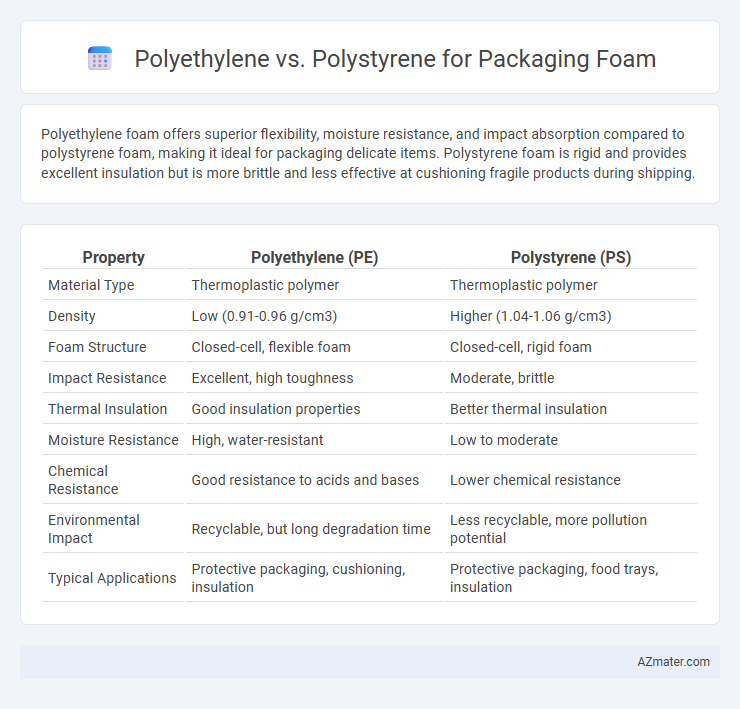
Polyethylene foam offers superior flexibility, moisture resistance, and impact absorption compared to polystyrene foam, making it ideal for packaging delicate items. Polystyrene foam is rigid and provides excellent insulation but is more brittle and less effective at cushioning fragile products during shipping.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene (PE) | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Density | Low (0.91-0.96 g/cm3) | Higher (1.04-1.06 g/cm3) |
| Foam Structure | Closed-cell, flexible foam | Closed-cell, rigid foam |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent, high toughness | Moderate, brittle |
| Thermal Insulation | Good insulation properties | Better thermal insulation |
| Moisture Resistance | High, water-resistant | Low to moderate |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and bases | Lower chemical resistance |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, but long degradation time | Less recyclable, more pollution potential |
| Typical Applications | Protective packaging, cushioning, insulation | Protective packaging, food trays, insulation |
Introduction to Packaging Foams
Packaging foams like polyethylene and polystyrene offer crucial cushioning and protection for fragile goods during shipping and storage. Polyethylene foam exhibits superior flexibility, resilience, and moisture resistance, making it ideal for absorbing shocks and vibrations. Polystyrene foam, characterized by its rigid structure and excellent thermal insulation, excels in safeguarding products requiring lightweight and impact-resistant packaging solutions.
What is Polyethylene Foam?
Polyethylene foam is a lightweight, closed-cell material known for its excellent cushioning and shock absorption properties, making it ideal for protective packaging applications. It offers high resistance to moisture, chemicals, and temperature variations, ensuring the safe transport of sensitive products. Compared to polystyrene foam, polyethylene foam provides better flexibility and durability, reducing the risk of damage during shipping and handling.
What is Polystyrene Foam?
Polystyrene foam, commonly known as Styrofoam, is a lightweight, rigid plastic material made from the polymerization of styrene monomers, widely used for packaging due to its excellent cushioning properties and thermal insulation. Its closed-cell structure provides superior shock absorption and moisture resistance, making it ideal for protecting delicate items during shipping. Compared to polyethylene foam, polystyrene foam offers higher rigidity but less flexibility and impact resistance, influencing its suitability depending on packaging requirements.
Key Physical Properties Compared
Polyethylene foam offers superior flexibility, higher impact resistance, and excellent moisture barrier properties compared to polystyrene foam, which provides greater rigidity and higher compressive strength. Polyethylene's lower density enhances cushioning performance, while polystyrene's brittleness limits its ability to absorb shocks effectively. Thermal insulation values favor polyethylene for temperature-sensitive packaging, whereas polystyrene excels in maintaining structural integrity under moderate loads.
Cushioning and Shock Absorption
Polyethylene foam offers superior cushioning and shock absorption due to its closed-cell structure, providing excellent resistance to impact and vibration during packaging. Polystyrene foam, typically expanded polystyrene (EPS), provides good rigidity but less effective energy absorption, making it more prone to cracking under sudden shocks. For packaging applications requiring enhanced protection against drops and vibrations, polyethylene foam is generally preferred over polystyrene foam.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Polyethylene foam offers superior moisture resistance, making it ideal for packaging sensitive items exposed to humidity or liquids, due to its closed-cell structure that prevents water absorption. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and rigid, has lower moisture resistance and can absorb water over time, leading to potential degradation in damp environments. Chemically, polyethylene demonstrates better resistance to a wide range of acids, bases, and solvents, whereas polystyrene is more susceptible to damage from oils and organic solvents, limiting its use in chemically aggressive packaging scenarios.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Polyethylene foam is favored for packaging due to its recyclability and relatively lower environmental footprint compared to polystyrene, which is less biodegradable and often ends up in landfills or oceans, contributing to persistent pollution. Polystyrene foam's production involves higher greenhouse gas emissions and toxic chemical release, making it less sustainable despite its excellent cushioning properties. Advances in biodegradable polyethylene blends and improved recycling infrastructure enhance its role as a more eco-friendly packaging foam alternative.
Common Applications in Packaging
Polyethylene foam is widely used for packaging fragile items such as electronics, appliances, and glassware due to its excellent cushioning and moisture resistance. Polystyrene foam commonly serves in protective packaging for food containers, disposable cups, and lightweight consumer goods because of its rigidity and thermal insulation properties. Both materials offer tailored solutions, with polyethylene preferred for flexibility and reusable packaging, while polystyrene excels in single-use, molded applications.
Cost Analysis: Polyethylene vs Polystyrene
Polyethylene foam generally offers a higher upfront material cost compared to polystyrene but provides superior durability and flexibility, leading to lower long-term replacement expenses. Polystyrene foam is typically cheaper per unit, making it cost-effective for single-use packaging, though its brittleness can increase product damage and associated costs. When evaluating cost efficiency, polyethylene's resilience often results in reduced logistics and waste management expenses, balancing initial price differences.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Needs
Polyethylene foam offers excellent impact absorption and chemical resistance, making it ideal for cushioning fragile items during shipping. Polystyrene foam provides superior rigidity and lightweight insulation but lacks the flexibility and durability found in polyethylene. Choose polyethylene foam for versatile and reusable packaging solutions, while selecting polystyrene foam for cost-effective protection and thermal insulation needs.
Infographic: Polyethylene vs Polystyrene for Packaging foam
 azmater.com
azmater.com