PLA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic petroleum-based plastic | Biodegradable bio-based polymer |
| Source | Fossil fuels (oil, natural gas) | Renewable resources (corn starch, sugarcane) |
| Biodegradability | Non-biodegradable, persists in environment | Compostable under industrial conditions |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 100degC (212degF) | Up to 60degC (140degF) |
| Strength & Rigidity | High rigidity, brittle | Moderate rigidity, less brittle |
| Environmental Impact | High carbon footprint, non-recyclable in many areas | Lower carbon footprint, supports circular economy |
| Cost | Lower cost, mass-produced | Higher cost, emerging production |
| Common Use | Disposable cutlery, food containers | Eco-friendly disposable cutlery, packaging |
Introduction to Polystyrene and Polylactic Acid
Polystyrene is a synthetic polymer derived from petroleum known for its rigidity, low cost, and ease of molding, making it a common choice in single-use cutlery. Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane, gaining popularity due to its eco-friendly compostable properties. Both materials offer distinct performance characteristics, with polystyrene excelling in durability and PLA emphasizing sustainability in cutlery applications.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Polystyrene, a synthetic polymer derived from styrene monomers, features a rigid aromatic benzene ring in its backbone, contributing to its stiffness and brittleness, while polylactic acid (PLA) is a biodegradable aliphatic polyester composed of lactic acid units with ester linkages promoting hydrolytic degradation. The aromatic rings in polystyrene result in high thermal resistance but low biodegradability, whereas PLA's semi-crystalline structure offers moderate strength and enhanced environmental friendliness due to its compostable nature. Polystyrene's linear polymer chain contrasts with PLA's chiral centers and stereochemical variations, affecting their mechanical properties and suitability for single-use cutlery applications.
Manufacturing Processes
Polystyrene cutlery is produced through injection molding, offering rapid cycle times and high-volume output with consistent precision, making it cost-effective for mass production. Polylactic acid (PLA) cutlery manufacturing involves extrusion and thermoforming techniques that require controlled temperature settings to maintain biodegradability and mechanical strength. The energy consumption of PLA processing tends to be higher than polystyrene, but it supports sustainability goals by utilizing renewable resources and offering compostability in industrial facilities.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polystyrene exhibits higher rigidity and impact resistance, making it suitable for durable cutlery that withstands significant mechanical stress. Polylactic Acid offers moderate mechanical strength with superior biodegradability but tends to be more brittle under mechanical load. The choice depends on balancing stiffness and environmental sustainability requirements for cutlery applications.
Biodegradability and Environmental Impact
Polylactic acid (PLA) cutlery offers superior biodegradability compared to polystyrene, as PLA is derived from renewable resources like corn starch and composts fully in industrial facilities within 1 to 3 months, reducing landfill waste. Polystyrene, a petroleum-based plastic, can take hundreds of years to decompose and contributes significantly to microplastic pollution and environmental toxicity. Choosing PLA cutlery supports lower carbon emissions and less harmful ecological footprint, making it a more sustainable option for single-use utensils.
Heat Resistance and Durability
Polystyrene cutlery offers moderate heat resistance up to 100degC, making it suitable for cold or room-temperature use but prone to melting or warping with hot foods. Polylactic acid (PLA) cutlery withstands slightly higher temperatures, approximately 120degC, providing better performance with warm foods while maintaining biodegradability. Durability-wise, polystyrene is more rigid and less prone to breaking under pressure, whereas PLA cutlery tends to be more brittle, impacting its practicality for heavy or prolonged use.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Polystyrene cutlery offers significant cost advantages due to its low production expenses and wide market availability, making it a dominant choice for disposable utensils. Polylactic Acid (PLA) cutlery incurs higher costs reflecting its biodegradable nature and more complex manufacturing process, limiting its market penetration despite growing environmental demand. Market availability favors polystyrene with extensive global distribution networks, whereas PLA is concentrated in niche segments prioritizing sustainability and premium pricing.
Food Safety and Regulatory Approvals
Polystyrene cutlery, widely used for its durability and low cost, may pose food safety concerns due to potential chemical leaching, especially when exposed to heat or oily foods, leading to stricter regulatory scrutiny in several regions. Polylactic Acid (PLA) cutlery, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, benefits from safer food contact approvals, including FDA and EU regulations, promoting its use as a biodegradable and non-toxic alternative. Regulatory standards prioritize materials free from harmful additives and compliant with migration limits, positioning PLA as a favorable choice for sustainable and food-safe disposable utensils.
Consumer Preferences and Industry Trends
Polylactic Acid (PLA) cutlery is gaining popularity among eco-conscious consumers due to its biodegradability and renewable origins, in contrast to traditional Polystyrene (PS), which is favored for its durability and lower cost. Industry trends show a steady shift towards PLA as regulatory pressures and sustainability goals drive manufacturers to adopt compostable alternatives. Consumer preferences increasingly prioritize environmental impact, pushing the cutlery market towards materials that align with green initiatives while balancing performance and price.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Cutlery
Polylactic Acid (PLA) offers a biodegradable and compostable option ideal for environmentally conscious cutlery, while Polystyrene (PS) provides superior durability and heat resistance suitable for heavy-duty use. The choice between PLA and PS cutlery hinges on balancing sustainability goals with performance requirements, as PLA excels in reducing plastic waste but may soften with heat, whereas PS maintains structural integrity but poses environmental disposal challenges. Selecting the right material depends on specific application needs, prioritizing either eco-friendliness with PLA or cost-effective, reliable use with PS.
Infographic: Polystyrene vs Polylactic Acid for Cutlery
 azmater.com
azmater.com