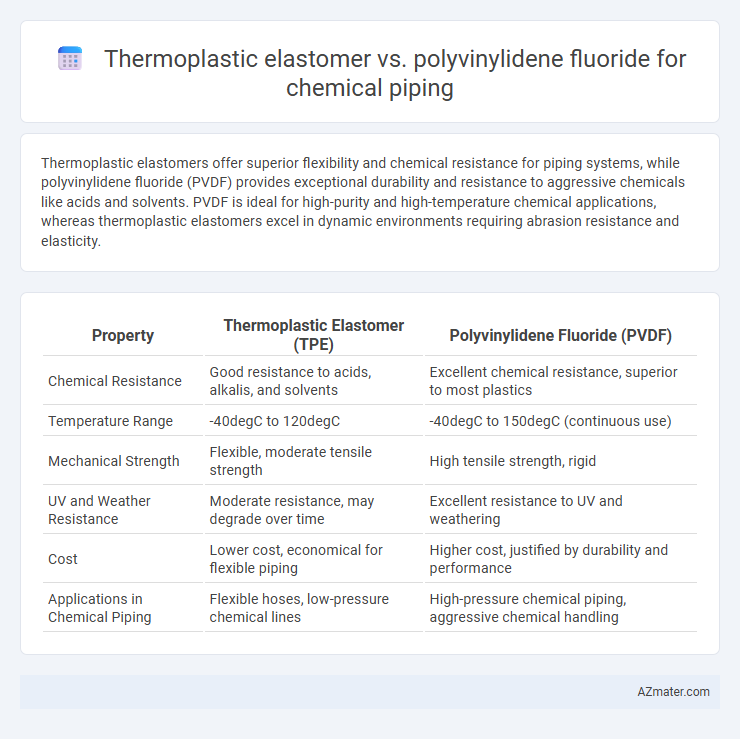
Thermoplastic elastomers offer superior flexibility and chemical resistance for piping systems, while polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) provides exceptional durability and resistance to aggressive chemicals like acids and solvents. PVDF is ideal for high-purity and high-temperature chemical applications, whereas thermoplastic elastomers excel in dynamic environments requiring abrasion resistance and elasticity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids, alkalis, and solvents | Excellent chemical resistance, superior to most plastics |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -40degC to 150degC (continuous use) |
| Mechanical Strength | Flexible, moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength, rigid |
| UV and Weather Resistance | Moderate resistance, may degrade over time | Excellent resistance to UV and weathering |
| Cost | Lower cost, economical for flexible piping | Higher cost, justified by durability and performance |
| Applications in Chemical Piping | Flexible hoses, low-pressure chemical lines | High-pressure chemical piping, aggressive chemical handling |
Introduction to Chemical Piping Materials
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) are prominent materials used in chemical piping due to their chemical resistance and mechanical properties. TPE offers flexibility, excellent impact resistance, and good chemical compatibility with a wide range of acids and bases, making it suitable for applications requiring dynamic movement or thermal expansion. PVDF excels in high-purity chemical handling environments, providing exceptional resistance to aggressive chemicals, UV radiation, and thermal stability up to 150degC, making it ideal for corrosive fluid transfer in chemical processing industries.
Overview of Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE)
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) combine the flexibility of rubber with the processability of plastics, making them ideal for chemical piping applications requiring resilience and chemical resistance. TPEs offer excellent resistance to abrasion, acids, and solvents, with temperature tolerance typically ranging from -60degC to 120degC, depending on the formulation. Their ability to be repeatedly melted and reshaped enhances manufacturing efficiency and recyclability compared to rigid polymers like polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF).
Key Properties of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers exceptional chemical resistance, withstanding a wide range of acids, bases, and solvents, making it highly suitable for aggressive chemical piping applications. Its high thermal stability supports continuous use at temperatures up to 150degC, outperforming many thermoplastic elastomers that degrade at lower temperatures. PVDF also exhibits excellent mechanical strength, low permeability, and resistance to UV radiation, ensuring long-lasting, reliable performance in harsh industrial environments.
Chemical Resistance: TPE vs. PVDF
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer good chemical resistance against a range of solvents, acids, and bases but can degrade when exposed to harsh chemicals and high temperatures over time. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior chemical resistance, particularly against strong acids, bases, and hydrocarbons, making it ideal for aggressive chemical piping environments. PVDF's robust molecular structure provides excellent long-term stability and minimal permeability compared to TPE, ensuring greater durability and reliability in demanding chemical applications.
Temperature and Pressure Ratings Comparison
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) typically operate effectively within a temperature range of -40degC to 120degC and withstand pressure ratings up to 200 psi in chemical piping applications. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior thermal resistance, functioning reliably between -40degC and 150degC with pressure ratings exceeding 300 psi, making it suitable for more demanding chemical environments. PVDF's higher temperature and pressure tolerance provide enhanced durability and safety in high-performance chemical piping systems compared to TPEs.
Installation and Handling Differences
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer flexible installation with easier bending and joining using heat fusion or mechanical fittings, which reduces labor time compared to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF). PVDF requires precise solvent or thermal welding techniques, demanding skilled labor to ensure leak-free joints, and is more rigid, making handling in tight spaces challenging. The lightweight nature of TPE facilitates quicker handling and alignment, while PVDF's chemical resistance demands careful handling to avoid damage during installation.
Lifespan and Maintenance Requirements
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer moderate chemical resistance with a typical lifespan of 5 to 10 years in chemical piping applications but require frequent maintenance due to susceptibility to chemical swelling and abrasion. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) demonstrates superior chemical resistance and mechanical integrity, providing a lifespan often exceeding 20 years while demanding minimal maintenance. PVDF's stability under harsh chemical environments reduces the frequency of inspections and replacements, making it a more durable and cost-effective choice for long-term chemical piping systems.
Cost Analysis: TPE vs. PVDF
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) generally offer a lower initial material cost compared to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) in chemical piping applications, making them an attractive choice for budget-conscious projects. PVDF, however, provides superior chemical resistance and longevity, which can reduce long-term maintenance and replacement expenses, potentially offsetting its higher upfront price. Lifecycle cost analysis reveals that while TPE may save on initial investment, PVDF often delivers better value in aggressive chemical environments due to durability and reduced downtime.
Industry Applications and Suitability
Thermoplastic elastomers offer excellent flexibility, chemical resistance, and ease of fabrication, making them suitable for applications in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and water treatment where moderate chemical exposure and dynamic movement are common. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) stands out for its superior chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for highly corrosive chemical piping in semiconductor manufacturing, chemical processing, and industrial wastewater systems. Selecting PVDF ensures long-term durability in harsh chemical environments, whereas thermoplastic elastomers provide cost-effective performance in less aggressive industrial applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Chemical Piping
Thermoplastic elastomers offer excellent flexibility and chemical resistance suitable for moderate chemical exposure, while polyvinylidene fluoride provides superior chemical inertness and high-temperature tolerance for aggressive chemical environments. Selecting the right material depends on the specific chemical compatibility, operating temperature, and mechanical stress requirements of the piping system. Polyvinylidene fluoride generally outperforms thermoplastic elastomers in long-term durability for highly corrosive applications, making it the preferred choice for demanding chemical piping installations.
Infographic: Thermoplastic elastomer vs Polyvinylidene fluoride for Chemical piping
 azmater.com
azmater.com