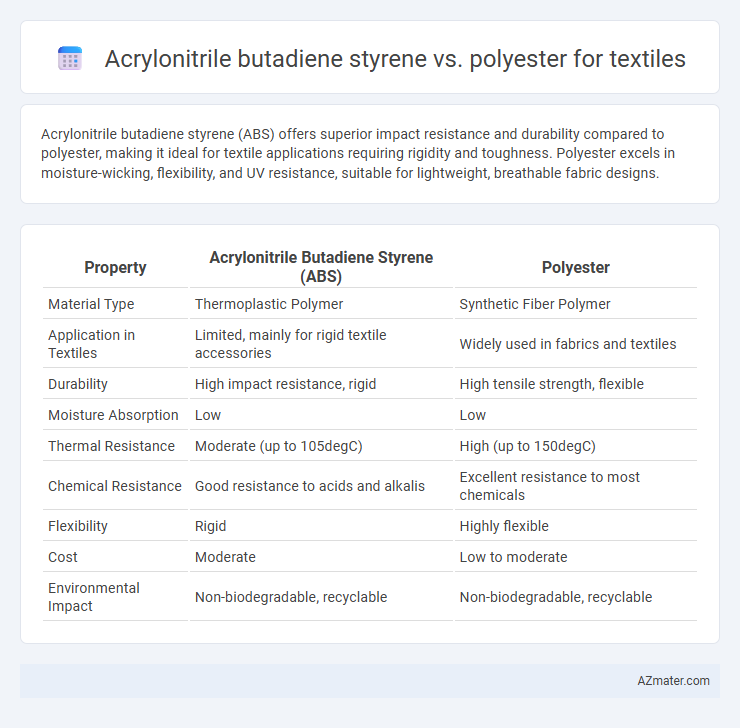
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance and durability compared to polyester, making it ideal for textile applications requiring rigidity and toughness. Polyester excels in moisture-wicking, flexibility, and UV resistance, suitable for lightweight, breathable fabric designs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polyester |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polymer | Synthetic Fiber Polymer |
| Application in Textiles | Limited, mainly for rigid textile accessories | Widely used in fabrics and textiles |
| Durability | High impact resistance, rigid | High tensile strength, flexible |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | Low |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate (up to 105degC) | High (up to 150degC) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and alkalis | Excellent resistance to most chemicals |
| Flexibility | Rigid | Highly flexible |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, recyclable | Non-biodegradable, recyclable |
Introduction to ABS and Polyester in Textiles
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its toughness, impact resistance, and ease of processing, making it suitable for durable textile applications such as protective clothing and composite fibers. Polyester, a synthetic polymer primarily composed of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), dominates the textile industry due to its high tensile strength, wrinkle resistance, and moisture-wicking properties. Both ABS and polyester offer distinct advantages in textile manufacturing, with ABS providing enhanced durability and polyester excelling in comfort and breathability for apparel and home textiles.
Composition and Chemical Structure
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a terpolymer composed of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, providing a combination of chemical resistance, toughness, and rigidity due to its multi-phase structure. Polyester, primarily polyethylene terephthalate (PET), consists of long-chain synthetic polymers derived from ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid, characterized by ester functional groups that confer excellent tensile strength and resistance to shrinking and stretching. The chemical structure of ABS features nitrile groups (-CN) that increase polarity, whereas polyester's ester linkages (-COO-) contribute to its hydrophobic and crystalline properties, making each polymer suitable for different textile applications based on mechanical and chemical requirements.
Manufacturing Processes
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is manufactured through emulsion or mass polymerization, resulting in a tough, impact-resistant thermoplastic commonly used for durable textile components like zippers and buttons. Polyester production involves polycondensation of purified terephthalic acid (PTA) and monoethylene glycol (MEG), forming long-chain polymers that are melt-spun into fibers, enabling scalable fabric manufacturing with high tensile strength. Differences in processing conditions, such as temperature and catalyst usage, significantly influence the mechanical properties and application suitability of ABS and polyester in textile manufacturing.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance and toughness compared to polyester, making it ideal for applications requiring high durability and flexibility. Polyester exhibits higher tensile strength and better resistance to UV degradation and chemicals, providing enhanced performance in environments exposed to sunlight and harsh chemicals. Both materials differ significantly in mechanical properties, with ABS favoring impact absorption and polyester excelling in strength and environmental resistance for textile applications.
Durability and Longevity
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance and toughness compared to polyester, making it highly durable in applications requiring structural strength. Polyester fibers provide excellent abrasion resistance and UV stability, contributing to longer fabric life in outdoor or high-wear environments. Both materials exhibit strong longevity characteristics, but ABS is favored for rigid components while polyester excels in flexible textile durability.
Comfort and Wearability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) in textiles offers high durability but lacks breathability, making it less comfortable for prolonged wear compared to polyester. Polyester fibers provide superior moisture-wicking properties and flexibility, enhancing overall comfort and wearability in active and casual clothing. The lightweight nature of polyester combined with its quick-drying capability makes it a preferred choice for comfortable textile applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a petroleum-based plastic with low biodegradability and high carbon footprint, contributing to environmental pollution and microplastic accumulation. Polyester, though also derived from fossil fuels, offers better recycling potential through chemical recycling processes and can be produced from recycled PET bottles, reducing waste and resource consumption. Both materials pose sustainability challenges, but advancements in recycling technologies and the integration of bio-based feedstocks improve the environmental profile of polyester compared to ABS in textile applications.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) tends to have higher raw material costs compared to polyester, impacting overall production expenses in textile applications. Polyester benefits from lower manufacturing costs and widespread availability, making it a more cost-effective option for large-scale textile production. Economic considerations favor polyester due to its durability, ease of recycling, and established supply chains, which reduce long-term expenditure.
Common Applications in Textiles
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is rarely used directly in textiles but is essential in producing components for textile machinery due to its high impact resistance and durability. Polyester dominates the textile industry as a synthetic fiber widely used in apparel, home furnishings, and industrial fabrics because of its strength, wrinkle resistance, and moisture-wicking properties. Common applications for polyester include activewear, upholstery, and outdoor textiles, while ABS serves more as a material for manufacturing textile equipment parts rather than fabric.
Choosing the Right Material: ABS vs Polyester
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance and rigidity compared to polyester, making it ideal for textile applications requiring durability and structural integrity. Polyester excels in moisture-wicking, breathability, and flexibility, providing comfort and ease of care for apparel and performance textiles. Choosing between ABS and polyester depends on prioritizing either strength and shape retention or flexibility and moisture management in textile products.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polyester for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com