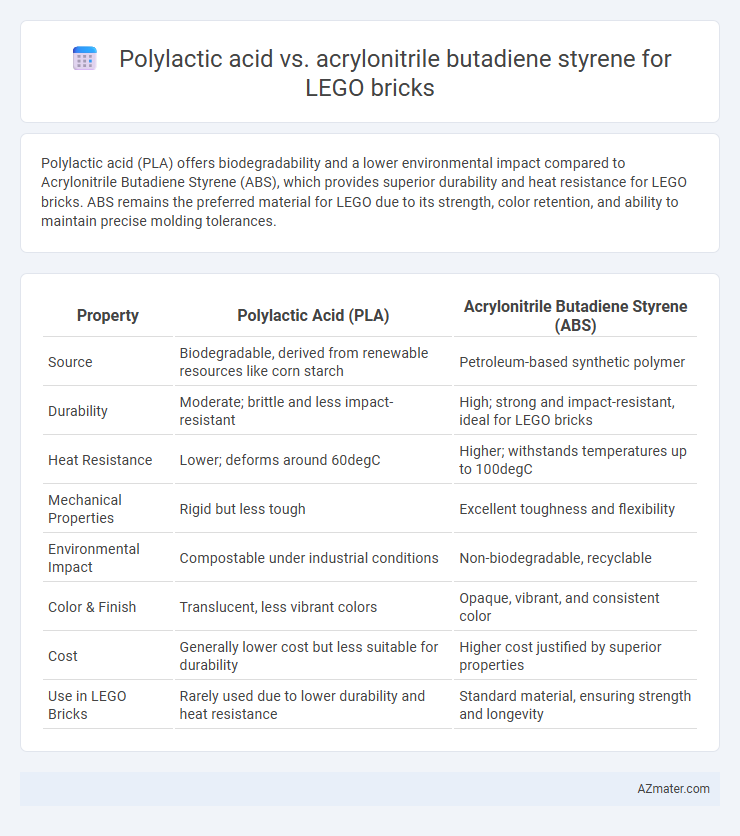
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers biodegradability and a lower environmental impact compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which provides superior durability and heat resistance for LEGO bricks. ABS remains the preferred material for LEGO due to its strength, color retention, and ability to maintain precise molding tolerances.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polylactic Acid (PLA) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Biodegradable, derived from renewable resources like corn starch | Petroleum-based synthetic polymer |
| Durability | Moderate; brittle and less impact-resistant | High; strong and impact-resistant, ideal for LEGO bricks |
| Heat Resistance | Lower; deforms around 60degC | Higher; withstands temperatures up to 100degC |
| Mechanical Properties | Rigid but less tough | Excellent toughness and flexibility |
| Environmental Impact | Compostable under industrial conditions | Non-biodegradable, recyclable |
| Color & Finish | Translucent, less vibrant colors | Opaque, vibrant, and consistent color |
| Cost | Generally lower cost but less suitable for durability | Higher cost justified by superior properties |
| Use in LEGO Bricks | Rarely used due to lower durability and heat resistance | Standard material, ensuring strength and longevity |
Introduction: Polylactic Acid vs Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene in LEGO Bricks
Polylactic Acid (PLA) and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) represent two prominent materials used in the manufacturing of LEGO bricks, each with distinct properties influencing performance and sustainability. ABS offers exceptional durability, impact resistance, and vibrant color retention, making it the traditional choice for LEGO parts designed to withstand rough play and repeated assembly. PLA, a biodegradable polymer derived from renewable resources, presents an eco-friendly alternative but tends to exhibit lower heat resistance and mechanical strength compared to ABS, thereby affecting its long-term usability in LEGO brick production.
Material Composition: PLA and ABS Explained
Polylactic acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane, offering a lower environmental impact compared to traditional plastics. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a petroleum-based polymer known for its high strength, impact resistance, and durability, making it ideal for LEGO bricks that require resilience and longevity. PLA's composition results in a stiffer, less heat-resistant material, whereas ABS's combination of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene provides flexibility and toughness essential for interlocking LEGO pieces.
Environmental Impact: Biodegradability and Sustainability
Polylactic acid (PLA), derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers enhanced biodegradability compared to traditional petroleum-based Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) used in LEGO bricks. PLA breaks down under industrial composting conditions, significantly reducing long-term environmental pollution, whereas ABS can persist in landfills for centuries due to its resistance to natural degradation. The sustainability advantage of PLA lies in its lower carbon footprint during production and its potential to close the plastic lifecycle loop, making it a preferable choice for eco-conscious LEGO manufacturing.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Polylactic acid (PLA) exhibits lower mechanical strength and impact resistance compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), making ABS more suitable for the durability demands of LEGO bricks. ABS offers superior toughness, dimensional stability, and resistance to wear, ensuring bricks maintain structural integrity during repeated assembly and disassembly. PLA tends to be more brittle and less heat-resistant, which limits its durability under mechanical stress typical in LEGO play.
Color and Finish: Visual Differences in PLA and ABS LEGO Bricks
Polylactic acid (PLA) LEGO bricks exhibit a matte finish with a slightly softer and muted color palette, resulting from the natural translucency and lower heat resistance of PLA. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) LEGO bricks offer a vibrant, glossy appearance with sharp, consistent color saturation due to ABS's higher impact strength and better heat resistance. The enhanced durability of ABS allows for a smoother, shinier finish, making its color more resistant to fading and wear compared to PLA bricks.
Manufacturing and Processing Techniques
Polylactic acid (PLA) for LEGO bricks requires precise temperature control during extrusion and molding due to its lower melting point and biodegradability, making injection molding slightly more challenging compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). ABS benefits from well-established manufacturing processes including high-temperature injection molding, which grants excellent durability and dimensional stability for LEGO bricks. Processing PLA demands careful moisture control as it is hygroscopic, whereas ABS is less sensitive, enabling more flexible production conditions in mass manufacturing.
Safety Considerations for Children’s Toys
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers a safer alternative to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) for LEGO bricks due to its non-toxic, biodegradable properties derived from renewable resources such as corn starch. ABS, while durable and impact-resistant, poses potential health risks because it is petroleum-based and may release harmful chemicals during manufacturing or if ingested. Safety considerations prioritize PLA's hypoallergenic and environmentally friendly profile for children's toys, minimizing exposure to hazardous substances without compromising structural integrity.
Cost Analysis: PLA vs ABS for LEGO Production
Polylactic acid (PLA) generally incurs higher raw material costs compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), impacting overall LEGO brick production expenses. ABS offers superior durability and heat resistance, making it more cost-effective in long-term manufacturing despite slightly lower material prices. The production efficiency and recyclability of ABS further reduce processing costs, while PLA's biodegradability introduces potential benefits balanced against increased initial expenses.
Consumer Perception and Market Trends
Polylactic acid (PLA) is gaining traction in the LEGO market due to its biodegradable nature and appeal to eco-conscious consumers, reflecting a growing trend toward sustainable materials in toys. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) remains the industry standard, valued for its durability, color retention, and safety, which strongly influence positive consumer perception and brand loyalty. Market trends indicate a gradual shift where consumer demand for environmentally friendly products is pushing manufacturers to explore PLA, despite ABS's established performance advantages.
Future Prospects for PLA and ABS in LEGO Manufacturing
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers significant environmental advantages due to its biodegradability and renewable sources, making it a prime candidate for sustainable LEGO brick production. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides superior durability, impact resistance, and color retention, ensuring long-lasting playability and high-quality aesthetics for LEGO bricks. Future prospects indicate a potential blend of PLA and ABS to balance eco-friendliness with mechanical performance, driving innovation in LEGO's manufacturing processes to meet growing consumer demand for sustainable yet robust building materials.
Infographic: Polylactic acid vs Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene for LEGO brick
 azmater.com
azmater.com